
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
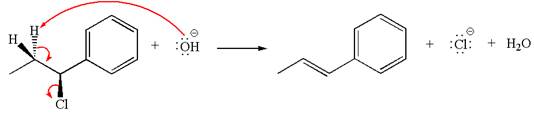
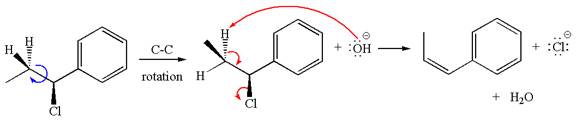
The
Explanation of Solution
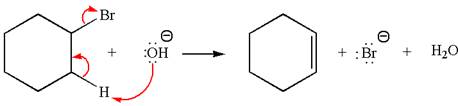
The given reaction equation is:
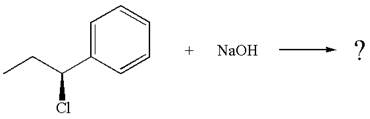
In the given reaction,
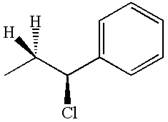
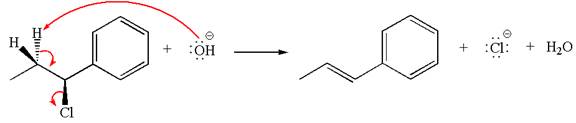
The hydrogen atom, indicated with the dash bond, is anti to
If the hydrogen atom, indicated with wedge bond, tends to eliminate, it must orient anti to
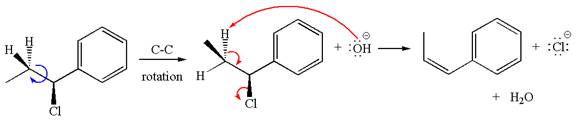
In
The products formed for the given reaction from both
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
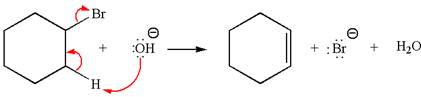
The
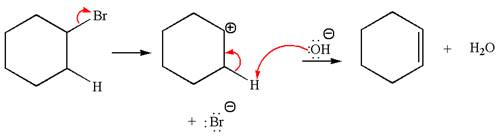
Explanation of Solution
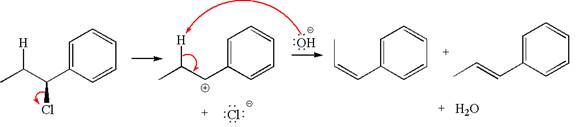
The given reaction equation is:
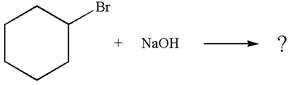
In the given reaction,
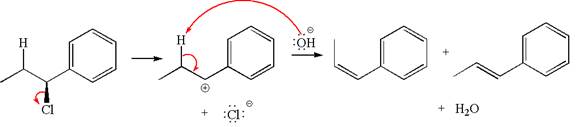
In
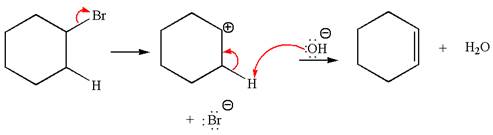
The products formed for the given reaction from both
(c)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
The
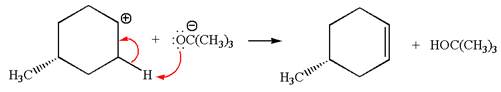
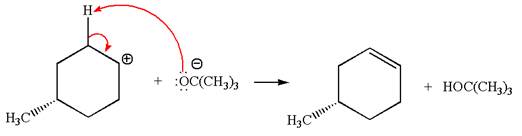
Explanation of Solution
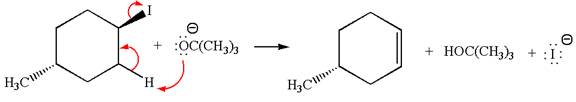
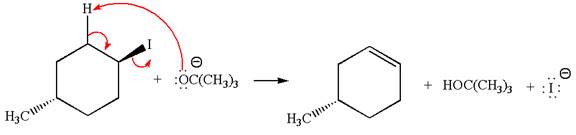
The given reaction equation is:
