
Concept explainers
Refer to the information given in the preceding case for Lehighton Chalk Company.
Required:
- 1. Reconcile Lehighton’s operating income reported under absorption and variable costing, during each year, by comparing the following two amounts on each income statement:
- Cost of goods sold
- Fixed cost (expensed as a period expense)
- 2. What was Lehighton’s total operating income across both years under absorption costing and under variable costing?
- 3. What was the total sales revenue across both years under absorption costing and under variable costing?
- 4. What was the total of all costs expensed on the operating income statements across both years under absorption costing and under variable costing?
- 5. Subtract the total costs expensed across both years [requirement (4)] from the total sales revenue across both years [requirement (3)]: (a) under absorption costing and (b) under variable costing.
- 6. Comment on the results obtained in requirements (1), (2), (3), and (4) in light of the following assertion: Timing is the key in distinguishing between absorption and variable costing.
1.
Reconcile the reported operating income of company L for each year under absorption and variable costing, by comparing the cost of goods sold and fixed cost on each income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Absorption Costing: “Absorption costing is a method that allocates “direct labor, direct materials, fixed manufacturing overhead and variable manufacturing overhead” to products and it is required by GAAP for the purpose of external reporting”.
Variable Costing: Managers frequently use variable costing for internal purposes for taking decision making. The cost of goods manufactured includes direct materials, direct labor, and variable factory overhead. Fixed factory overhead treated as period (fixed) expense.
Reconcile the reported operating income of company L for each year under absorption and variable costing as follows:
For year 1:
