
Interpretation:
Nucleophilic centers in the given compound have to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Nucleophile is the one which are capable of donating a pair of electrons. The one which is capable of accepting a pair of electrons are known as electrophiles. The ions which possess a negative charge (lone pair of electrons) over it can act as a good nucleophile. Some of them are,
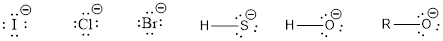
The compounds that contain lone pair of electrons also can act as nucleophile. Even though there is absence of negative charge, the presence of lone pair of electrons can make them to act as a good nucleophile. Some of the compounds are,
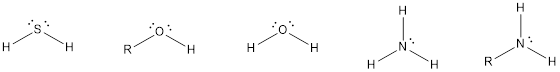
The compounds that contain unsaturated bonds also can act as nucleophile. This is because the unsaturated bonds are the regions where there is high electron density in space. Some of the compounds are,
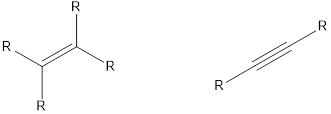
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forwardPredict the major products of this reaction: ་ ་ + H NaOH ? Δ excess Note that the second reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the second reactant than the first. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





