
Concept explainers
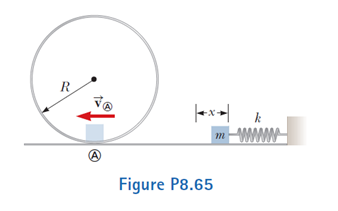
A block of mass 0.500 kg is pushed against a horizon-tal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x (Fig. P8.65). The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the block travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point Ⓐ, the bottom of a vertical circular track of radius R = 1.00 m, and continues to move up the track. The block’s speed at the bottom of the track is vⒶ = 12.0 m/s, and the block experiences an average friction force of 7.00 N while sliding up the track. (a) What is x? (b) If the block were to reach the top of the track, what would be its speed at that point? (c) Does the block actually reach the top of the track, or does it fall off before reaching the top?
(a)
The value of compression in the spring
Answer to Problem 8.65AP
The value of compression in the spring
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the block is
The formula to calculate the initial kinetic energy of the block is,
Here,
The initial velocity of the block is 0 as it is at rest then the initial kinetic energy of the block is 0.
The formula to calculate the final kinetic energy is,
Here,
The formula to calculate initial potential energy is,
Here,
The formula to calculate the final potential energy is,
Here,
Thus, the final potential energy of the block is
The formula to calculate the initial energy is,
Here,
The final compression distance is 0 as the spring does not move after striking to the block then the final potential energy is 0.
Substitute
Thus, the initial energy is
The formula to calculate the final energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the final energy is
From the law of conservation of the energy,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above formula for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of
(b)
The speed of the block at the top of the track.
Answer to Problem 8.65AP
The speed of the block at the top of the track is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the block is
The formula to calculate the work done by the frictional force is,
Here,
The formula to calculate the initial kinetic energy of the block is,
Here,
The formula to calculate the final kinetic energy is,
Here,
The formula to calculate initial potential energy is,
Here,
The initial height of the block is 0 as the block is at the bottom of the track then the initial potential energy is 0.
The formula to calculate the final potential energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the final potential energy of the block is
The formula to calculate the initial energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the initial energy is
The formula to calculate the final energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the final energy is
The formula to calculate the law of conservation of energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above formula for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the block at the top of the track is
(c)
Whether the block reach the top of the track or fall off before reaching the top.
Answer to Problem 8.65AP
The block stays at the top of the track.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the block is
The formula to calculate the centripetal acceleration of the block at the top of the track is,
Here,
Substitute
if the centripetal acceleration of the block at the top of the track is less than the acceleration due to gravity then the block fall but centripetal acceleration of the block at the top of the track is greater than the acceleration due to gravity that concludes that the block actually reaches the top of the track.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the block stays at the top of the track.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 1, Chapters 1-22
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Iarrow_forwardHow would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?arrow_forward14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forwardCheckpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forward
- What is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





