(a)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
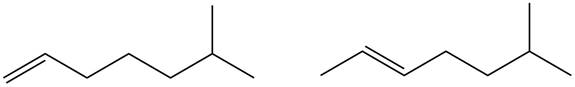
Figure 1
Disubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, two
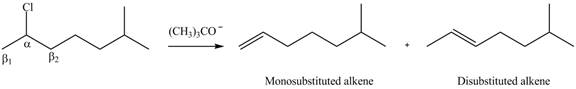
Figure 2
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(b)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Figure 3
Monosubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, only one
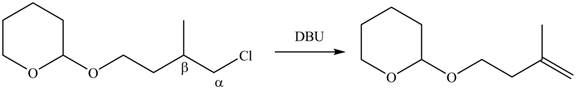
Figure 4
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(c)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
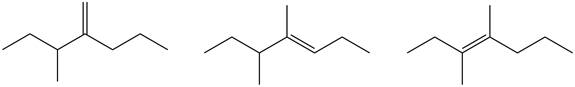
Figure 5
Tetrasubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, three
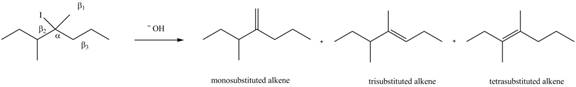
Figure 6
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(d)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
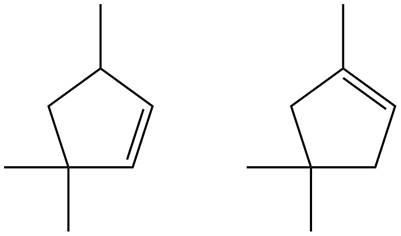
Figure 7
Trisubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, two
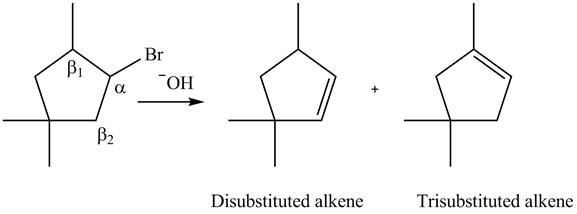
Figure 8
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Draw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the oxidation of 3-bromo-cyclohexan-1-ol.arrow_forwardConvert the following Fischer projection to Haworth projections. show work and show the arrows please.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
