
Find the maximum negative bending moment at point B.
Answer to Problem 1P
The maximum negative bending moment at point B is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The concentrated live load (P) is 75 kN.
Calculation:
Apply a 1 kN unit moving load at a distance of x from left end A.
Sketch the free body diagram of beam as shown in Figure 1.
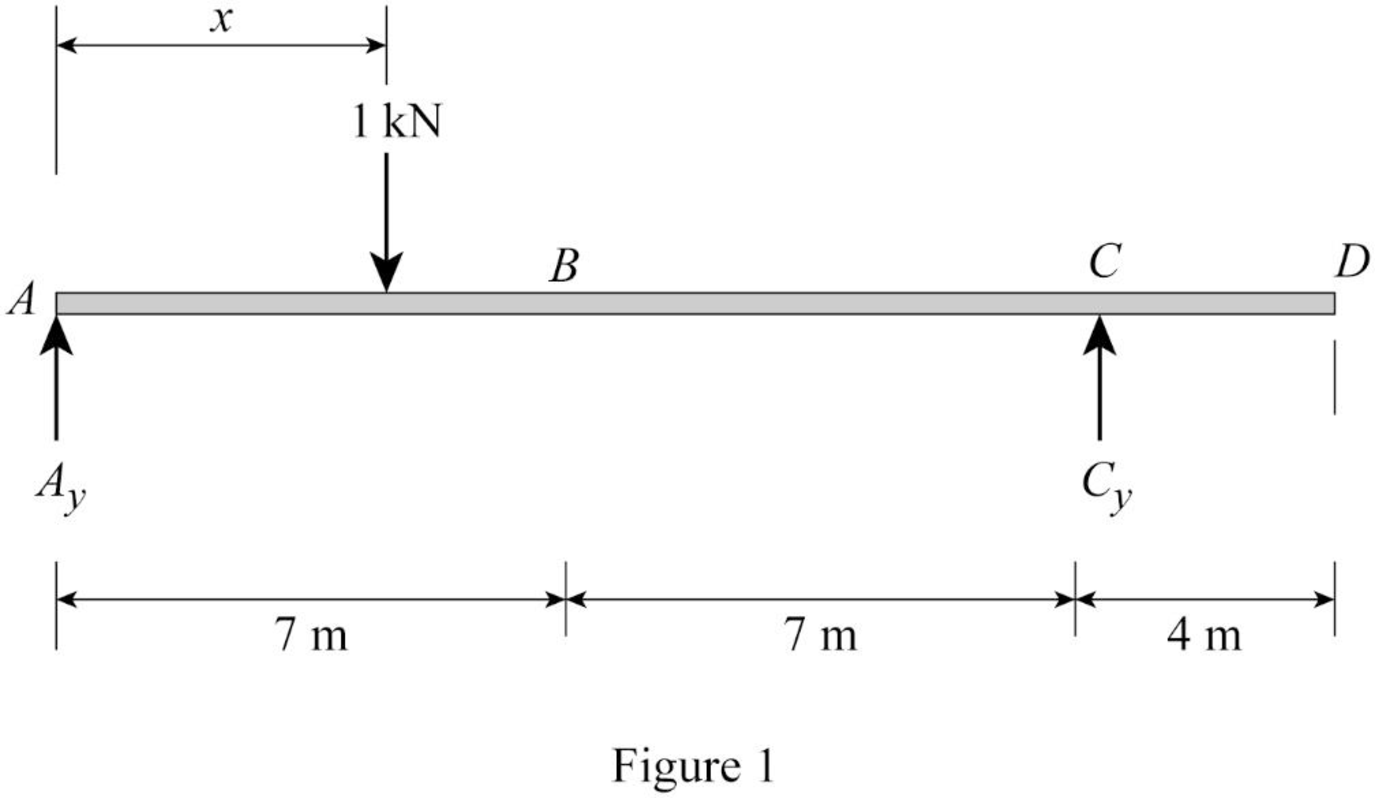
Refer Figure 1.
Find the equation of support reaction
Take moment about point A.
Consider moment equilibrium at point A.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Sum of moment at point A is zero.
Find the equation of support reaction
Apply vertical equilibrium equation of forces.
Consider upward force as positive
Substitute
Find the equation of moment at B.
Apply 1 kN at just left of B
Sketch the free body diagram of the section AB as shown in Figure 2.
