
(a)
To complete the table.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Since the total cost when the production is zero is $50, it is the total fixed cost. The total fixed cost is $50 and remains fixed through all the levels of production.
The total variable cost can be calculated using Equation (1) as follows:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the total variable cost at output 1 unit.
The total variable cost of producing first unit of output is $20.
The
Substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to calculate the average variable cost at output 1 unit.
The average variable cost is $20.
The
Substitute the respective values in Equation (3) to calculate the average total cost at output 1 unit.
The average total cost is $70.
Marginal cost can be calculated using the following formula:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to calculate the average total cost at quantity 1 unit.
The marginal cost of producing first unit is $20.
Table 1 shows the values of total fixed cost, total variable cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost calculated using Equations (1), (2), (3), and (4).
Table 1
| Quantity of output | TC | TFC | TVC | AVC | ATC | MC |
| 0 | $50 | $50 | $0 | — | — | — |
| 1 | 70 | 50 | 20 | 20 | 70 | 20 |
| 2 | 80 | 50 | 30 | 15 | 40 | 10 |
| 3 | 90 | 50 | 40 | 13.3 | 30 | 10 |
| 4 | 110 | 50 | 60 | 15 | 27.5 | 20 |
| 5 | 140 | 50 | 90 | 18 | 28 | 30 |
| 6 | 175 | 50 | 125 | 20.8 | 29.2 | 35 |
| 7 | 220 | 50 | 170 | 24.3 | 31.4 | 45 |
| 8 | 280 | 50 | 230 | 28.8 | 35 | 60 |
| 9 | 360 | 50 | 310 | 34.4 | 40 | 80 |
| 10 | 450 | 50 | 400 | 40 | 45 | 90 |
Fixed cost: Fixed cost is defined as the cost that is independent of the level of output or production of a firm.
Variable cost: Variable cost is defined as the cost that depends on the level of production or output of a firm.
Marginal cost: Marginal cost is defined as the additional cost that is incurred due to the production of an extra unit of output.
Total cost: Total cost is defined as the sum of variable cost and fixed cost.
Average variable cost: Average variable cost is defined as the total variable cost divided by the quantity of output.
Average cost: Average cost is defined as the total cost divided by the quantity of output.
(b)
To graph the average variable cost curve, average total cost, and marginal cost curves.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 shows the cost curves of the given function.
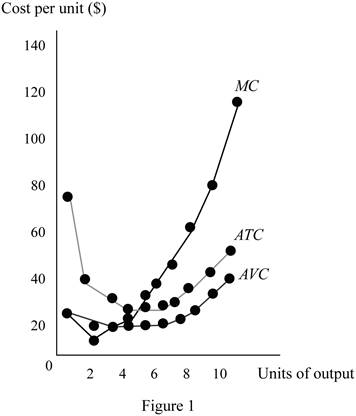
The horizontal axis of Figure 1 measures the quantity of output, and the vertical axis measures the cost per unit. When the marginal cost is below the average variable cost curve or average total cost, the average variable cost curve and the average total cost curve also decrease. When the marginal cost rises above these costs, the average variable cost curve and average total cost curve increase. The marginal cost curve cuts both the average cost curve and the average variable cost curve from their minimum points.
Marginal cost: Marginal cost is defined as the additional cost that is incurred due to the production of an extra unit of output.
Average variable cost: Average variable cost is defined as the total variable cost divided by the quantity of output.
Average cost: Average cost is defined as the total cost divided by the quantity of output.
(c)
The output and profit produced by the firm in the short run when
(c)
Explanation of Solution
When the price is $20, the maximum quantity of output that can be produced is 8 units. This is because the marginal cost of producing 8 units is equal to $20. When the 5th unit is produced, the marginal cost is higher than the price and hence the output is 4.
The total revenue can be calculated using Equation (5) as follows:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (5) to calculate the total revenue at quantity at 4 units.
The total revenue is $80.
The profit or loss can be calculated using Equation (6) as follows:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (6) to calculate the total profit/loss at quantity 4 units.
Thus, production of 4 units leads to a loss of $30.
Total revenue: Total revenue is defined as the total income earned from the output produced.
Total cost: Total cost is defined as the sum of fixed cost and variable cost.
Loss: Loss is defined as the excess cost incurred over the total revenue earned by the production.
(d)
The output and profit produced by the firm in the short run when price is $60.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
When the price is $60, the maximum quantity of output that can be produced is 4 units. This is because the marginal cost of producing 4 units is equal to $60. When the 9th unit is produced, the marginal cost is higher than the price, and hence the output is 8.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (5) to calculate the total revenue at quantity 8 units.
The total revenue is $480.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (6) to calculate the total profit/loss at quantity 8 units.
Thus, production of 8 units leads to a profit of $200.
Total revenue: Total revenue is defined as the total income earned from the output produced.
Total cost: Total cost is defined as the sum of fixed cost and variable cost.
