
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305401969
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 8.4QQ
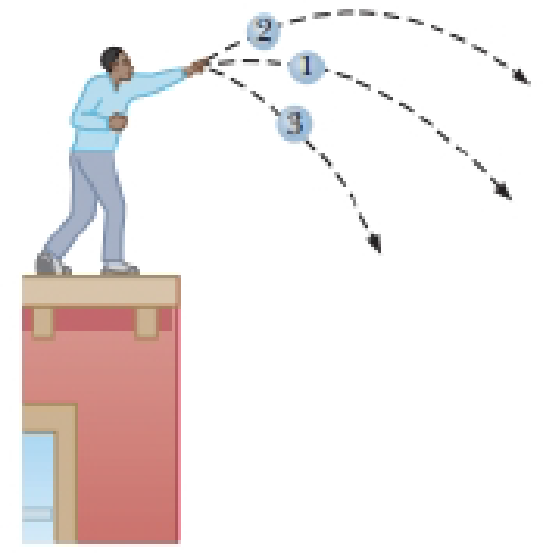
Three identical balls are thrown from the top of a building, all with the same initial speed. As shown in Figure 8.3, the first is thrown horizontally, the second at some angle above the horizontal, and the third at some angle below the horizontal. Neglecting air resistance, rank the speeds of the balls at the instant each hits the ground.
Figure 8.3 (Quick Quiz 8.3) Three identical balls are thrown with the same initial speed from the top of a building.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A 1.40-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of v₁ = 3.50 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been
compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e).
d
m
v=0
-D- www
(a) Find the distance of compression d (in m).
m
(b) Find the speed v (in m/s) at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d).
m/s
(c) Find the distance D (in m) where the object comes to rest.
m
(d) What If? If the object becomes attached securely to the end of the spring when it makes contact, what is the new value of the distance D (in m) at which the object will come to…
As shown in the figure, a 0.580 kg object is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x. The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the object travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point A, the bottom of a
vertical circular track of radius R = 1.00 m, and continues to move up the track. The speed of the object at the bottom of the track is VA = 13.0 m/s, and the object experiences an average frictional force of 7.00 N while sliding up the track.
R
(a) What is x?
m
A
(b) If the object were to reach the top of the track, what would be its speed (in m/s) at that point?
m/s
(c) Does the object actually reach the top of the track, or does it fall off before reaching the top?
O reaches the top of the track
O falls off before reaching the top
○ not enough information to tell
A block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest.
wwww
wwwwww
a
F
x = 0
0
b
i
(a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum.
ст
(b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation?
cm
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
Ch. 8.1 - Consider a block sliding over a horizontal surface...Ch. 8.2 - A rock of mass m is dropped to the ground from a...Ch. 8.2 - Three identical balls are thrown from the top of a...Ch. 8.3 - You are traveling along a freeway at 65 mi/h. Your...Ch. 8 - Prob. 1OQCh. 8 - Two children stand on a platform at the top of a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 3OQCh. 8 - An athlete jumping vertically on a trampoline...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5OQCh. 8 - In a laboratory model of cars skidding to a stop,...
Ch. 8 - Prob. 7OQCh. 8 - Prob. 8OQCh. 8 - Prob. 9OQCh. 8 - One person drops a ball from the top of a building...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2CQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CQCh. 8 - Prob. 4CQCh. 8 - Prob. 5CQCh. 8 - Prob. 6CQCh. 8 - In the general conservation of energy equation,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8CQCh. 8 - A block is connected to a spring that is suspended...Ch. 8 - Prob. 10CQCh. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - Prob. 2PCh. 8 - Prob. 3PCh. 8 - A 20.0-kg cannonball is fired from a cannon with...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5PCh. 8 - A block of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point...Ch. 8 - Prob. 7PCh. 8 - Prob. 8PCh. 8 - A light, rigid rod is 77.0 cm long. Its top end is...Ch. 8 - At 11:00 a.m, on September 7, 2001, more than one...Ch. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - Prob. 12PCh. 8 - A sled of mass m is given a kick on a frozen pond....Ch. 8 - A crate of mass 10.0 kg is pulled up a rough...Ch. 8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8 - A 40.0-kg box initially at rest is pushed 5.00 m...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17PCh. 8 - At time ti, the kinetic energy of a particle is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19PCh. 8 - As shown in Figure P8.10, a green bead of mass 25...Ch. 8 - Prob. 21PCh. 8 - Prob. 22PCh. 8 - Prob. 23PCh. 8 - A 1.50-kg object is held 1.20 m above a relaxed...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25PCh. 8 - An 80.0-kg skydiver jumps out of a balloon at an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 27PCh. 8 - Prob. 28PCh. 8 - Prob. 29PCh. 8 - The electric motor of a model train accelerates...Ch. 8 - Prob. 31PCh. 8 - Prob. 32PCh. 8 - An energy-efficient lightbulb, taking in 28.0 W of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 34PCh. 8 - Prob. 35PCh. 8 - An older-model car accelerates from 0 to speed v...Ch. 8 - Prob. 37PCh. 8 - Prob. 38PCh. 8 - Prob. 39PCh. 8 - Energy is conventionally measured in Calories as...Ch. 8 - A loaded ore car has a mass of 950 kg and rolls on...Ch. 8 - Prob. 42APCh. 8 - Prob. 43APCh. 8 - Prob. 44APCh. 8 - Prob. 45APCh. 8 - Review. As shown in Figure P8.26, a light string...Ch. 8 - Prob. 47APCh. 8 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 8 - Prob. 49APCh. 8 - Prob. 50APCh. 8 - Jonathan is riding a bicycle and encounters a hill...Ch. 8 - Jonathan is riding a bicycle and encounters a hill...Ch. 8 - Consider the blockspringsurface system in part (B)...Ch. 8 - As it plows a parking lot, a snowplow pushes an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 55APCh. 8 - Consider the popgun in Example 8.3. Suppose the...Ch. 8 - As the driver steps on the gas pedal, a car of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 58APCh. 8 - A horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60APCh. 8 - Prob. 61APCh. 8 - Prob. 62APCh. 8 - Prob. 63APCh. 8 - Prob. 64APCh. 8 - A block of mass 0.500 kg is pushed against a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 66APCh. 8 - Prob. 67APCh. 8 - A pendulum, comprising a light string of length L...Ch. 8 - Prob. 69APCh. 8 - Review. Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 8 - Prob. 71APCh. 8 - Prob. 72APCh. 8 - Prob. 73APCh. 8 - Prob. 74APCh. 8 - Prob. 75APCh. 8 - Prob. 76APCh. 8 - Prob. 77APCh. 8 - Prob. 78APCh. 8 - Prob. 79CPCh. 8 - Starting from rest, a 64.0-kg person bungee jumps...Ch. 8 - Prob. 81CPCh. 8 - Prob. 82CPCh. 8 - Prob. 83CPCh. 8 - A uniform chain of length 8.00 m initially lies...Ch. 8 - Prob. 85CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have a new internship, where you are helping to design a new freight yard for the train station in your city. There will be a number of dead-end sidings where single cars can be stored until they are needed. To keep the cars from running off the tracks at the end of the siding, you have designed a combination of two coiled springs as illustrated in the figure below. When a car moves to the right in the figure and strikes the springs, they exert a force to the left on the car to slow it down. Total force (N) 2000 1500 1000 500 Distance (cm) 10 20 30 40 50 60 i Both springs are described by Hooke's law and have spring constants k₁ = 1,900 N/m and k₂ = 2,700 N/m. After the first spring compresses by a distance of d = 30.0 cm, the second spring acts with the first to increase the force to the left on the car in the figure. When the spring with spring constant k₂ compresses by 50.0 cm, the coils of both springs are pressed together, so that the springs can no longer compress. A typical…arrow_forwardA spring is attached to an inclined plane as shown in the figure. A block of mass m = 2.71 kg is placed on the incline at a distance d = 0.285 m along the incline from the end of the spring. The block is given a quick shove and moves down the incline with an initial speed v = incline angle is 0 = 20.0°, the spring constant is k = 505 N/m, and we can assume the surface is frictionless. By what distance (in m) is the spring compressed when the block momentarily comes to rest? m k www m 0.750 m/s. Thearrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.50 kg situated on an incline at an angle of k=100 N/m www Ө m = 50.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (Fig. P8.54). The pulley and incline are frictionless. The block is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. (a) How far does it move down the frictionless incline before coming to rest? m (b) What is its acceleration at its lowest point? Magnitude m/s2 Direction O up the incline down the inclinearrow_forward
- (a) A 15.0 kg block is released from rest at point A in the figure below. The track is frictionless except for the portion between points B and C, which has a length of 6.00 m. The block travels down the track, hits a spring of force constant 2,100 N/m, and compresses the spring 0.250 m from its equilibrium position before coming to rest momentarily. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface between points B and C. 3.00 m -A B C -6.00 m (b) What If? The spring now expands, forcing the block back to the left. Does the block reach point B? ○ Yes No If the block does reach point B, how far up the curved portion of the track does it reach, and if it does not, how far short of point B does the block come to a stop? (Enter your answer in m.) marrow_forwardA ball of mass m = 1.95 kg is released from rest at a height h = 57.0 cm above a light vertical spring of force constant k as in Figure [a] shown below. The ball strikes the top of the spring and compresses it a distance d = 7.80 cm as in Figure [b] shown below. Neglecting any energy losses during the collision, find the following. т h m a d T b (a) Find the speed of the ball just as it touches the spring. m/s (b) Find the force constant of the spring. kN/marrow_forwardTruck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as shown in the figure below. When the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, the helper spring engages and then helps to support any additional load. Suppose the leaf spring constant is 5.05 × 105 N/m, the helper spring constant is 3.50 x 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m. Truck body yo Main leaf spring -"Helper" spring Axle (a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 6.00 × 105 N? m (b) How much work is done in compressing the springs? ]arrow_forward
- A block of mass m₁ = 10.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m₂ 34.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 34.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 200 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is unstretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 10.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 22.0 cm down the incline of angle = 40.0° and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the spring is again unstretched. Vm1 × 1.32 Vm2 = 1.32 × m/s m/sarrow_forwardA block of mass m₁ = 10.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m₂ = 34.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 34.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 200 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is unstretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 10.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 22.0 cm down the incline of angle 0 = 40.0° and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the spring is again unstretched. m/s Vm1 Vm2 m/s mi m2 k iarrow_forwardTruck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as in the figure below. The helper spring engages when the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, and then helps to support any additional load. Consider a leaf spring constant of 5.45 × 105 N/m, helper spring constant of 3.60 × 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m. Truck body Dyo Axle (a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 4.90 × 105 N? m (b) How much work is done compressing the springs? ]arrow_forward
- A skier of mass 75 kg is pulled up a slope by a motor-driven cable. (a) How much work is required to pull him 50 m up a 30° slope (assumed frictionless) at a constant speed of 2.8 m/s? KJ (b) What power (expressed in hp) must a motor have to perform this task? hparrow_forwardA block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest. a x = 0 x b (a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum. cm (b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation? cmarrow_forwardA block of mass m = 3.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 0 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 11.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k=100 N/m Ө marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7u6pIfUVy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY