
Concept explainers
Analyzing Allowance for Doubtful
Coca-Cola and PepsiCo are two of the largest and most successful beverage companies in the world in terms of the products that they sell and their receivables management practices. To evaluate their ability to collect on credit sales, consider the following rounded amounts reported in their annual reports (amounts in millions).
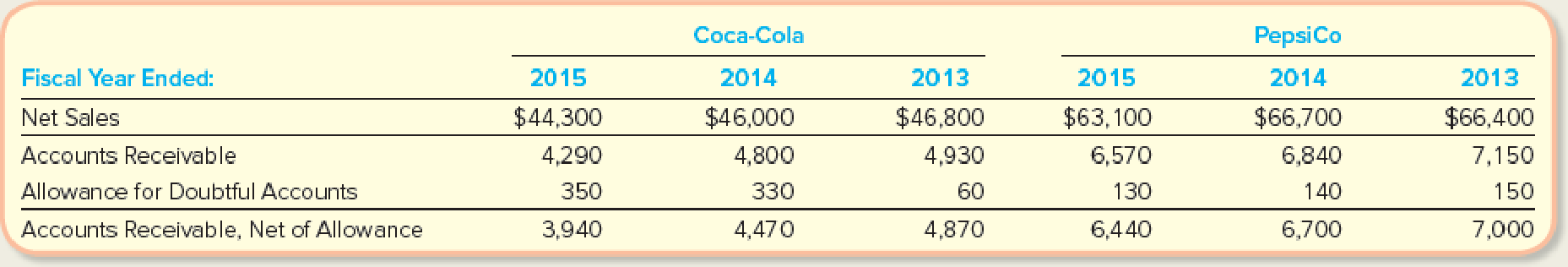
Required:
- 1. Calculate the receivables turnover ratios and days to collect for Coca-Cola and PepsiCo for 2015 and 2014. (Round to one decimal place.)
- 2. Which of the companies is quicker to convert its receivables into cash?
1.
Calculate the receivables turnover ratio and days to collect of Company C and Company P for 2015 and 2014.
Explanation of Solution
Accounts receivable turnover: This is the ratio which analyzes the number of times accounts receivables is collected and converted into cash during the period. This ratio gauges the efficacy of collecting receivables. The more times the ratio indicates the more efficient in collecting receivables.
Average days to collect accounts receivable (average collection period): This ratio measures the number of times receivables are collected in the period. This ratio analyzes the period receivables are outstanding. So, this ratio also gauges the efficacy of collecting receivables. Lower the ratio, more efficient the collection of receivables.
Calculate accounts receivables turnover ratio and days to collect for Company C for 2015 as follows:
Thus, the accounts receivables turnover ratio and the number of days to collect the receivables for Company C for the year 2015 are 10.53 times and 34.66 days respectively.
Calculate accounts receivables turnover ratio and days to collect for Company C for 2014 as follows:
Thus, the accounts receivables turnover ratio and the number of days to collect the receivables for Company C for the year 2014 are 9.9 times and 36.9 days respectively.
Calculate accounts receivables turnover ratio and days to collect for Company P for 2015 as follows:
Thus, the accounts receivables turnover ratio and the number of days to collect the receivables for Company P for the year 2015 are 9.6 times and 38 days respectively.
Calculate accounts receivables turnover ratio and days to collect for Company P for 2014 as follows:
Thus, the accounts receivables turnover ratio and the number of days to collect the receivables for Company P for the year 2014 are 9.7 times and 37.63 days respectively.
2.
Identify the company which has quicker ability to convert its receivables into cash in 2015 and 2014.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the company which has quicker ability to convert its receivables into cash in 2015 and 2014.
| Particulars | Company C | Company P | ||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | |
| Receivable turnover ratio | 9.9 times | 10.5 times | 9.7 times | 9.6 times |
| Days to collect ratio | 36.9 days | 34.6 days | 37.6 days | 38 days |
Table (1)
A company which has higher receivables turnover ratio and lower days to collect the receivables is considered as the best company in converting its receivables to cash.
In 2014, Company C’s receivables turnover ratio is higher and days to collect is lower in comparison with Company P.
In 2015, Company C’s receivables turnover ratio is higher and days to collect is lower in comparison with Company P.
Therefore, Company C has the quicker ability to convert its receivables into cash in both the years.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this Financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this Financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardEcho Tone Technologies reports annual sales of $90,000, and it expects sales to increase to $135,000 next year. The company has a degree of operating leverage (DOL) of 4.2. By what percentage should net income increase? A. 70% B. 189% C. 150% D. 210%arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forward
