
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The map coordinates for location of the hub.
Introduction: Location is one of the important element for a business that controls the cost and expenses. Location strategies support in framing other strategies for a firm where optimal location point will provide competitive advantage to a firm.
a)
Answer to Problem 20P
The map coordinates for the location of hub is (5.15, 7.30).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
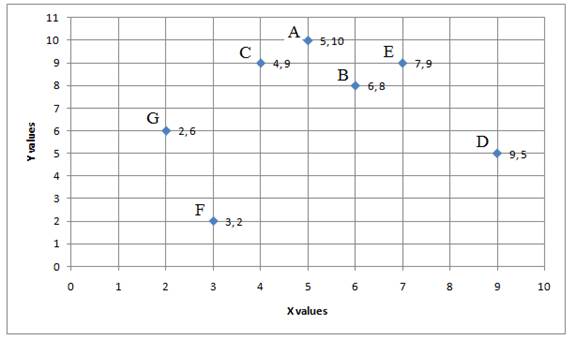
| City | Map Coordinates (X,Y) | Shipping load |
| A | (5, 10) | 5 |
| B | (6, 8) | 10 |
| C | (4, 9) | 15 |
| D | (9, 5) | 5 |
| E | (7, 9) | 15 |
| F | (3, 2) | 10 |
| G | (2, 6) | 5 |
Calculation of map coordinates for location of the hub:
Given the map coordinates and shipping loads for each city location as shown below, use the Centre of Gravity method as shown in the sequential steps described below.
Show the city locations in a graph as shown below.
The x coordinate of the centre of gravity Cx is given by the formula
where dix is the x coordinate of the location i and Qi is the shipping load to and from the location i
The y coordinate of the centre of gravity Cy is given by the formula
where diy is the y coordinate of the location i and Qi is the shipping load to and from the location i
Use equation (1) and calculate Cx as follows
Use equation (2) and calculate Cy as follows,
The coordinates of the Centre of Gravity are given as (5.15,7.30).
The proposed hub highlighted in red color in figure shown below should be close to the coordinates (5.15, 7.30) to minimize the transportation costs.
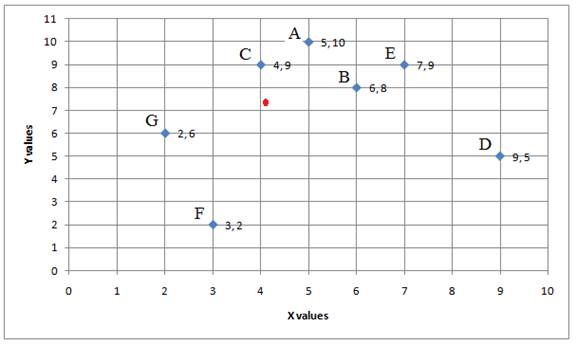
Hence, the map coordinates for the location of hub is (5.15, 7.30).
b)
To determine: The change in the map coordinates for location of the hub when shipment A is tripled.
Introduction: Location is one of the important element for a business that controls the cost and expenses. Location strategies support in framing other strategies for a firm where optimal location point will provide competitive advantage to a firm.
b)
Answer to Problem 20P
The hub location should be as close to the coordinates (5.13, 7.67) as possible to minimize transport costs.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Shipment A is tripled.
| City | Map Coordinates (X,Y) | Shipping load |
| A | (5, 10) | 15 |
| B | (6, 8) | 10 |
| C | (4, 9) | 15 |
| D | (9, 5) | 5 |
| E | (7, 9) | 15 |
| F | (3, 2) | 10 |
| G | (2, 6) | 5 |
Calculation of change in the map coordinates for location of the hub when shipment A is tripled:
If the shipments from City A triple, calculate the center of gravity as per calculations shown later.
Use equation (1) and calculate Cx as follows,
Use equation (2) and calculate Cy as follows,
Hence, the hub location should be as close to the coordinates (5.13, 7.67) as possible to minimize transport costs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Pearson eText Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Choose a specific cars company. E.g Toyota, Volkswagen, Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Honda, Ford, Audi, Tesla Define a list of required machinery, equipment, workstations, offices, rest areas, materials, etc. Develop and define the location of machinery, equipment, workstations, offices, rest areas, materials. Make the distribution in the manufacturing facility the most efficient way possible. Develop a process distribution for one specific product. Explain why you consider this is the most efficient distribution for this specific manufacturing facility. demonstrate the benefits of optimizing a production line with the best distribution of its equipment and spaces. To be more productive and profitable.arrow_forwardProvide a Synposis of the Articlearrow_forwardThe goal of understanding personality in negotiation is to better predict behavior, such as the counterparty's acceptance or rejection of a negotiation offer. One investigation used acoustic and visual cues to predict the likely behavior of a counterparty to a proposal. The best visual cue predictor of the counterparty (55%) was whether they _____. A. tilted their head B. had their arms and legs crossed C. steepled their fingers D. tapped a penarrow_forward
- Women who ask for what they want in negotiation are less well-liked than women who do not self-advocate. However, nonassertive, other-advocating women suffer a leadership backlash and are regarded as less competent because their behavior is regarded to be _____ and _____. A. high-negative feminine; low-positive masculine B. high-positive feminine; high-positive masculine C. high-negative masculine; low-negative feminine D. low-positive masculine; low-positive femininearrow_forwardThere are five most recognized personality traits that can reliably be measured and predict negotiator behavior in a number of different situations. All of the following are one of those "Big 5" personality traits except _____. A. conscientiousness B. introversion C. agreeableness D. openness to experiencearrow_forwardWith regard to reputation in negotiation, negotiators who use adversarial, stubborn, and ethically questionable behavior often have the effect of _____. A. improving their business relationships B. decreasing their effectiveness as a negotiator C. improving their business relationships D. decreasing their group statusarrow_forward
- When it comes to assertiveness, there is only a modest link between negotiators' self-views and how the counterparty sees them. Many negotiators come away from a negotiation thinking they came on too strong with the counterparty. The _____ refers to the fact that negotiators believe they are coming on too strong with the counterparty, but they actually are not. A. Collective trap illusion B. Attribution error C. Aggressive anchoring bias D. Line-crossing illusionarrow_forwardAs you think about the issue of using chatbots in contract negotiations, consider whether other facets and concepts of negotiations that we have discussed and whether they would be adequately addressed.arrow_forwardWhile I am not a fan of AI as of yet, I do understand the endless possibilities. Based on the research, it is clear that AI has great potential for negotiation (Yang, 2025). Herold et al. (2025) suggested that AI can flag potential risks and liabilities, allowing negotiators to address them and mitigate potential problems proactively. AI can draft new contract templates by examining industry standards and past contracts, and AI technology can help lawyers spot errors and inconsistencies in contract drafts. In relation to risk management, AI can flag possible risks and liabilities, allowing negotiators to proactively address them and lessen potential problems, which can speed up the negotiation process, making the negotiation efficient because AI can industrialize tasks like document review, redlining, and finding potential issues, significantly reducing negotiation time. Lastly, AI can analyze vast amounts of data and identify errors, inconsistencies, and irregularities in…arrow_forward
- What is a main thought on using AI in contract negotiations?arrow_forwardWhat are some people thoughts on using AI in contract negotiations?arrow_forward3. Develop a high-level or summary: a. Risk Management Plan Focus on specific, actionable steps for each risk and mitigation strategy.Provide detailed timelines for procurement, stakeholder engagement, and risk monitoring.Avoid over-simplifying and add more technical details in areas like quality assurance and financial control measures. Add a risk prioritization method and mention how risks will be monitored and reviewed throughout the project lifecycle. Overall, it is well organized andc overs key risks.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub



