
Concept explainers
Draw the influence lines for the reaction moment at support A, the vertical reactions at supports A and B and the shear at the internal hinge C.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Influence line for vertical reaction at support B.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Sketch the free body diagram of frame as shown in Figure 1.
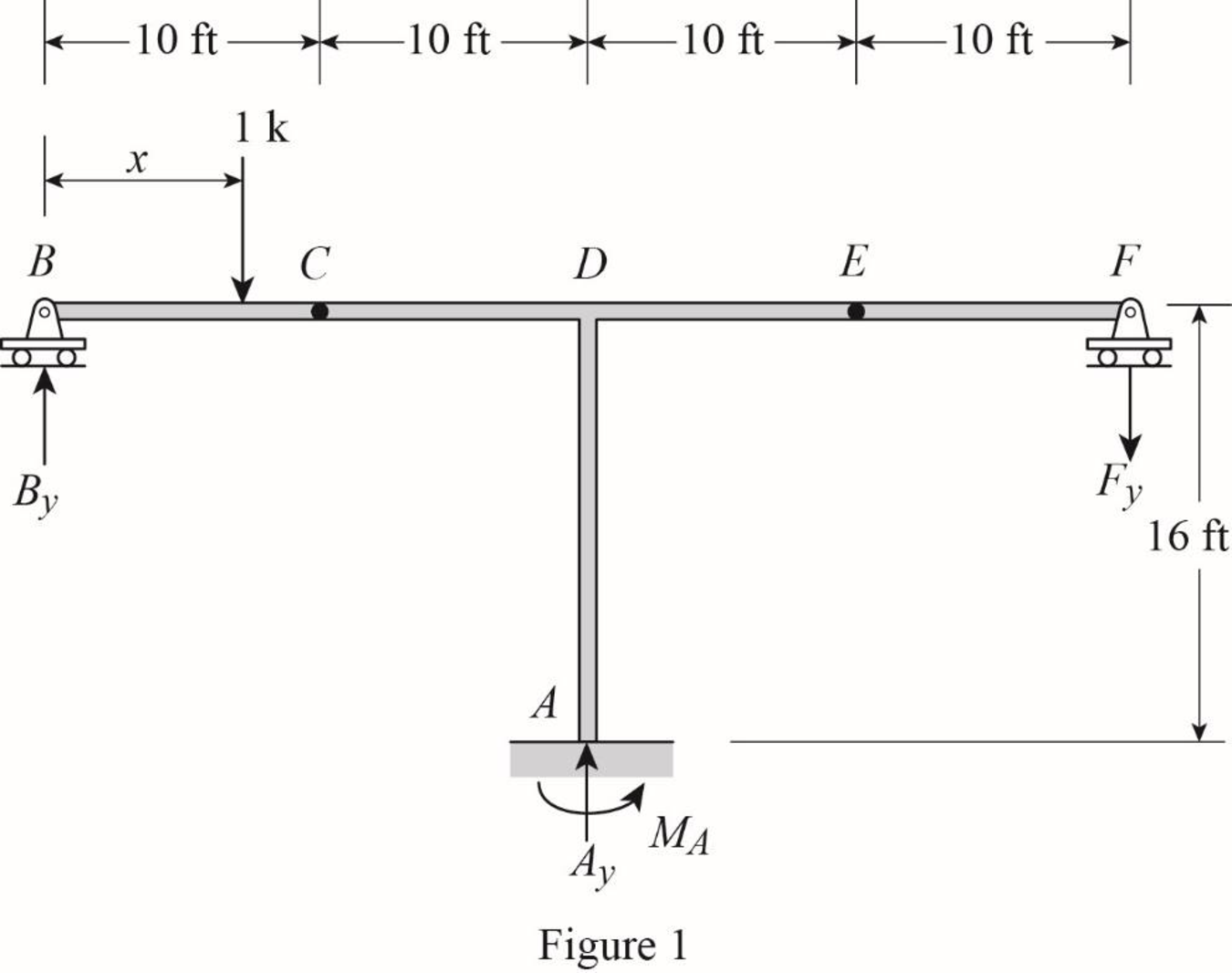
Refer Figure 1.
Apply 1 k load just left of C
Consider section BC.
Consider moment equilibrium at C.
Take moment at C from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Apply 1 k load just right of C
Consider section BC.
Consider moment equilibrium at C.
Take moment at C from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
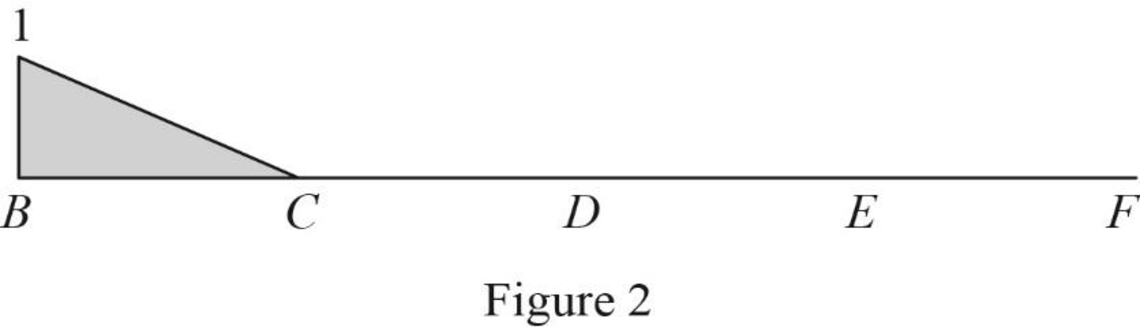
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at B as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 0 for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 1 |
| 10 | C | 0 |
| 20 | D | 0 |
| 30 | E | 0 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for vertical support reaction at B using Table 1 as shown in Figure 2.
Influence line for vertical reaction at support A.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end C.
Refer Figure 1.
Find the vertical support reaction
Apply 1 k load just left of E
Consider section EF.
Consider moment equilibrium at point E.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative
Apply 1 k load just right of E
Consider section EF.
Consider moment equilibrium at point E.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at F as follows,
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Refer Figure 1.
Apply vertical equilibrium in the system.
Consider upward force as positive and downward force as negative.
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
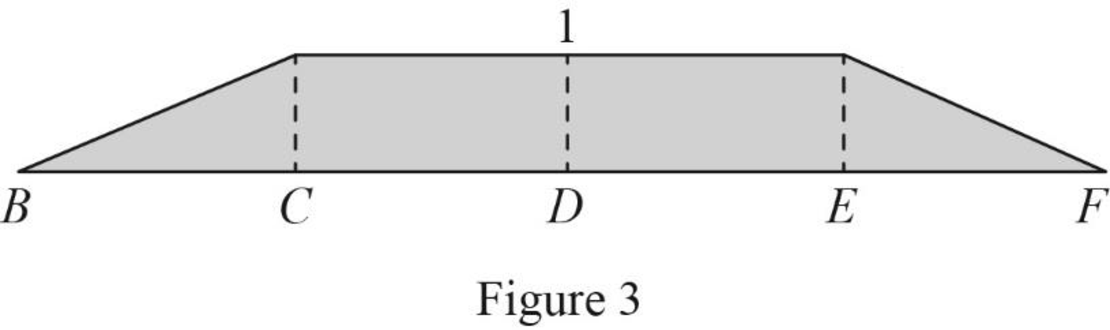
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at A as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 40 ft for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | C | 1 |
| 20 | D | 1 |
| 30 | E | 1 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for the vertical reaction at support A using Table 3 as shown in Figure 3.
Influence line for moment at support A.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Refer Figure 1.
Apply 1 k load just left of C
Take moment at A from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of C to just left of D
Take moment at A from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of D to just left of E
Take moment at A from F.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of E
Take moment at A from F.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
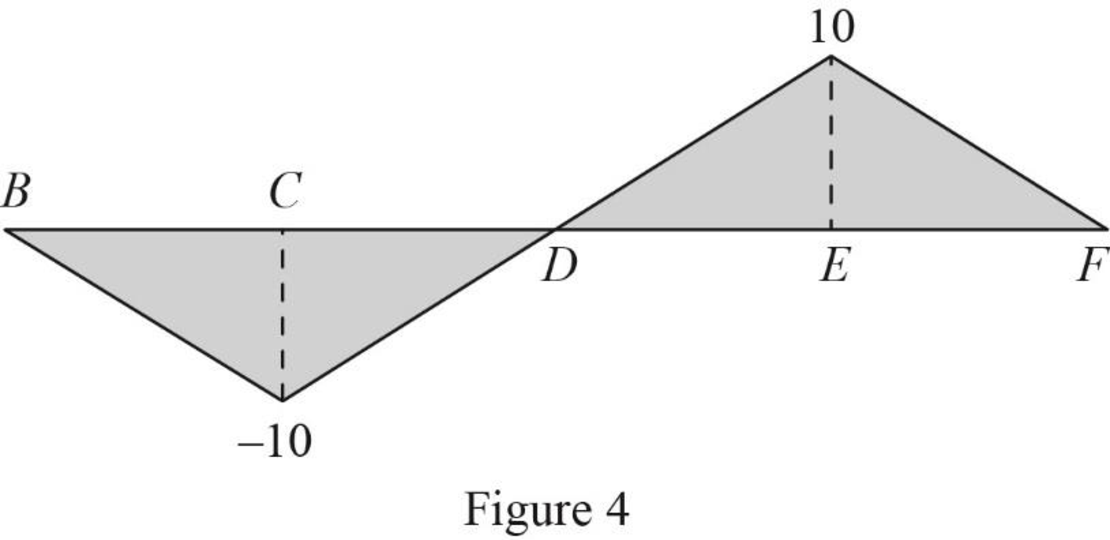
Thus, the equation of moment at A as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 0 for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | C | ‑10 |
| 20 | D | 0 |
| 30 | E | 10 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for the moment at support A using Table 3 as shown in Figure 4.
Influence line for shear at point C.
Find the equation of shear force at C of portion BC
Sketch the free body diagram of the section BC when 1 k load placed between BC as shown in Figure 5.
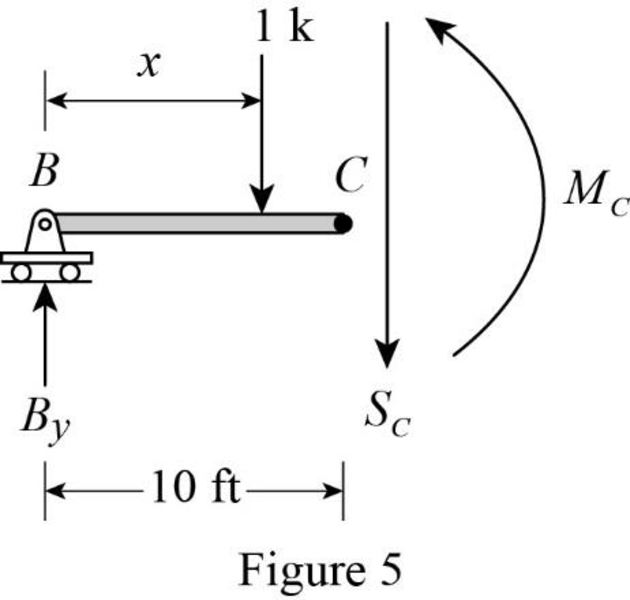
Refer Figure 5.
Apply equilibrium equation of forces.
Consider upward force as positive
Substitute
Find the equation of shear force at C of portion CF
Sketch the free body diagram of the section BC when 1 k load placed between CF as shown in Figure 6.
