
Concept explainers
A 1.5 m square footing carries a column with a service load of 105 kN. It is founded at a depth of 2 m on a medium stiff clay with an undrained shear strength of 42 kPa, an overconsolidation ratio of 4, and a plasticity index of 35. The clay layer is 5 m thick and overlies a very stiff shale. Estimate the undrained settlement of the footing using the generalized elastic method with Christian and Carrier’s (1978) influence factors.
The undrained settlement of the footing using the generalized elastic method with Christian and Carriers (1978) influence factors.
Answer to Problem 8.1QPP
3.1 mm
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Size of footing = 1.5m
Service load = 105kN
Depth = 2m
Undrained shear strength = 42kPa
Overconsolidation ratio = 4
Plasticity index = 35
Thickness of clay layer = 5m
Formula used:
The ratio of depth to width of footing is
The influence factor accounting for depth of footing from the following figure is
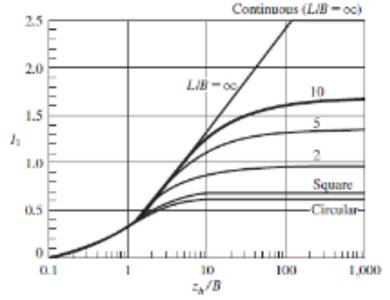
The aspect ratio of footing is
The relative thickness of compressible layer is
The influence factor accounting for shape of footing and compressible layer thickness from the above figure is
The average soil modulus over depth of compressible layer is
Substituting the values in the above equation,
The undrained settlement of the footing is
Conclusion:
The undrained settlement of the footing is 3.1 mm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
- Star Star to Dalta EX: find the Reg Resistance Sthan A and B 10 A ML lon MWL lon 102 ww bo monedasarrow_forwardF1 ୪ α В F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? = Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = 2405 direction in degrees, B = -7.72 × N × degarrow_forwardNeed hekoarrow_forward
- A B 0 B F C The force F = 319 N acts on the frame shown in picture. Resolve this force into components acting along memebers AB and AC to determine the magnitude of each component. The angle mesurements are 0 = 33° and B = 40°. magnitude in member AB in Newton: N magnitude in memeber AC in Newton: Narrow_forwardThe force vector F has a magnitude of F = 450 lb and acts 15.7° with respect to vertical as at point A at an angle → = shown. The force F is balanced by the tension forces parallel to the two rods AC and AB such that the vector equation → F+F AC + FAB = 0 is satisfied. Determine the tension forces in the two rods in Cartesian Vector Notation. с a b B CC + BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom A NF Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 5.9 ft b C 3 ft 3.1 ft FAC = FAB= ĵ) lb lb + +arrow_forwardF2 Y B V 5 4 3 F1 X F3 → The given forces are F₁ = 20 kN, F2= 28 kN, and F3 = 61 kN, with given ratio for F₁ and angles of B = 51° and y = 67°. Find the resultant force. First in Cartesian Vector Notation: FR = 2 + j) kN Then, find the magnitude and direction: magnitude in kN: kN conventional direction (counter clockwise from positive X axis) in degrees: degarrow_forward
- Y F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forwardMy desk has a weight of 193.044 lbf on the Earch's surface where the acceleration of gravity is 32.174 ft $2 What is its weight in pounds force (lbf) on Mars and its mass in pounds mass (lbm) on Mars where the acceleration of gravity is 5.35 ft $2 Weightmars = lbf, Massmars = Ibmarrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward
- Y F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forwardPlease show all steps and give answers in the cartesian coordinate system providedarrow_forwardPlease show all stepsarrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



