
Concept explainers
Explain why touching your toes while you are seated on the floor with outstretched legs produces less stress on the lower spinal column than when touching your toes from a standing position. Use a diagram.
Explain why touching your toes while you are seated on the floor with outstretched legs produces less stress on the spinal column than when touching your toes from a standing position. Use a diagram.
Answer to Problem 14Q
Solution:
Touching the toes while sitting on the floor with the legs extended produces less tension in the spine than when you touch the toes from a standing position because the lever arm of the upper body is less and therefore the torque made is less. In this way the tension in the spine is less when you are sitting on the floor with your legs extended.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Touching your toes while you are seated on the floor with outstretched legs. Touching your toes from a standing position.
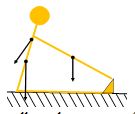 Take the pivot at waist height for a person sitting with legs extended (figure on the left). Consider the weight of the upper half of the body doing torque clockwise, for this force the lever arm is relatively small as is the torque made by the arms, therefore the muscles of the back do not do much tension due to the small total torque performed.
Take the pivot at waist height for a person sitting with legs extended (figure on the left). Consider the weight of the upper half of the body doing torque clockwise, for this force the lever arm is relatively small as is the torque made by the arms, therefore the muscles of the back do not do much tension due to the small total torque performed.
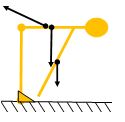 For the case of a person touching your toes from a standing position (figure on the right)In the case of a person the lever arm of the upper part of the body and of the arms is greater than in the previous case, therefore the torque performed is much greater and therefore the tension in the spine is greater than in the previous case.
For the case of a person touching your toes from a standing position (figure on the right)In the case of a person the lever arm of the upper part of the body and of the arms is greater than in the previous case, therefore the torque performed is much greater and therefore the tension in the spine is greater than in the previous case.
Conclusion:
Touching the toes while sitting on the floor with the legs extended produces less tension in the spine than when you touch the toes from a standing position because the lever arm of the upper body is less and therefore the torque made is less. In this way the tension in the spine is less when you are sitting on the floor with your legs extended.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- pls help on thesearrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