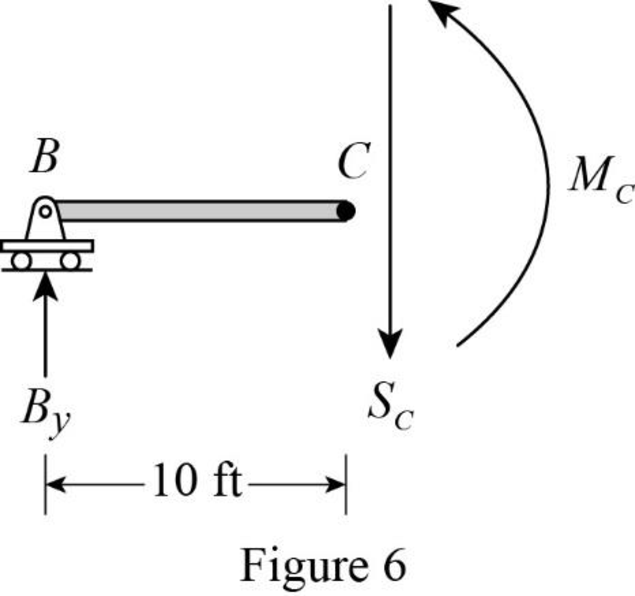
Refer Figure 5.
Apply equilibrium equation of forces.
Consider upward force as positive
Substitute
Thus, the equations of the influence line for
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 10 m for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Find the shear force of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | ‑1 | |
| 20 | 0 | |
| 30 | E | 0 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Draw the influence lines for the shear force at point C using Table 4 as shown in Figure 7.
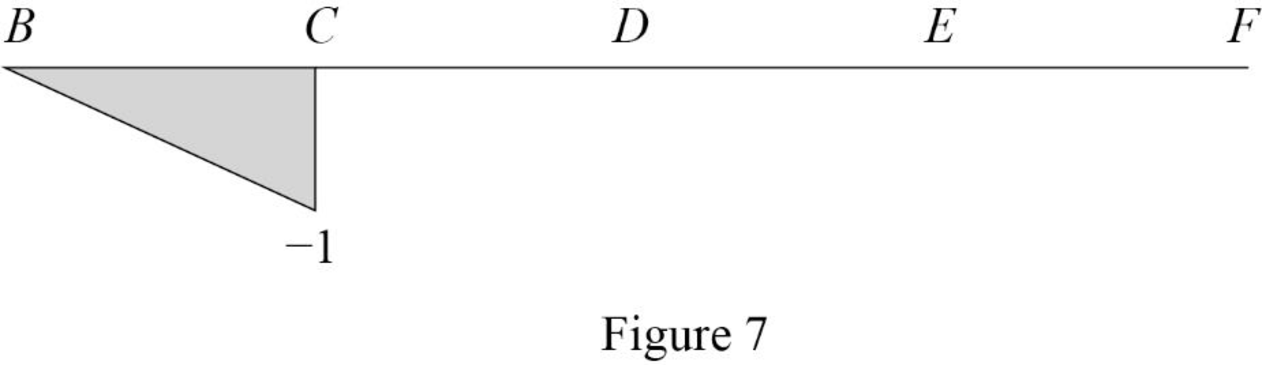
Therefore, the influence lines for the moment at support A and the vertical reactions at supports A and B and the influence lines for the shear hinge C are drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
- 10.37 What is ffor the flow of water at 10°C through a 30-cm cast iron pipe with a mean velocity of 24 m/s?arrow_forward10.60 As shown, water (15°C) is draining from a tank through a galvanized iron pipe. The pipe length is L = 2 m, the tank depth is H = 1 m, and the pipe is a 0.5-inch NPS schedule 40. Calculate the velocity in the pipe. Neglect component head loss. H Pipe of diameter D L Problems 10.59 and 10.60arrow_forward10.53 Water is pumped through a vertical 10-cm new steel pipe to an elevated tank on the roof of a building. The pressure on the discharge side of the pump is 1.6 MPa. What pressure can be expected at a point in the pipe 110 m above the pump when the flow is 0.02 m³/s? Assume T = 20°C.arrow_forward
- 10.61 A pipeline is to be designed to carry crude oil (SG = 0.93, v = 10-5 m²/s) with a discharge of 0.10 m³/s and a head loss per kilometer of 50 m. What diameter of steel pipe is needed? What power output from a pump is required to maintain this flow? Available pipe diameters are 20, 22, and 24 cm.arrow_forwardCalculate the active earth pressure (exerted by the supported soil mass on the right) against the 10-meter-long, dense and smooth sheet pile wall shown in Figure E2:1. The ground surface is loaded with heavy construction machinery applying a pressure of q = 10.0 kPa. Other data is according to the figure.Assume the sheet pile moves sufficiently to the left to reach active failure conditions behind it, and passive failure conditions develop in the soil mass below the excavation bottom. Will the sheet pile wall hold without rain? (Calculate the forces.) Will the sheet pile wall hold if it rains? (Assume water-filled cracks.) If the sheet pile does not hold in any of the above cases – how deep would it need to be embedded in order to hold? Draw diagrams for active and passive earth pressure as well as the resultant earth pressure. gvy=grownd water levelarrow_forwardThe composite beam shown in the figure is subjected to a bending moment Mz=8 kNmMz=8kNm.The elastic moduli for the different parts are E1=30 GPa, E2=20 GPa, and E3=60GPa. a) Determine the reduced moment of inertia IredIred for the entire beam. b) Sketch the bending stress distribution in the beam.arrow_forward