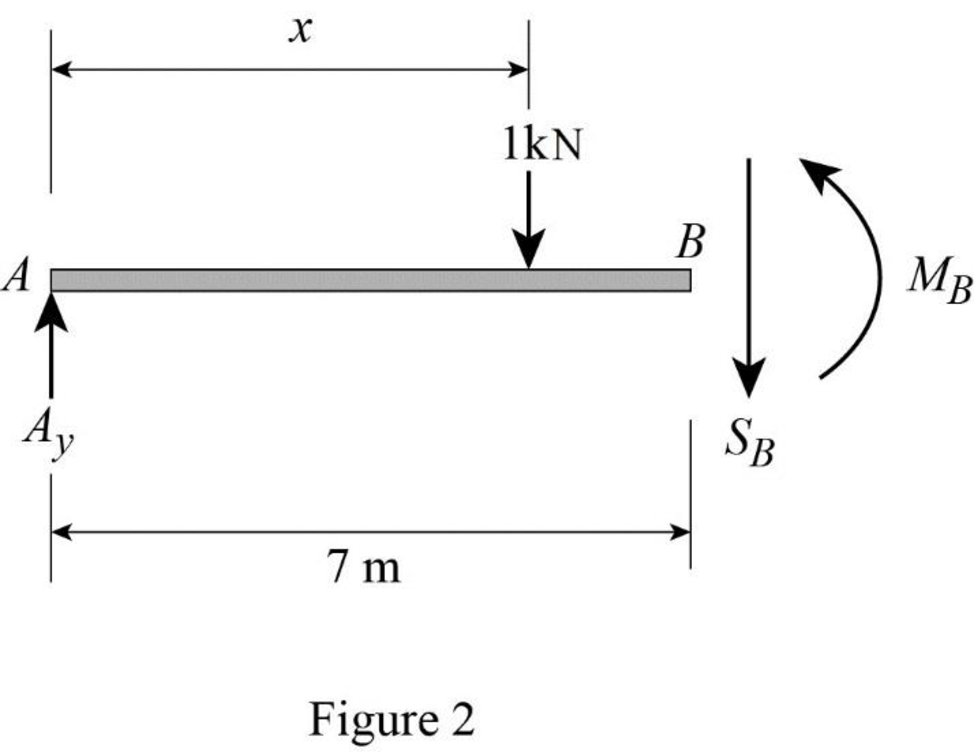
Refer Figure 2.
Consider moment at B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 kN at just right of B
Sketch the free body diagram of the section BD as shown in Figure 3.
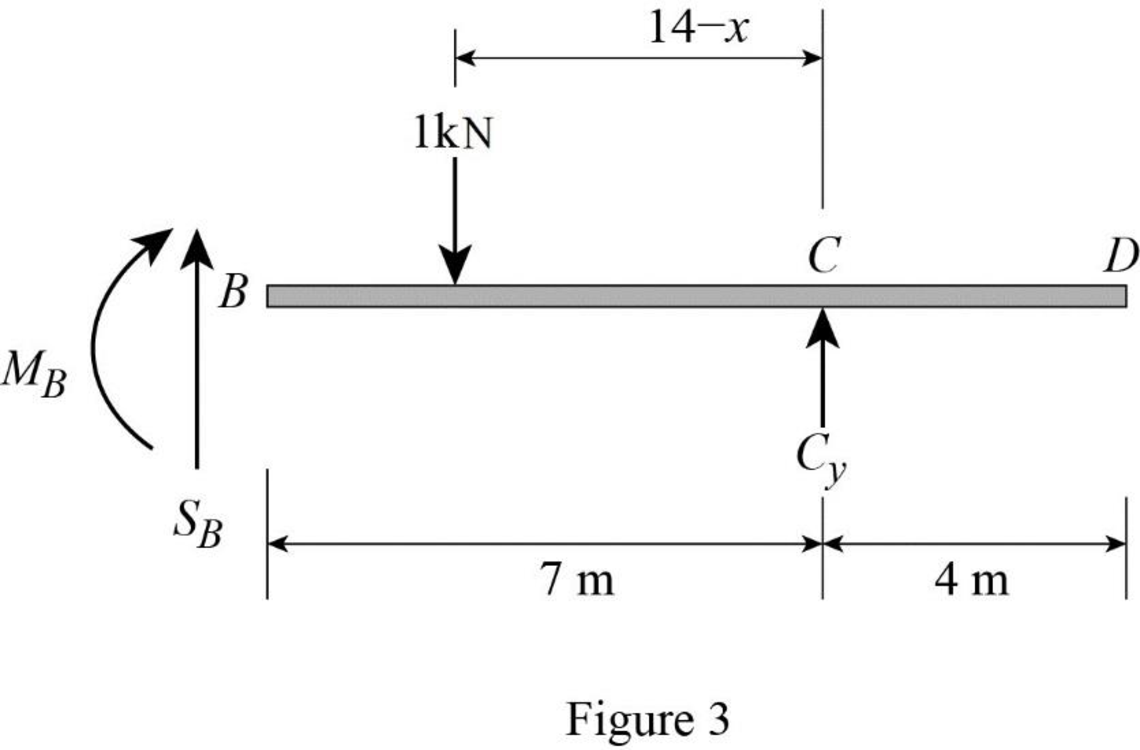
Refer Figure 3.
Consider moment at B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Find the equation of moment at B of portion BC
Substitute
Thus, the equations of the influence line for
Find the value of influence line ordinate of moment at various points of x using the Equations (3) and (4) and summarize the value as in Table 1.
| x | |
| 0 | 0 |
| 7 | |
| 14 | 0 |
| 28 | –2 |
Draw the influence lines for the moment at point B using Table 4 as shown in Figure 4.
