
Concept explainers
Which of the following molecules is(are) polar? For each polar molecule indicate the direction of polarity—that is, which is the negative end, and which is the positive end of the molecule.
- (a) BeCl2
- (b) HBF2
- (c) CH3Cl
- (d) SO3
(a)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
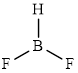
This molecule has a trigonal planar geometry. The fluorine atoms occupied on the negative end of the dipole and the hydrogen atom on the positive end.
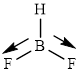
Thus,
(c)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end (dipole) and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
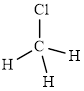
This molecule has a tetrahedral geometry. The chlorine atom occupied on the negative end of the dipole and the hydrogen atom on the positive end.
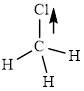
Thus,
(d)
Interpretation: Check whether the given molecule is polar or not. If the molecule is polar then the direction of polarity has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Polar molecules are the molecules having a positive and negative end and so there will be a charge separation.
A polar molecule is a molecule where the polar bonds are asymmetrically arranged (the dipoles do not cancel)
A nonpolar molecule is a molecule with no polar bonds or a molecule where the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged.
In polar molecule the charge separation occurred with respect to the difference in electronegativity of atoms in the molecule.
Direction of dipole moment in a molecule is can be represented as follows,

Different types of molecules and their geometry in accordance with the VSEPR theory are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
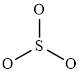
This molecule has trigonal planer geometry. The direction dipole moment in the molecule is represented below,
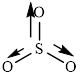
Thus,
However
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Hybrid Edition (with OWLv2 24-Months Printed Access Card)
- Hi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION with its parts spread out till part (g), please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all calculations step by step EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION, please answer EACH part PART A AND PART B!!!!! till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. this is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts JUST ONE QUESTION, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forward
- 8b. Explain, using key intermediates, why the above two products are formed instead of the 1,2-and 1,4- products shown in the reaction below. CIarrow_forward(5pts) Provide the complete arrow pushing mechanism for the chemical transformation depicted below Use proper curved arrow notation that explicitly illustrates all bonds being broken, and all bonds formed in the transformation. Also, be sure to include all lone pairs and formal charges on all atoms involved in the flow of electrons. CH3O H I I CH3O-H H I ① Harrow_forward6. Draw the products) formed from the following reactions. (a) HIarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward1. For each of the following, predict the products of the reaction by writing a balance net ionic equation for each. If no reaction is expected, then write NO REACTION. (a) AgNO3 (aq) is mixed with Na2CO3 (aq). (b) An aqueous solution of ammonium sulfate is added to an aqueous solution of calcium chloride. (c) RbI (aq) is added to Pb(NO3)2 (aq). (d) NaCl (s) is added to AgNO3 (aq).arrow_forward
- 4. Determine the amount in grams of AgCl (s) formed when 2.580 g AgNO3(s) is added to 45.00 mL of a 0.1250 M CrCl3 (aq) (The other product is aqueous chromium (III) nitrate) 5. Determine the amount (in grams) of Cobalt (II) phosphate formed when an aqueous solution of 30.0 ml of 0.450 M Sodium Phosphate is mixed with 20.0 mL of 0.500 M aqueous solution of cobalt (II) nitrate. (The other product is aqueous sodium nitrate)arrow_forward7. Consider the following reaction that describes the dissolution of copper metal in nitric acid: Cu (s) + 4 HNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 H₂O (1) + 2 NO2 (g) How many mL of 3.50 M HNO3 (aq) are required to dissolve 20.00 g Cu?arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning



