
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The retrosynthesis analysis and the actual synthesis are to be written for the preparation of each target molecule from the given starting molecule.
Concept introduction:
>The retrosynthesis is a reaction that involves
on acid catalyzed dehydration, an alcohol gives the corresponding more substituted alkene as the major product.
>The alkene, on reaction with halogen in water, undergoes addition of halogen and hydroxyl group across the double bond in a way that the halogen atom is bonded to the less substituted double bonded carbon atom and hydroxyl group is bonded to the more substituted double bonded carbon atom.
>Alkenes react with hydrogen halide and yield haloalkane.
>Alkenes, on hydration, form more substituted alcohol.
>Alkenes, on hydroboration-oxidation, form less substituted alcohol.
>Alkenes, in presence of peroxy acid, undergo
In presence of a strong base,
Answer to Problem 50P
Solution:
The retrosynthetic analysis and the actual synthesis for the preparation of each target molecule from the given starting compound are as follows:
a)
Retrosynthesis:
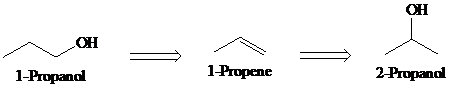
Synthesis:
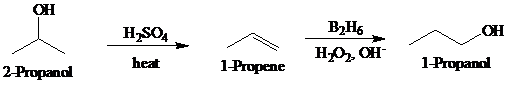
b)
Retrosynthesis:
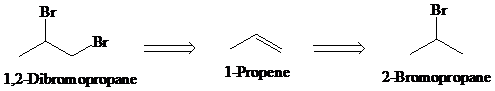
Synthesis:
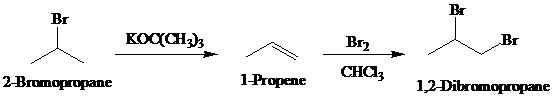
c)
Retrosynthesis:
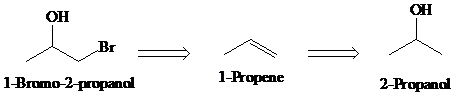
Synthesis:
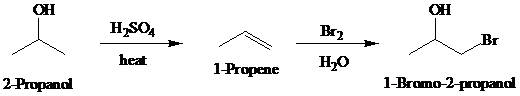
d)
Retrosynthesis:
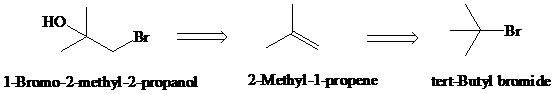
Synthesis:
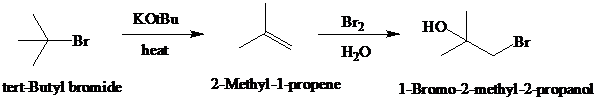
e)
Retrosynthesis:
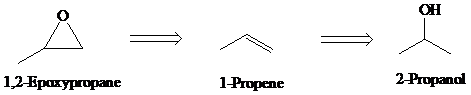
Synthesis:

f)
Retrosynthesis:
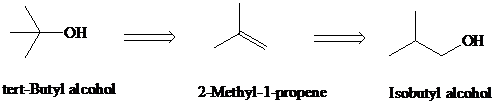
Synthesis:

g)
Retrosynthesis:
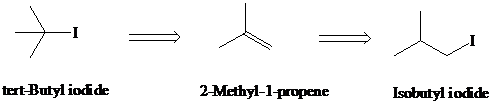
Synthesis:

h)
Retrosynthesis:
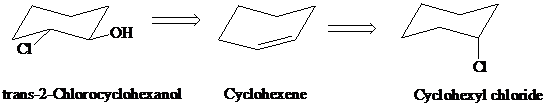
Synthesis:

Explanation of Solution
a)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
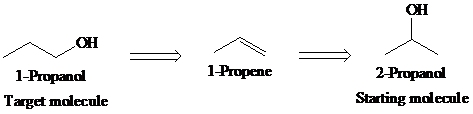
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
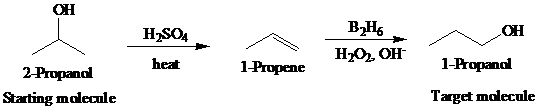
b)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
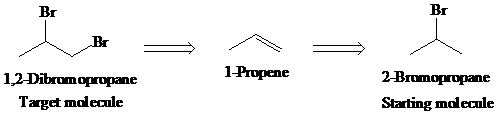
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
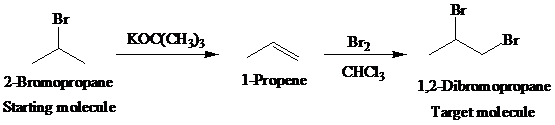
c)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
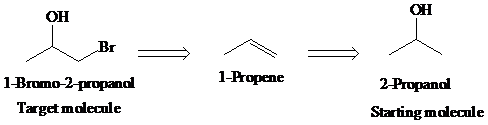
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
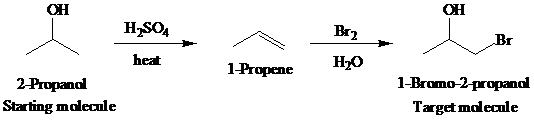
d)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
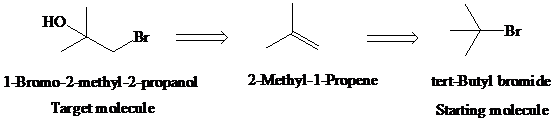
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
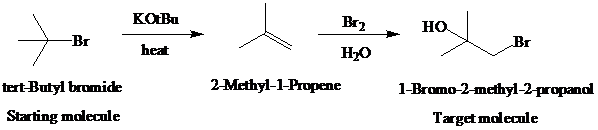
e)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
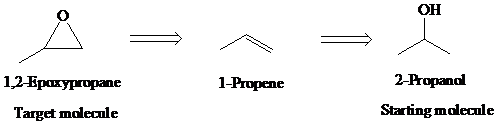
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
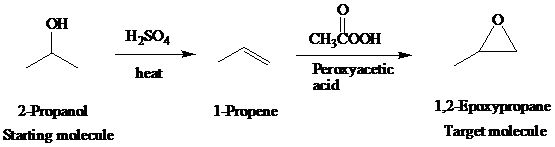
f)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
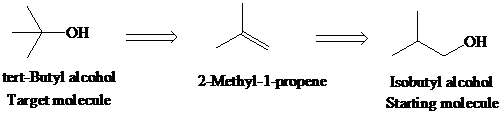
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
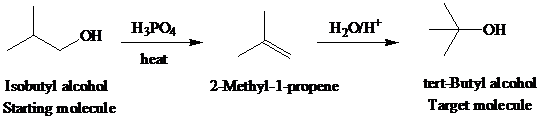
g)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule
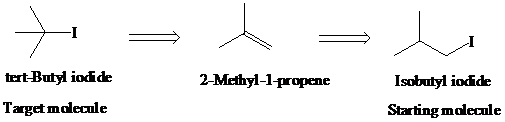
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:
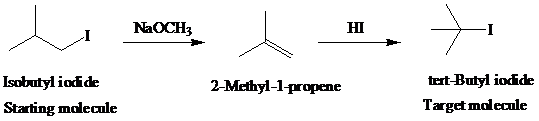
h)
Retrosynthetic analysis for the target molecule

The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthesis is as follows:

Therefore, the retrosynthesis and synthesis reactions for the given compounds were proposed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- The compound in the figure is reacted with 10 n-butyllihium, 2° propanone, and 3º H2O. Draw and name the products obtained. SiMe3arrow_forwardCaffeine (C8H10N4O2, pictured below) is a weak base. The pKb of caffeine is 10.4. What is the pH of a 0.0155 M solution of caffeine?arrow_forward2-Cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of 1-cyclohexyl-2,2-dimethylpropan-1-one with CH3CO3H (). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardWrite chemical equations for: the reaction of benzoic acid chloride with grignard reagent [CH3MgX] the reaction of butanoic acid with methyl amine [CH3NH2]arrow_forward2-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve number 2arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 오 Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O Problem 22 of 35 A Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O H2/Pt B pressure OH 1. NaBH4 C 2. H3O+ D DMP (Dess-Martin Periodinane) CH2Cl2 CrO3 Done Dramabana_Minor Submitarrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of Cycloheptanone with pyrrolidine (cat. H+). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of 2-(3-aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one with H2SO4. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane with H3O+. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardQuestion 4 For the molecule shown below, (7 marks): A) Sketch the Newman projection for the view looking along the bond from the perspective of the arrow. B) Then, draw the Newman projection for each 60° rotation along the bond until it returns to the starting point. C) Clearly indicate which Newman projection is the one we see in the structure shown below, and clearly indicate which Newman projection is the highest in energy and which is the lowest in energy. H H Me 'H Me Mearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