Profit: Profit is defined as the excess revenue earned over the total cost by the firm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles Of Microeconomics
- Title: Does the educational performance depend on its literacy rate and government spending over the last 10 years? In the introduction, there are four things to include:a) Clearly state your research topic follows by country’s background in terms of (population density; male/female ratio; and identify the problem leading up to the study of it, such as government spending and adult literacy rate. How does the US perform compared to other countries.b) State the research question that you wish to resolve: Does the US economic performance depend on its government spending on education and the literacy rate over the last 10 years. Define performance (Y) as the average income per capita, an indicator of the country’s economy growing over time. For example, an increase in government spending leads to higher literacy rates and subsequently higher productivity in the economy. Also, mention that you will use a sample size of 10 years of secondary data from the existing literature,…arrow_forwardTitle: Does the educational performance depend on its literacy rate and government spending over the last 10 years? In the introduction, there are four things to include:a) Clearly state your research topic follows by country’s background in terms of (population density; male/female ratio; and identify the problem leading up to the study of it, such as government spending and adult literacy rate. How does the US perform compared to other countries.b) State the research question that you wish to resolve: Does the US economic performance depend on its government spending on education and the literacy rate over the last 10 years. Define performance (Y) as the average income per capita, an indicator of the country’s economy growing over time. For example, an increase in government spending leads to higher literacy rates and subsequently higher productivity in the economy. Also, mention that you will use a sample size of 10 years of secondary data from the existing literature,…arrow_forwardExplain how the introduction of egg replacers and plant-based egg products will impact the bakery industry. Provide a graphical representation.arrow_forward
- Explain Professor Frederick's "cognitive reflection" test.arrow_forward11:44 Fri Apr 4 Would+You+Take+the+Bird+in+the+Hand Would You Take the Bird in the Hand, or a 75% Chance at the Two in the Bush? BY VIRGINIA POSTREL WOULD you rather have $1,000 for sure or a 90 percent chance of $5,000? A guaranteed $1,000 or a 75 percent chance of $4,000? In economic theory, questions like these have no right or wrong answers. Even if a gamble is mathematically more valuable a 75 percent chance of $4,000 has an expected value of $3,000, for instance someone may still prefer a sure thing. People have different tastes for risk, just as they have different tastes for ice cream or paint colors. The same is true for waiting: Would you rather have $400 now or $100 every year for 10 years? How about $3,400 this month or $3,800 next month? Different people will answer differently. Economists generally accept those differences without further explanation, while decision researchers tend to focus on average behavior. In decision research, individual differences "are regarded…arrow_forwardDescribe the various measures used to assess poverty and economic inequality. Analyze the causes and consequences of poverty and inequality, and discuss potential policies and programs aimed at reducing them, assess the adequacy of current environmental regulations in addressing negative externalities. analyze the role of labor unions in labor markets. What is one benefit, and one challenge associated with labor unions.arrow_forward
- Evaluate the effectiveness of supply and demand models in predicting labor market outcomes. Justify your assessment with specific examples from real-world labor markets.arrow_forwardExplain the difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics? 2.) Explain what fiscal policy is and then explain what Monetary Policy is? 3.) Why is opportunity cost and give one example from your own of opportunity cost. 4.) What are models and what model did we already discuss in class? 5.) What is meant by scarcity of resources?arrow_forward2. What is the payoff from a long futures position where you are obligated to buy at the contract price? What is the payoff from a short futures position where you are obligated to sell at the contract price?? Draw the payoff diagram for each position. Payoff from Futures Contract F=$50.85 S1 Long $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50.85 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 Shortarrow_forward
- 3. Consider a call on the same underlier (Cisco). The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The owner of the call has the choice or option to buy at the strike. They get to see the market price S1 before they decide. We assume they are rational. What is the payoff from owning (also known as being long) the call? What is the payoff from selling (also known as being short) the call? Payoff from Call with Strike of k=$50.85 S1 Long $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50.85 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 Shortarrow_forward4. Consider a put on the same underlier (Cisco). The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The owner of the call has the choice or option to buy at the strike. They get to see the market price S1 before they decide. We assume they are rational. What is the payoff from owning (also known as being long) the put? What is the payoff from selling (also known as being short) the put? Payoff from Put with Strike of k=$50.85 S1 Long $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50.85 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 Shortarrow_forwardThe following table provides information on two technology companies, IBM and Cisco. Use the data to answer the following questions. Company IBM Cisco Systems Stock Price Dividend (trailing 12 months) $150.00 $50.00 $7.00 Dividend (next 12 months) $7.35 Dividend Growth 5.0% $2.00 $2.15 7.5% 1. You buy a futures contract instead of purchasing Cisco stock at $50. What is the one-year futures price, assuming the risk-free interest rate is 6%? Remember to adjust the futures price for the dividend of $2.15.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





