
Essential University Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134988559
Author: Wolfson, Richard
Publisher: Pearson Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.3, Problem 8.2GI
Suppose the paths in Fig. 8.8 are the paths of four projectiles. Rank each path (circular, elliptical, parabolic, and hyperbolic) according to the initial speed of the corresponding projectile. Assume all are launched front their common point at the top of the figure.
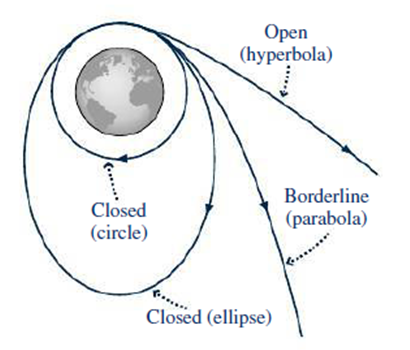
FIGURE 8.8 Closed and open orbits.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Hi Expert,
I have uploaded picture, could you please name the Greek alphabet and their name in English?
Hi Expert in Physics,
I have uploaded pictures with respect to some physics equations. Could please name all Greek alphabet and their English name?
81 SSM Figure 29-84 shows a cross
section of an infinite conducting
sheet carrying a current per unit
x-length of 2; the current emerges
perpendicularly out of the page.
(a) Use the Biot-Savart law and
symmetry to show that for all points
B
P
P. BD
P'
Figure 29-84 Problem 81.
x
P above the sheet and all points P' below it, the magnetic field B
is parallel to the sheet and directed as shown. (b) Use Ampere's
law to prove that B = ½µλ at all points P and P'.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essential University Physics
Ch. 8.2 - Suppose the distance between two objects is cut in...Ch. 8.3 - Suppose the paths in Fig. 8.8 are the paths of...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.3GICh. 8 - What do Newtons apple and the Moon have in common?Ch. 8 - Prob. 2FTDCh. 8 - When you stand on Earth, the distance between you...Ch. 8 - The force of gravity on an object is proportional...Ch. 8 - A friend who knows nothing about physics asks what...Ch. 8 - Could you put a satellite in an orbit that keeps...Ch. 8 - Why are satellites generally launched eastward and...
Ch. 8 - Given Earths mass, the Moons distance and orbital...Ch. 8 - How should a satellite be launched so that its...Ch. 8 - Does the gravitational force of the Sun do work on...Ch. 8 - Space explorers land on a planet with the same...Ch. 8 - Use data for the Moons orbit from Appendix E to...Ch. 8 - Prob. 13ECh. 8 - Prob. 14ECh. 8 - Two identical lead spheres with their centers 14...Ch. 8 - Whats the approximate value of the gravitational...Ch. 8 - A sensitive gravimeter is carried to the top of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Find the speed of a satellite in geostationary...Ch. 8 - Marss orbit has a diameter 1.52 times that of...Ch. 8 - Calculate the orbital period for Jupiters moon Io,...Ch. 8 - An astronaut hits a golf ball horizontally from...Ch. 8 - The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter circles the red...Ch. 8 - Earths distance from the Sun varies from 147 Gm at...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25ECh. 8 - A rocket is launched vertically upward from Earths...Ch. 8 - What vertical launch speed is necessary to get a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 28ECh. 8 - Determine escape speeds from (a) Jupiters moon...Ch. 8 - Prob. 30ECh. 8 - Prob. 31ECh. 8 - Prob. 32ECh. 8 - Example 8.2: Find the altitude and speed of a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 34ECh. 8 - Prob. 35ECh. 8 - Example 8.4: A coronal mass ejection (CME) is an...Ch. 8 - Example 8.4: In September 2017, the Cassini...Ch. 8 - The gravitational acceleration at a planets...Ch. 8 - Prob. 39PCh. 8 - If youre standing on the ground 15 m directly...Ch. 8 -
On January 1, 2019, the450-kg New Horizons...Ch. 8 - Equation 7.9 relates force to the derivative of...Ch. 8 - During the Apollo Moon landings, one astronaut...Ch. 8 - Prob. 44PCh. 8 - Prob. 45PCh. 8 - Prob. 46PCh. 8 - Prob. 47PCh. 8 - Satellites A and B are in circular orbits, with A...Ch. 8 - The asteroid that exploded over Chelyabinsk,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 50PCh. 8 - Prob. 51PCh. 8 - Neglecting air resistance, to what height would...Ch. 8 - Show that an object released from rest very far...Ch. 8 - Prob. 54PCh. 8 -
In 2017 North Korea developed ballistic missile...Ch. 8 - Prob. 56PCh. 8 - Prob. 57PCh. 8 - Prob. 58PCh. 8 - Prob. 59PCh. 8 - Two meteoroids are 160,000 km from Earths center...Ch. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - A missiles trajectory takes it to a maximum...Ch. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - Mercurys orbital speed varies from 38.8 km/s at...Ch. 8 - Prob. 66PCh. 8 - Two satellites are in geostationary orbit but in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Prob. 69PCh. 8 - We derived Equation 8.4 on the assumption that the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 71PCh. 8 - As a member of the 2040 Olympic committee, youre...Ch. 8 - The Olympic Committee is keeping you busy! Youre...Ch. 8 - Tidal forces are proportional to the variation in...Ch. 8 - Spacecraft that study the Sun are often placed at...Ch. 8 - Prob. 76PPCh. 8 - Prob. 77PPCh. 8 - Prob. 78PPCh. 8 - The Global Positioning System (GPS) uses a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Draw the following orbitals: a. 3s orbital b. 4s orbital c. 3p orbital
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Foods packed in plastic for microwaving are a. dehydrated. b. freeze-dried. c. packaged aseptically. d. commerc...
