
Concept explainers
(a) Show that the beam of Prob. 8.41 cannot be moved if the top surface of the dolly is slightly lower than the platform. (b) Show that the beam can be moved if two 175-lb workers stand on the beam at B, and determine how far to the left the beam can be moved.
8.41 A 10-ft beam, weighing 1200 lb, is to be moved to the left onto the platform as shown. A horizontal force P is applied to the dolly, which is mounted on frictionless wheels. The coefficients of friction between all surfaces are μs = 0.30 and μs = 0.25, and initially, χ = 2 ft. Knowing that the top surface of the dolly is slightly higher than the platform, determine the force P required to start moving the beam. (Hint: The beam is supported at A and D.)
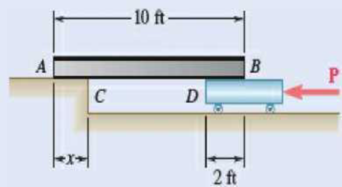
Fig. P8.41
(a)
Show that the beam cannot be moved if the top surface of the dolly is slightly lower than the platform.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is 10 ft.
The weight of the beam is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the beam AB as in Figure 1.
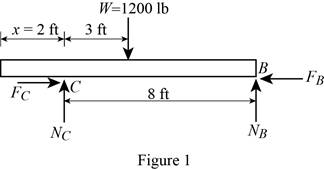
Find the normal force at point B by taking moment about end C.
Find the normal force at point C by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Find the maximum friction force at point C
Substitute 0.30 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
The maximum friction force at point B is less than the maximum friction force at point C.
The sliding is about to happen at point B.
Therefore, the beam
(b)
Show that the beam can be moved if two 175-lb workers stand on the beam at B.
Find the distance the beam moves to the left.
Answer to Problem 8.42P
The distance the beam moves to the left is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is 10 ft.
The weight of the beam is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the beam AB as in Figure 2.
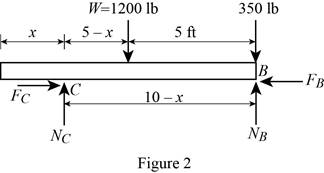
Find the normal force at point B by taking moment about end C.
Find the normal reaction at point C by taking moment about point B.
When two 175 lb workers stand on the end B:
Substitute 2 ft for x in Equation (1).
Substitute 2 ft for x in Equation (2).
Find the maximum friction force at point C
Substitute 0.30 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
The maximum friction force at point B is greater than the maximum friction force at point C.
The sliding is about to happen at point C.
Therefore, the beam
The beam will stop moving when the friction force at point C is equal to the maximum friction force at point B.
Find the friction force at point C
Substitute 0.25 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
Substitute
Therefore, the distance the beam moves to the left is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- 4-1 Q4: Q5: (20 Marks) Find √48 using False Position Method with three iterations. Hint: the root lies between 3 and 4. (20 Marks)arrow_forwardDetermine the angle between vectors FA and FB that is less than 180 degrees. FA is the vector drawn from the origin to point A (-4, 4, 2) while FB is the vector drawn from the origin to point B (3, 1, -3).arrow_forwardFind the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.arrow_forward
- A 2-kW resistance heater wire with thermal conductivity of k=20 W/mK, a diameter of D=4mm, and a length of L=0.9m is used to boil water. If the outer surface temp of the resistance wire is Ts=110 degrees C, determine the temp at the center of the wire.arrow_forwardA flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has emmisssivity and an absorptivity of 0.9. The top surface where x=0 temp of the absorber is T0=35 degrees C, and solar radiation is incident on the basorber at 500 W/m^2 with a surrounding temp of 0 degrees C. The convection heat transfer coefficient at the absorber surface is 5 W/m^2 K, while the ambient temp is 25 degrees C. Show that the variation of the temp in the basorber plate can be expressed as T(x)=-(q0/k)x+T0, and determine net heat flux, q, absorbed by solar collector.arrow_forwardUsing properties of a saturated water, explain how you would determine the mole fraction of water vapor at the surface of a lake when the temp of the lake surface and the atmospheric pressure are specified.arrow_forward
- Consider a glass of water in a room at 15 degrees C and 97 kPa. If the relative humidity in the room is 100 percent and the water and the air are in thermal and phase equilibrium, determine the mole fraction of the water vapor in the air and the mole fraction of air in the water.arrow_forwardStaring with an energy balance on a cylindirical shell volume element, derive the steady one dimensional heat conduction equation for a long cylinder with constant thermal conductivity in which heat is generated at a rate of egen.arrow_forwardConsider a round potato being baked in an oven. Would you model the heat transfer to the potato as one, two, or three dimensional? Would the heat transfer be steady or transient? Also, which coordinate system would you use to solve this problem, and where would you place the origin? Explain.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





