
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of electrons in an atom with the
Concept introduction:
The quantum numbers provide complete information about the electron. There are four quantum numbers as follows:
1. The principal quantum number and it is represented by n. It tells about the shell to which the electron belongs.
2. The azimuthal quantum number and it is represented by l. It tells about the subshell of the electrons.
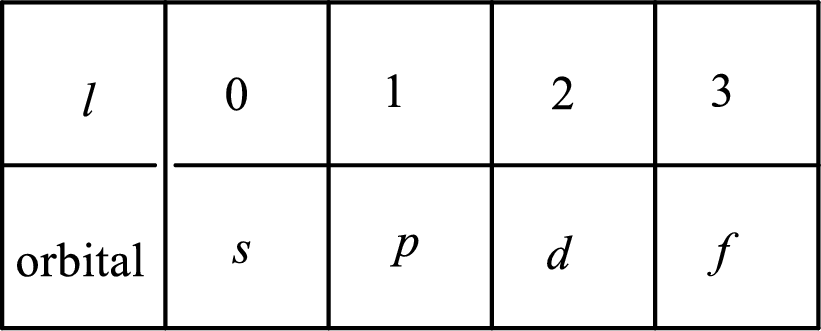
3. The magnetic quantum number and it is represented by
4. The spin quantum number and it is represented by
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of electrons in an atom with
Concept introduction:
The quantum numbers provide complete information about the electron. There are four quantum numbers as follows:
1. The principal quantum number and it is represented by n. It tells about the shell to which the electron belongs.
2. The azimuthal quantum number and it is represented by l. It tells about the subshell of the electrons.
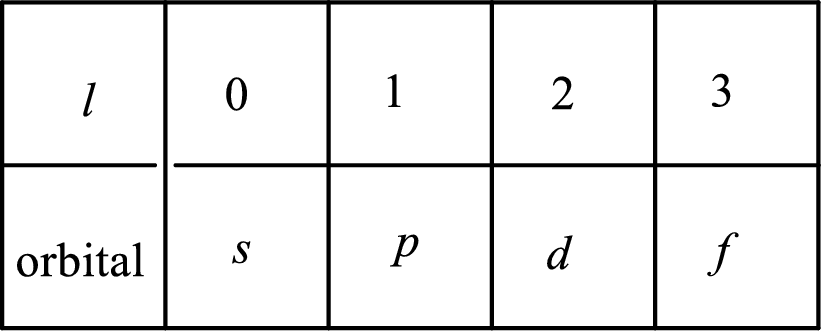
3. The magnetic quantum number and it is represented by
4. The spin quantum number and it is represented by
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of electrons in an atom with the
Concept introduction:
The quantum numbers provide complete information about the electron. There are four quantum numbers as follows:
1. The principal quantum number and it is represented by n. It tells about the shell to which the electron belongs.
2. The azimuthal quantum number and it is represented by l. It tells about the subshell of the electrons.
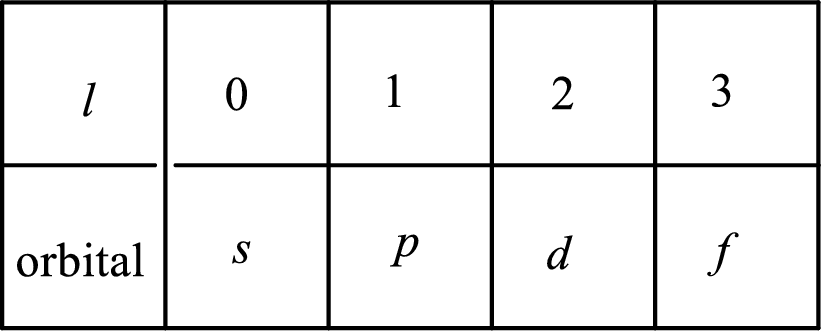
3. The magnetic quantum number and it is represented by
4. The spin quantum number and it is represented by
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: MOLECULAR...(LLF) W/CONNECT
- true or false The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.20. N2O4(g) ⇔ 2NO2(g) Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 5. 4NO2(g) ⇔ 2N2O4(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.20. N2O4(g) ⇔ 2NO2(g) Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.4. 2N2O4(g) ⇔ 4NO2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false Using the following equilibrium, if heat is added the equilibrium will shift toward the reactants. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇔ 2NH3(g) + heatarrow_forward
- True or False Using the following equilibrium, if heat is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. N2O4(g) + heat ⇔ 2NO2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false Using the following equilibrium, if solid carbon is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. C(s) + CO2(g) ⇔ 2CO(g)arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reaction below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges. Please also provide a reason to explain why the 1,4-adduct is preferred over the 1,3-adduct.arrow_forward
- Which of the following pairs are resonance structures of one another? I. III. || III IV + II. :0: n P !༠ IV. EN: Narrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) and byproducts (either organic or inorganic) for thefollowing reactions.arrow_forwardA 8.25 g sample of aluminum at 55°C released 2500 J of heat. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.900 J/g°C. The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/mL. Calculate the final temperature of the aluminum sample in °C.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