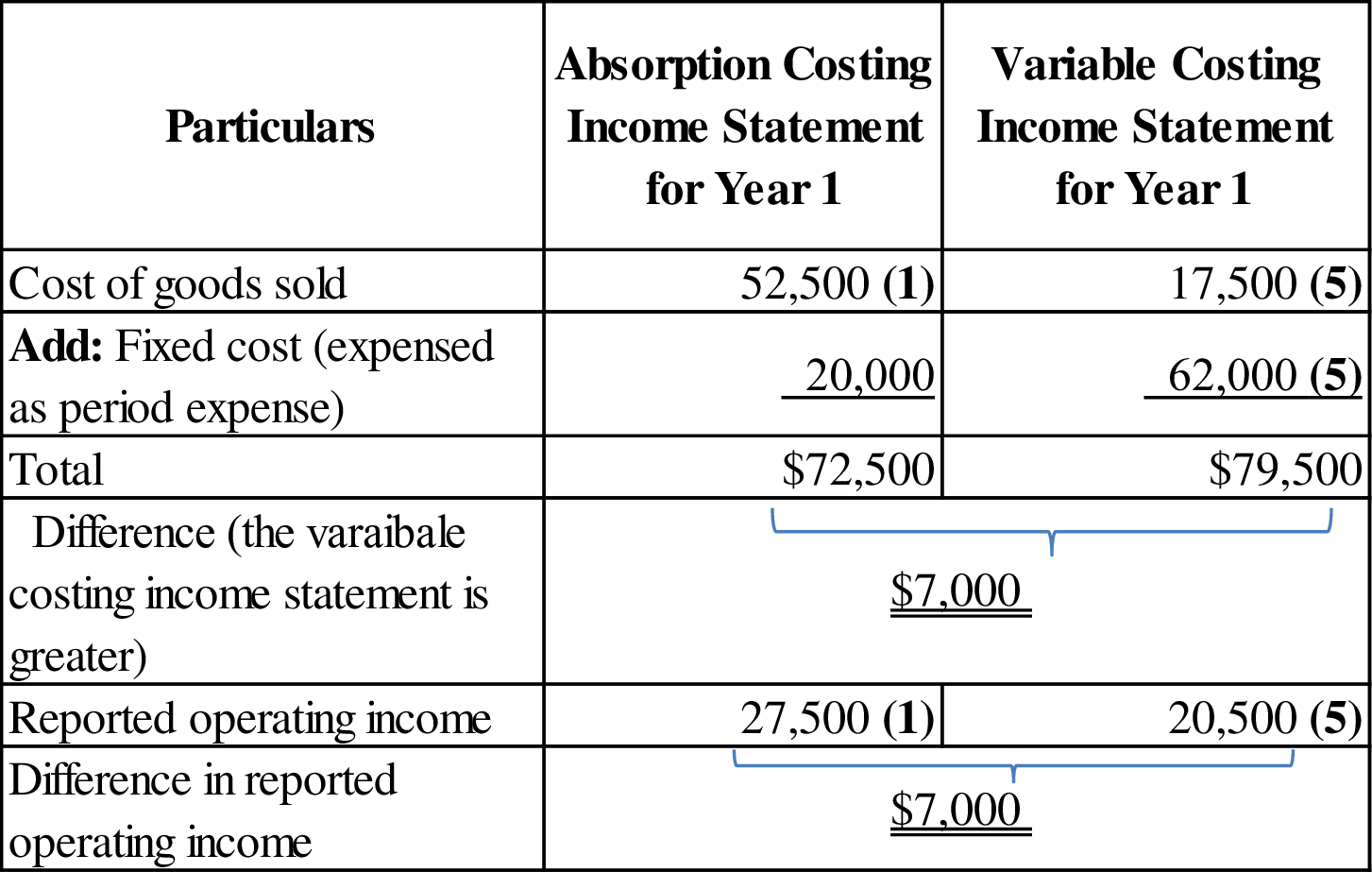
Figure (1)
For year 2:
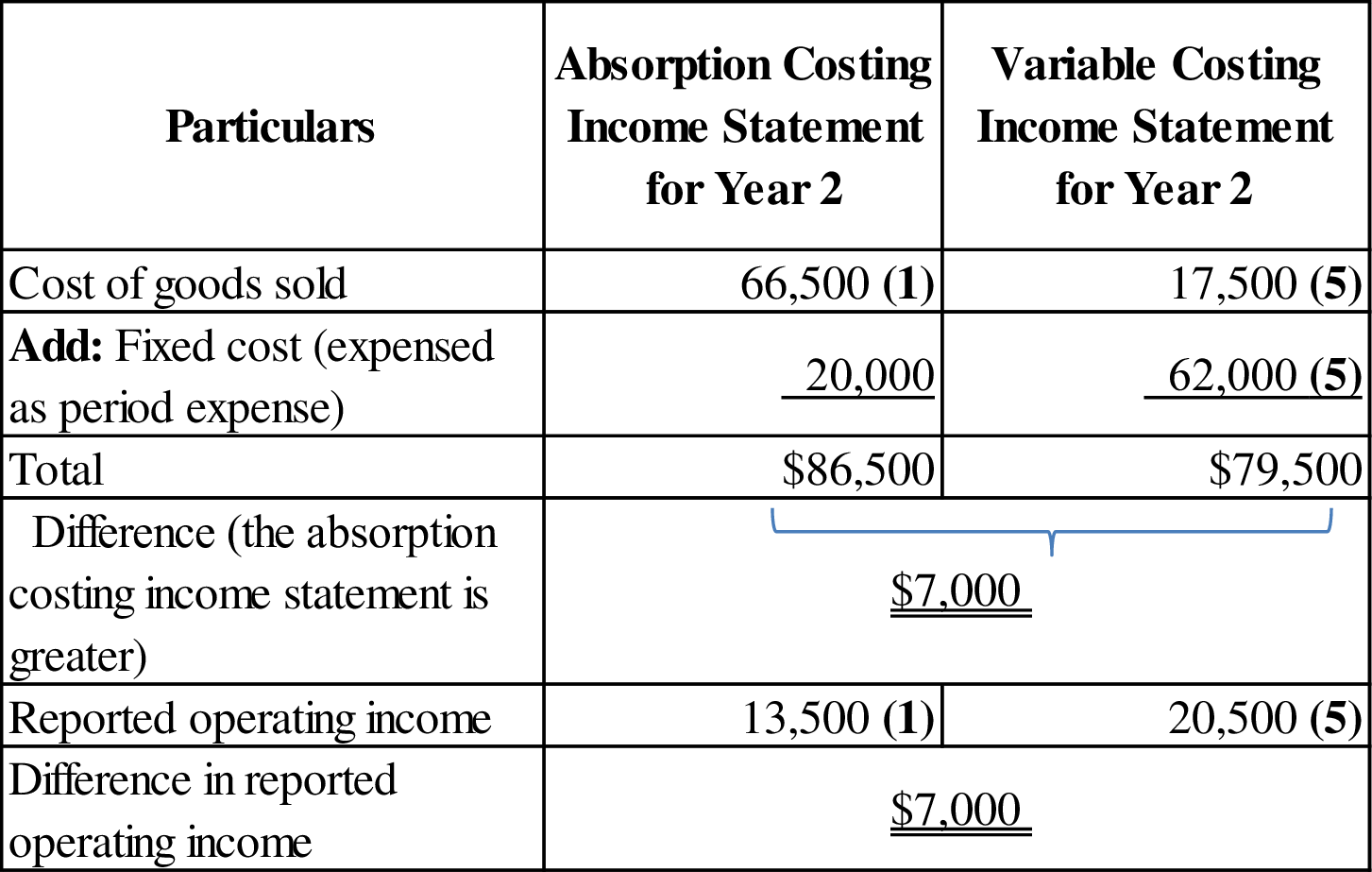
Figure (2)
Working note (1):
Prepare an operating income statement of Company L for both years under absorption costing method as follows:
| Operating income statement under absorption costing method | ||
| Particulars | Year 1 | Year 2 |
| Sales revenue (2) (C) | $ 125,000 | $ 125,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold: | ||
| Beginning finished-goods inventory (4) | $ 0 | $10,500 |
| Cost of goods manufactured (3) | 63,000 | 56,000 |
| Cost of goods available for sale | $63,000 | $66,500 |
| Ending finished-goods inventory (4) | 10,500 | $ 0 |
| Cost of goods sold (D) | $52,500 | $66,500 |
| Gross margin | $72,500 | $58,500 |
| Less: Selling and administrative expenses | $ 45,000 | $ 45,000 |
| Operating income | $27,500 | $13,500 |
Table (1)
Working note (2):
Calculate the value of sales revenue for both years.
| Particulars | Production units (A) | Year 1 |
Year 2 |
| Sales revenue | 2,500 units | $125,000 | $125,000 |
Table (2)
Working note (3):
Calculate the cost of goods manufactured for both years.
Year 1:
Year 2:
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of ending inventory for year 1:
Note: The ending inventory for year 1 is considered as the beginning inventory for year 2.
Working note (5):
Prepare an operating income statement of Company L for both years under variable costing method as follows:
| Particulars | Year 1 | Year 2 |
| Sales revenue (E) (1) | $ 125,000 | $ 125,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold: | ||
| Beginning finished-goods inventory | $ 0 | $3,500 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | 21,000 | 14,000 |
| Cost of goods available for sale | $21,000 | $17,500 |
| Ending finished-goods inventory (6) | $3,500 | $0 |
| Cost of goods sold | $17,500 | $17,500 |
| Add: Variable selling and administrative costs | $25,000 | $25,000 |
| Total variable costs (F) | $42,500 | $42,500 |