Microbiology: An Introduction
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Use a globe or map to determine, as accurately as possible, the latitude and longitude of Athens, Greece.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
How can the freezing of water crack boulders?
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Some organizations are starting to envision a sustainable societyone in which each generation inherits sufficie...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What All equations of Ountum physics?arrow_forwardPlease rewrite the rules of Quantum mechanics?arrow_forwardSuppose there are two transformers between your house and the high-voltage transmission line that distributes the power. In addition, assume your house is the only one using electric power. At a substation the primary of a step-down transformer (turns ratio = 1:23) receives the voltage from the high-voltage transmission line. Because of your usage, a current of 51.1 mA exists in the primary of the transformer. The secondary is connected to the primary of another step-down transformer (turns ratio = 1:36) somewhere near your house, perhaps up on a telephone pole. The secondary of this transformer delivers a 240-V emf to your house. How much power is your house using? Remember that the current and voltage given in this problem are rms values.arrow_forward
- The human eye is most sensitive to light having a frequency of about 5.5 × 1014 Hz, which is in the yellow-green region of the electromagnetic spectrum. How many wavelengths of this light can fit across a distance of 2.2 cm?arrow_forwardA one-dimensional harmonic oscillator of mass m and angular frequency w is in a heat bath of temperature T. What is the root mean square of the displacement of the oscillator? (In the expressions below k is the Boltzmann constant.) Select one: ○ (KT/mw²)1/2 ○ (KT/mw²)-1/2 ○ kT/w O (KT/mw²) 1/2In(2)arrow_forwardTwo polarizers are placed on top of each other so that their transmission axes coincide. If unpolarized light falls on the system, the transmitted intensity is lo. What is the transmitted intensity if one of the polarizers is rotated by 30 degrees? Select one: ○ 10/4 ○ 0.866 lo ○ 310/4 01/2 10/2arrow_forward
- Before attempting this problem, review Conceptual Example 7. The intensity of the light that reaches the photocell in the drawing is 160 W/m², when 0 = 18°. What would be the intensity reaching the photocell if the analyzer were removed from the setup, everything else remaining the same? Light Photocell Polarizer Insert Analyzerarrow_forwardThe lifetime of a muon in its rest frame is 2.2 microseconds. What is the lifetime of the muon measured in the laboratory frame, where the muon's kinetic energy is 53 MeV? It is known that the rest energy of the muon is 106 MeV. Select one: O 4.4 microseconds O 6.6 microseconds O 3.3 microseconds O 1.1 microsecondsarrow_forwardThe Lagrangian of a particle performing harmonic oscil- lations is written in the form L = ax² - Bx² - yx, where a, and are constants. What is the angular frequency of oscillations? A) √2/a B) √(+2a)/B C) √√Ba D) B/αarrow_forward
- The mean temperature of the Earth is T=287 K. What would the new mean temperature T' be if the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun was increased by 2%? Select one: ○ 293 K O 281 K ○ 273 K 284 Karrow_forwardTwo concentric current-carrying wire loops of radius 3 cm and 9 cm lie in the same plane. The currents in the loops flow in the same direction and are equal in magnitude. The magnetic field at the common center of the loops is 50 mT. What would be the value of magnetic field at the center if the direction of the two currents was opposite to each other (but their value is kept constant)? Select one: ○ 20 mT ○ 10 mT O 15 mT ○ 25 mTarrow_forwardAn ideal coil of inductivity 50 mH is connected in series with a resistor of 50 ohm. This system is connected to a 4.5 V battery for a long time. What is the current in the circuit? Select one: O 45 mA ○ 90 mA 00 mA O 150 mAarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY