
Concept explainers
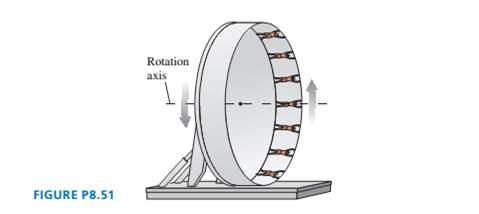
In an amusement park ride called The Roundup, passengers stand inside a 16-m-diameter rotating ring. After the ring has acquired sufficient speed, it tilts into a vertical plane, as shown in FIGURE P8.51.
a. Suppose the ring rotates once every 4.5 s. If a rider’s mass is 55 kg, with how much force does the ring push on her at the top of the ride? At the bottom?
b. What is the longest rotation period of the wheel that will prevent the riders from falling off at the top?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 8 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- Lab Assignment #3 Vectors 2. Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in cables A and B. 30° 30° 300KN 3. Determine the forces in members A and B of the following structure. 30° B 200kN Name: TA: 4. Determine the resultant of the three coplanar forces using vectors. F₁ =500N, F₂-800N, F, 900N, 0,-30°, 62-50° 30° 50° F₁ = 500N = 900N F₂ = 800Narrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors Name: TA: 1. With the equipment provided in the lab, determine the magnitude of vector A so the system is in static equilibrium. Perform the experiment as per the figure below and compare the calculated values with the numbers from the spring scale that corresponds to vector A. A Case 1: Vector B 40g Vector C 20g 0 = 30° Vector A = ? Case 2: Vector B 50g Vector C = 40g 0 = 53° Vector A ? Case 3: Vector B 50g Vector C 30g 0 = 37° Vector A = ?arrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 20.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between q1 and q2 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (A). Let q1=-1.30 µC, q2=-4.20µC, and q3= +4.30 µC. __________________ N/Carrow_forward
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forwardI do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forwardRank the six combinations of electric charges on the basis of the electric force acting on 91. Define forces pointing to the right as positive and forces pointing to the left as negative. Rank in increasing order by placing the most negative on the left and the most positive on the right. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) [most negative 91 = +1nC 92 = +1nC 91 = -1nC 93 = +1nC 92- +1nC 93 = +1nC -1nC 92- -1nC 93- -1nC 91= +1nC 92 = +1nC 93=-1nC 91 +1nC 92=-1nC 93=-1nC 91 = +1nC 2 = −1nC 93 = +1nC The correct ranking cannot be determined. Reset Help most positivearrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