| Contribution margin | $82,500 | $82,500 |
| Less: Fixed costs: | ||
| Manufacturing | $42,000 | $42,000 |
| Selling and administrative | $20,000 | $20,000 |
| Total fixed costs | $62,000 | $62,000 |
| Operating income | $20,500 | $20,500 |
Table (3)
Working note (6):
Calculate the cost of ending inventory for year 1:
Note: The ending inventory for year 1 is considered as the beginning inventory for year 2.
Under the fixed cost for year 1 only the selling and administrative cost are consider.
2.
Ascertain the total operating income of company L for both years under absorption costing and under variable costing.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the total operating income of company L for both years under absorption costing and under variable costing as follows:
Total operating income under absorption costing:
Total operating income under variable costing:
3.
Ascertain the total sales revenue of company L both years under absorption costing and under variable costing.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the total sales revenue of company L both years under absorption costing and under variable costing as follows:
Total sales revenue under absorption costing:
Total sales revenue under variable costing:
4.
Ascertain the total of all costs expensed on the operating income statements of company L for both years under absorption costing and under variable costing.
Explanation of Solution
Total of all costs expensed under absorption costing:
Total of all costs expensed under variable costing:
5.
Deduct the total costs expensed from the total sales revenue of company L for both years (a) under absorption costing and (b) under variable costing.
Explanation of Solution
a. Deduct the total costs expensed from the total sales revenue of company L for both years under absorption costing as follows:
b. Deduct the total costs expensed from the total sales revenue of company L for both years under variable costing as follows:
6.
Evaluate the results of the above calculation.
