
(a)
To graph : The given situation using
Given information :
The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale rates an earthquake's "shaking strength". In general, the rating decreases as distance from the earthquake's epicenter increases. Suppose an earthquake has a Mercalli rating of
Graph :
The graph representing the given situation will be as below:
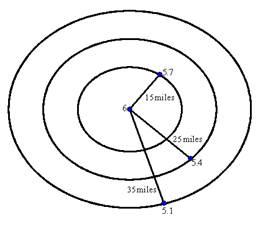
Interpretation :
The distance from the epicenter will be the radius of the circles.
(b)
To explain : An inequality for each circle describing the coordinates of locations with Mercalli rating at least as great as the Mercalli rating represented by the circle.
The three required equations are
Given information :
The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale rates an earthquake's "shaking strength". In general, the rating decreases as distance from the earthquake's epicenter increases. Suppose an earthquake has a Mercalli rating of
Explanation :
For the first earthquake having Mercalli rating
For the second earthquake having Mercalli rating
For the third earthquake having Mercalli rating
Therefore, the three required equations are
(c)
To calculate : The Mercalli rating
The prediction can be made using
Given information :
The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale rates an earthquake's "shaking strength". In general, the rating decreases as distance from the earthquake's epicenter increases. Suppose an earthquake has a Mercalli rating of
Explanation :
The value of Mercalli rating
Therefore, the prediction can be made using
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ALGEBRA 2
- In simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forwardWrite each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forward
- Step by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step how do you find the zeros of y = 6x2 + 24x - 192arrow_forwardStep by step Find the zeros of each quadratic relation. a) y = x2 - 16xarrow_forward
- In simplest step by step terms, how do you find the zeros of y = x2 - 16arrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Describe the shape and position of the parabola relative to the graph of y = x 2 y = - 80( x + 9) 2 + 10.8arrow_forwardas a Identify each equation Parabola, circle, ellipse perbola without completio the square. x²-6x-14 y = 33-y² 14y ofarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





