
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound as primary, secondary or tertiary alkyl halide and give a common name to the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide refers to those organic compounds that consist of halogen atom as a
In primary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
In secondary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
In tertiary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 8.1P
The common name of the given compound is isobutyl fluoride. It is a primary alkyl halide.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The fluorine atom is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom. Therefore, it is a primary alkyl halide.
The common name of the given compound is isobutyl fluoride. It is a primary alkyl halide.
(b)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound as primary, secondary or tertiary alkyl halide and give a common name to the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide refers to those organic compounds that consist of halogen atom as a functional group attached to the alkyl chain. The general formula is
In primary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
In secondary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
In tertiary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 8.1P
The common name of the given compound is n-hexyl iodide. It is a primary alkyl halide.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The iodine atom is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom. Therefore, it is a primary alkyl halide.
The common name of the given compound is n-hexyl iodide. It is a primary alkyl halide.
(c)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound as primary, secondary or tertiary alkyl halide and give a common name to the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide refers to those organic compounds that consist of halogen atom as a functional group attached to the alkyl chain. The general formula is
In primary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
In secondary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
In tertiary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 8.1P
The common name of the given compound is cyclopentyl bromide. It is a secondary alkyl halide.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
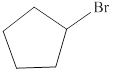
Figure 1
It contains a ring of five carbon atoms. Bromine is attached to the second carbon atom. Therefore, the common name of this compound is cyclopentyl bromide.
The bromine atom is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. Therefore, it is a secondary alkyl halide.
The common name of the given compound is cyclopentyl bromide. It is a secondary alkyl halide.
(d)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound as primary, secondary or tertiary alkyl halide and give a common name to the given compound.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide refers to those organic compounds that consist of halogen atom as a functional group attached to the alkyl chain. The general formula is
In primary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
In secondary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
In tertiary alkyl halide, the halogen group is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 8.1P
The common name of the given compound is neopentyl chloride. It is a primary alkyl halide.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
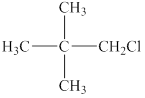
Figure 2
It contains five carbon atoms. Chlorine is attached to the first carbon atom and three methyl groups are attached to the second carbon atom. Therefore, the prefix –neo is used before the name of an alkyl halide. Therefore, the common name of this compound is neopentyl chloride.
The chloride atom is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom. Therefore, it is a primary alkyl halide.
The common name of the given compound is neopentyl chloride. It is a primary alkyl halide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