Explanation of Solution
- In this case, the company has sold same number of (2,500) units for both years, at a price of $50. Therefore, the total sales revenue is same for both years under absorption and variable costing and sales revenue has nothing to do with the costing method used.
- The total costs expensed ($209,000) for both years are also same under variable and absorption costing. Because the company has sold the same number of units for both years.
- The combined operating income of Company L for the two-year period is $41,000 under both absorption and variable costing. Because the total sales revenue and the total expenses of the company are same under both costing methods over the two-year.
- The analysis in requirement (1) indicates that the operating income of company L is distributed differently for both years under absorption and variable costing. Therefore, the operating income under the two costing methods is not the same within each year. Under absorption costing, the operating income is higher by $7,000 for year 1 and for year 2 it is lower by $7,000. Because the expenses under absorption costing are $7,000 lower in year 1 and $7,000 greater in year 2. However, it reported the same operating income across the two-year combined period under both costing methods.
- Therefore, the difference between absorption and variable costing is caused by the timing with which expenses are recognized. For instance: Under absorption costing, the fixed manufacturing overhead is not expensed until year 2. Whereas, under variable costing all of the fixed manufacturing overhead is expensed in year 1 as a period cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
- I want the correct answer is accountingarrow_forwardIn a 4-6 slide powerpoint, you and your partners want to sell your company's water purification product in underserved international markets. Markets for water purification devices are nearly unlimited since one-third of people in the world do not have access to safe drinking water (World Health Organization, 2019). The following resources offer more information on this topic: Allied Analytics, LLP. (2023, June 18). Water purifier market size at $92.1 (2031) is set to witness a growth rate of 10.1%Links to an external site.. EIN Presswire. Fortune Business Insights. (2023, April 24). Water purifier market to worth USD 50.66 billion by 2029Links to an external site.. Globe NewsWire. United States Mission to the United Nations. (2023, March 22). Fact sheet: United States announces $49 billion in commitments to global water security and sanitation.Links to an external site. Identify a market in an underserved country and analyze the opportunities and challenges associated with this…arrow_forwardThis week we focused on national differences from the standpoint of political, economic, and legal differences. For this discussion, consider the following scenario: Your career is expanding with an opportunity to support your company's growth in a non-U.S. country. Choose a country that you believe is a viable expansion option. Support your choice for this country by learning about the country's political, economic, and legal system. Share this information with your classmates by summarizing how these areas would contribute to the successful expansion project.arrow_forward
- Mega Company believes the price of oil will increase in the coming months. Therefore, it decides to purchase call options on oil as a price-risk-hedging device to hedge the expected increase in prices on an anticipated purchase of oil.On November 30, 20X1, Mega purchases call options for 14,000 barrels of oil at $30 per barrel at a premium of $2 per barrel with a March 1, 20X2, call date. The following is the pricing information for the term of the call: Date Spot Price Futures Price (for March 1, 20X2, delivery) November 30, 20X1 $ 30 $ 31 December 31, 20X1 31 32 March 1, 20X2 33 The information for the change in the fair value of the options follows: Date Time Value Intrinsic Value Total Value November 30, 20X1 $ 28,000 $ –0– $ 28,000 December 31, 20X1 6,000 14,000 20,000 March 1, 20X2 42,000 42,000 On March 1, 20X2, Mega sells the options at their value on that date and acquires 14,000 barrels of oil at the spot price. On June 1, 20X2, Mega sells the…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardAbcarrow_forward
- Wildhorse Windows manufactures and sells custom storm windows for three-season porches. Wildhorse also provides installation service for the windows. The installation process does not involve changes in the windows, so this service can be performed by other vendors. Wildhorse enters into the following contract on July 1, 2025, with a local homeowner. The customer purchases windows for a price of $2,650 and chooses Wildhorse to do the installation. Wildhorse charges the same price for the windows irrespective of whether it does the installation or not. The customer pays Wildhorse $1,988 (which equals the standalone selling price of the windows, which have a cost of $1,230) upon delivery and the remaining balance upon installation of the windows. The windows are delivered on September 1, 2025, Wildhorse completes installation on October 15, 2025, and the customer pays the balance due. (a) Wildhorse estimates the standalone selling price of the installation based on an estimated cost of…arrow_forwardPlease given answer general accountingarrow_forwardPlease help me this question general accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