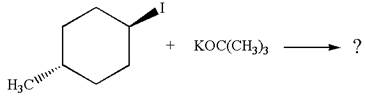
In the given reaction,
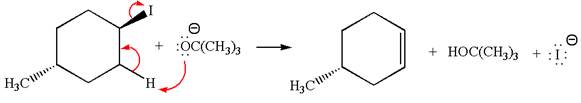
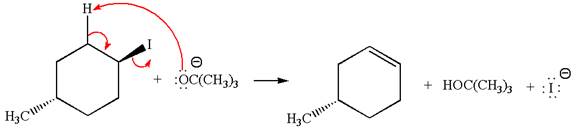
In
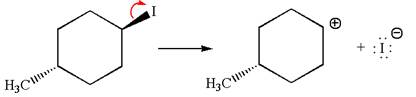
In the second step, the base abstracts the proton from the carbon adjacent to the positively charged carbon. Two products are possible because the proton gets eliminated from two different carbon atoms. The detailed mechanism is shown below:

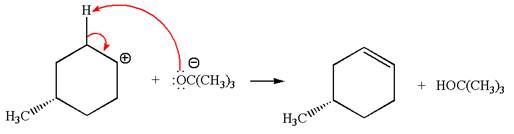
The products formed for the given reaction from both
(d)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
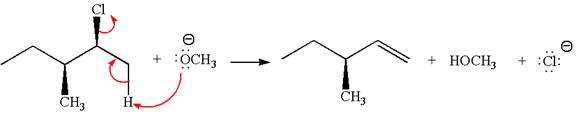
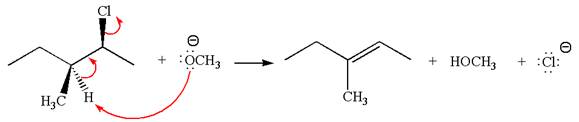
The
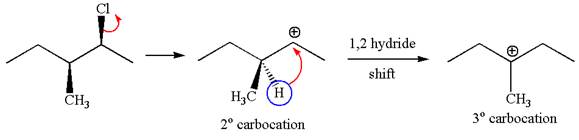
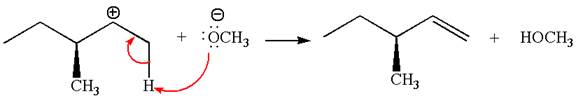
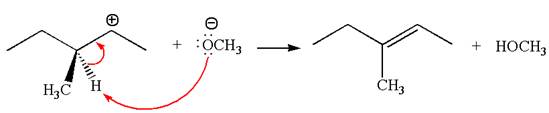
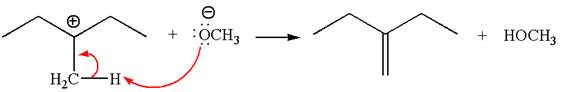
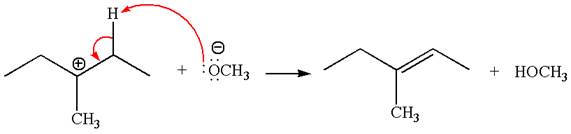
Explanation of Solution
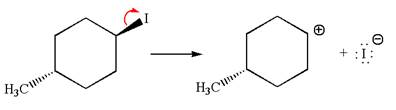
The given reaction equation is:
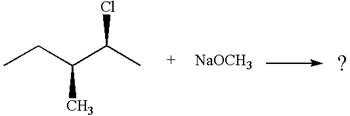
In the given reaction,
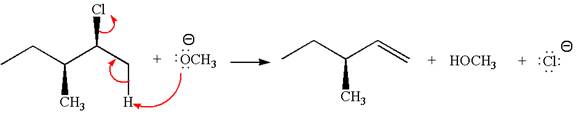
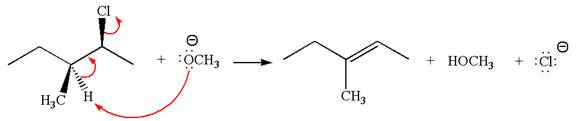
In
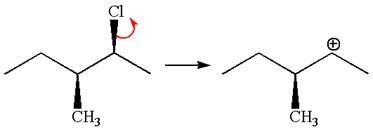
In the second step, the base abstracts the proton from the carbon adjacent to the positively charged carbon. Two products are possible from the secondary carbocation because the proton is eliminated from two different carbon atoms.

