
Centroid of the surface generated by revolving the parabola about x axis
Answer to Problem 8.75P
The centroid
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
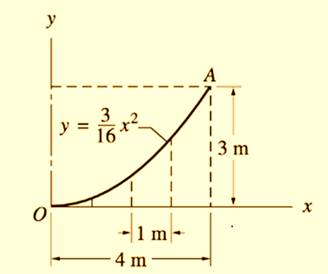
The centroid of the surface is defined as:
Calculation:
Consider the surface element, a ring obtained by rotating the line of length
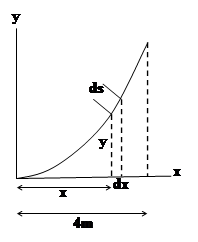
We know that
Differentiate
The differential area
The centroidal coordinate
The area A of the element
The first moment
Apply Simpson's rule to evaluate above integrals.
| x (m) | y (m) | | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.1875 | 0.20025 | 0.20025 |
| 2 | 0.75 | 0.9375 | 1.875 |
| 3 | 1.6875 | 2.54 | 7.62 |
| 4 | 3.0 | 5.408 | 21.633 |
The Area A of the element
The first moment
The point of action
Due to symmetry
Conclusion:
The centroid
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics 4th Edition
- 70. Compute the number of cubic centimeters of iron required for the cast-iron plate shown. The plate is 3.50 centimeters thick. Round the answer to the nearest cubic centimeter. 50.0 cm 40.0 cm Radius 150° 115.0 cm- 81.0 cmarrow_forwardLaw of Sines Solve the following problems using the Law of Sin 7. Find side x. All dimensions are in inches. -°-67°-37° 81° x Sin A 8.820 X 67°00' 32°00' a sin A b C sin B sin Carrow_forward35. a. Determine B. b. Determine side b. c. Determine side c. 5.330 in.- ZB 73°30'arrow_forward
- Consider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15 degrees C throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15 degrees C at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forwardnote n=number of link(dont include the ground link (fixed))arrow_forward6.(单选题) The DOF of the following mechanism is E A F=3x4-2x5-0=2 B F=3x3-2x4-0=1 F=3x3-2x3-2=1 D F=3x4-2x5-1=1arrow_forward
- VIMAarrow_forward1. Calculation Calculate the DOF of the following mechanis m 2 3 1 Please enter the answerarrow_forwarda) Determine state of stress at all points (a, b and c). These points are located on the exteriorsurface of the beam. Point a is located along the centreline of the beam, point b is 15mmfrom the centreline and point c is located on the edge of the beam. Present yourresults in a table and ensure that your sign convention is clearly shownb) Construct Mohrs circle at this point andcalculate the principal stresses and maximum in‐plane shear stress (τmax) at pointc. sketch the resulting state of stress at this point clearly indicating themagnitude of the stresses and any angles associated with the state of stress (principal ormaximum in‐plane shear).arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