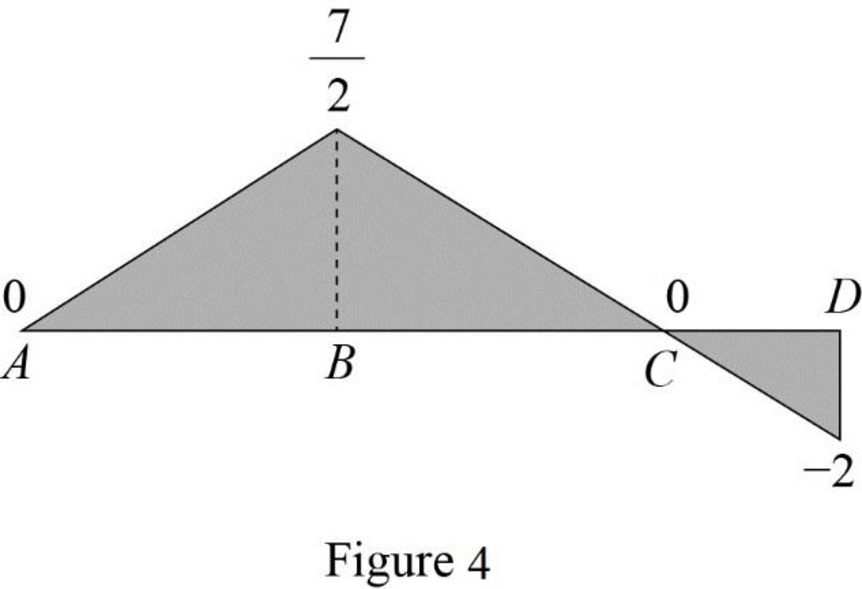
Refer Figure 4,
The maximum negative influence line ordinate of bending moment at B is
Find the maximum negative bending moment at point B using the equation.
Substitute 75 kN for P and
Therefore, the maximum negative bending moment at point B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Structural Analysis, Si Edition
- Post-tensioned AASHTO Type II girders are to be used to support a deck with unsupported span equal to 10 meters. Two levels of Grade 250, 10 x 15.2 mm Ø 7-wire strand are used to tension the girders with 5 tendons per level, where the tendons on top stressed before the ones on the bottom. The girder is simply supported at both ends. The anchors are located 100 mm above the neutral axis at the supports while the eccentricity is measured at 400 mm at the midspan. The tendon profile follows a parabolic shape using a rigid metal sheathing. A concrete topping (slab) 130 mm thick is placed above the beam with a total tributary width of 4 meters. Use maximum values for ranges (table values). Assume that the critical section of the beam is at 0.45LDetermine the losses (friction loss, anchorage, elastic shortening, creep, shrinkage, relaxation). Determine the stresses at the top fibers @ critical section before placing a concrete topping, right after stress transfer. Determine the stress at the…arrow_forwardPlease solve this question in hand writting step by step with diagram drawingarrow_forwardSolve this question pleasearrow_forward
- Please draw shear and moment diagrams with provided information.arrow_forwardShow step by step solutionarrow_forwardDraw the shear and the moment diagrams for each of the frames below. If the frame is statically indeterminate the reactions have been provided. Problem 1 (Assume pin connections at A, B and C). 30 kN 2 m 5 m 30 kN/m B 60 kN 2 m 2 m A 22 CO Carrow_forward
- This is an old exam practice question. The answer key says the answer is Pmax = 52.8kN but I am confused how they got that.arrow_forwardF12-45. Car A is traveling with a constant speed of 80 km/h due north, while car B is traveling with a constant speed of 100 km/h due east. Determine the velocity of car B relative to car A. pload Choose a File Question 5 VA - WB VBA V100 111413 + *12-164. The car travels along the circular curve of radius r = 100 ft with a constant speed of v = 30 ft/s. Determine the angular rate of rotation è of the radial liner and the magnitude of the car's acceleration. Probs. 12-163/164 pload Choose a File r = 400 ft 20 ptsarrow_forwardPlease show step by step how to solve this and show formulararrow_forward
- Please solve this question step by step with dia gramarrow_forwardUse the second picture to answer the question, Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardP6.16 A compound shaft (Figure P6.16) consists of a titanium alloy [G= 6,200 ksi] tube (1) and a solid stainless steel [G= 11,500 ksi] shaft (2). Tube (1) has a length L₁ = 40 in., an outside diameter D₁ = 1.75 in., and a wall thickness t₁ = 0.125 in. Shaft (2) has a length 42 = 50 in. and a diameter d₂ = 1.25 in. If an external torque TB = 580 lb ft acts at pulley B in the direction shown, calculate the torque Tcrequired at pulley C so that the rotation angle of pulley Crelative to A is zero. B Te (2) TB (1) FIGURE P6.16arrow_forward