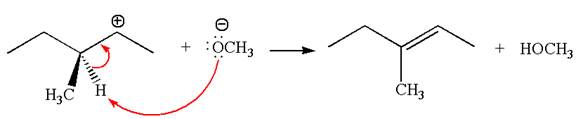
The carbocation formed is a secondary carbocation, which can be rearranged to a more stable tertiary carbocation by
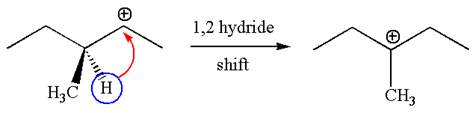
Two products are possible from the tertiary carbocation because the proton is eliminated from two different carbon atoms.
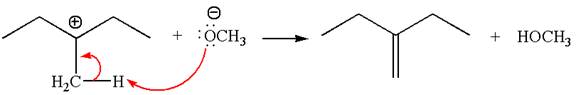
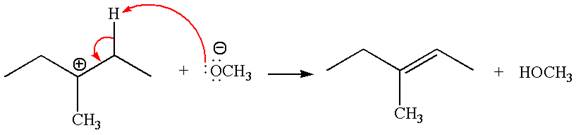
Thus, in all the reactions above, the products are formed by
The products formed for the given reaction from both
(e)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
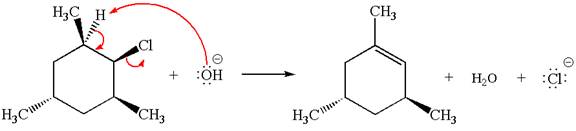
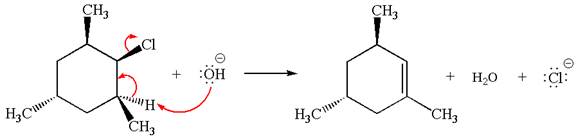
The
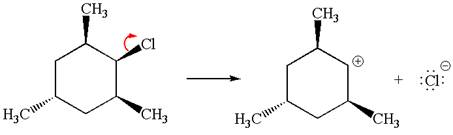
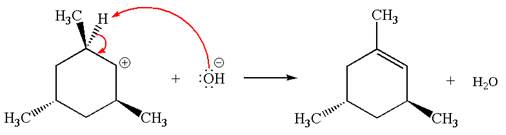
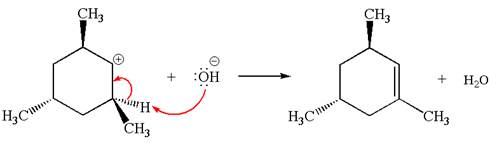
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction equation is:
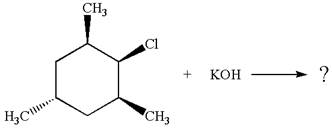
In the given reaction,
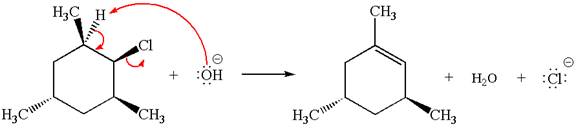

In

In the second step, the base abstracts the proton from the carbon adjacent to the positively charged carbon. Two products are possible because the proton is eliminated from two different carbon atoms. The detailed mechanism is shown below:


The products formed for the given reaction from both
(f)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanisms for the given reaction occurring via
Concept introduction:
The
In case of
Answer to Problem 8.44P
The
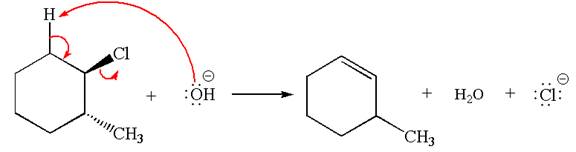
The
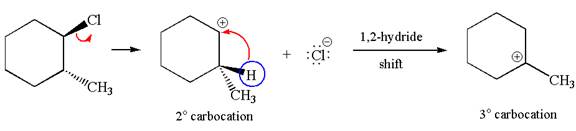
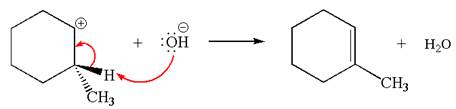
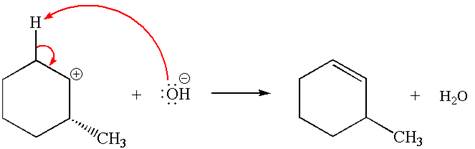
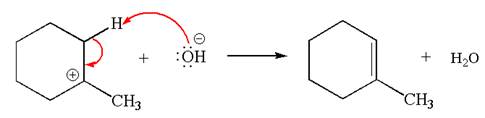
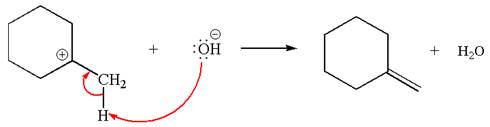
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction equation is:
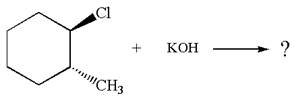
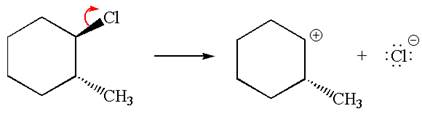
In the given reaction,
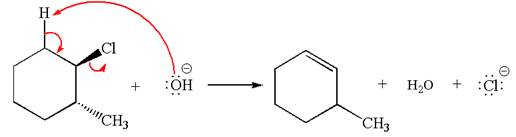
In
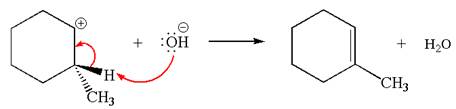
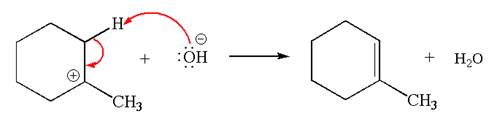
In the second step, the base abstracts the proton from the carbon adjacent to positively charged carbon. Two products are possible because the proton is eliminated from two different carbon atoms. The detailed mechanism is shown below:
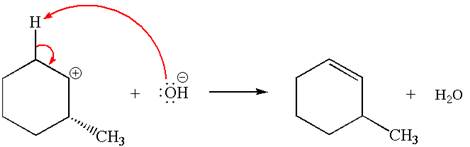
The carbocation formed is a secondary carbocation, which can be rearranged to form more stable tertiary carbocation by
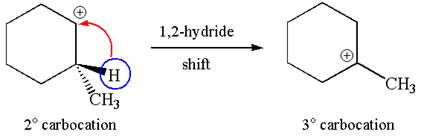
Two products are possible from the tertiary carbocation because the proton IS eliminated from two different carbon atoms.