- USING THE ATTACHED SKETCH , DETERMINE THE FOLLOWING: 1. INVERSE DISTANCE, NORTH AZIMUTH AND BEARING BETWEEN CP-102 AND THE SOUTHWEST BUILDING CORNER.2. DETERMINE THE INTERIOR ANGLE AT CP-101 - CP-102 AND THE SOUTHWEST BUILDING CORNER.3. WHAT ARE THE COORDINATES (N,E) AT POINT A AND POINT B IN THE ATTACHED SKETCH?arrow_forwardGiven the following Right Triangle, find the " Area by Coordinates" (Not B*H/2). Report to the nearest Sq. Ft. and to the nearest thousandth of an acre.arrow_forward1) 4,739,281 SQ.FT. = ______________________ ACRES? 2) S 90°00'00" W IS ALSO KNOW AS WHAT CARDINAL DIRECTION? 3) CALCULATE THE NORTH AZIMUTH (NAZ) OF THE FOLLOWING BEARINGS: N 31° 22' 22" E=___________________________NAZ? S 87° 29' 17" W=___________________________NAZ? S 27° 43' 27" E=___________________________NAZ? N 43° 17' 43" E=___________________________NAZ?arrow_forward
- 1) 187.25597°=_____________________________________(DEG-MIN-SEC FORMAT)? 2) CALCULATE THE BEARING AND DIRECTION IN DEG-MIN-SEC OF THE FOLLOWING: NAZ 142°49'18"=____________________________(BEARING/DIRECTION DEG-MIN-SEC)? NAZ 180°00'00"=____________________________(BEARING/DIRECTION DEG-MIN-SEC)? NAZ 270°00'00"=____________________________(BEARING/DIRECTION DEG-MIN-SEC)?arrow_forwardA traffic signal has a 60-second cycle length (Red time + Green time). For the travel direction of interest, the red and green times are 30 seconds each, the arrival rate is constant at 20 [veh/min] and the saturation flow (i.e., the departure rate) is 1 [veh/sec]. a. Calculate the average delay (for all vehicles) for the travel direction of interest. b. Assume a work zone on the street downstream of the intersection so that only 25 [veh/min] (in the direction of interest) can pass. Calculate the average delay caused by the work zone to a vehicle leaving the intersection. Assume that the queue at the work zone never backs- up into the intersection. c. Discuss qualitatively the implications of queue spillback from the work zone on the delay of the system. Traffic Direction (a) Traffic Direction (b)arrow_forwardCalculate the active earth pressure (exerted by the supported soil mass on the right) against the 10-meter-long, dense and smooth sheet pile wall shown in Figure E2:1. The ground surface is loaded with heavy construction machinery applying a pressure of q = 10.0 kPa. Other data is according to the figure.Assume the sheet pile moves sufficiently to the left to reach active failure conditions behind it, and passive failure conditions develop in the soil mass below the excavation bottom. Draw diagrams for active and passive earth pressure as well as the resultant earth pressure. Questions to Answer: Will the sheet pile wall hold without rain? (Calculate the forces.) Will the sheet pile wall hold if it rains? (Assume water-filled cracks.) If the sheet pile does not hold in any of the above cases – how deep would it need to be embedded in order to hold?arrow_forward