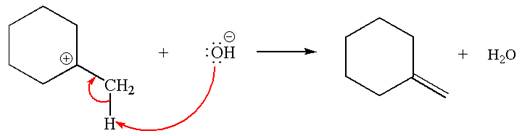
The products formed for the given reaction from both
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardcan you please answer both these questions and draw the neccesaryarrow_forwardcan you please give the answer for both these pictures. thankyouarrow_forward
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) | Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalinarrow_forwardQuestion 19 0/2 pts 3 Details You have a mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl) dissolved in water and want to separate out the Cl- ions by precipitating them out using silver ions (Ag+). The chemical equation for the net ionic reaction of NaCl and KCl with silver nitrate, AgNO3, is shown below. Ag+(aq) + Cl(aq) → AgCl(s) The total mass of the NaCl/KCl mixture is 1.299 g. Adding 50.42 mL of 0.381 M solution precipitates out all of the Cl-. What are the masses of NaCl and KCl in the mixture? Atomic masses: g: Mass of NaCl g: Mass of KCL Ag = 107.868 g mol- 1 Cl = 35.453 g mol- 1 K = 39.098 g mol- N = 14.007 g mol−1 Na = 22.99 g mol−1 0 = 15.999 g mol 1 Question Help: ✓ Message instructor Submit Questionarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerolarrow_forward
- Identify the missing starting materials/ reagents/ products in the following reactions. Show the stereochemistry clearly in the structures, if any. If there is a major product, draw the structures of the major product with stereochemistry clearly indicated where applicable. Show only the diastereomers (you do not have to draw the pairs of enantiomers). If you believe that multiple products are formed in approximately equal amounts (hence neither is the major product), draw the structures of the products, and show the detailed mechanism of these reactions to justify the formation of the multiple products. If you believe no product is formed, explain why briefly. (6 mark for each, except f and g, which are 10 mark each)arrow_forward3. What starting material would you use to synthesize 3-hydroxypentanoic acid using a NaBH4 reduction?arrow_forward1. Give stereochemical (Fischer projection) formulas for all (but no extras) the stereoisomers that could theoretically form during the reduction of a. the carbonyl group of 2-methyl-3--pentanone b. both carbonyl groups of 2,4-pentanedione (careful!) 2. Predict the products of the reduction of O=CCH2CH2CH2C=O with a. LiAlH4 b. NaBH4 CH3 OHarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
