
To discuss:
Annual average return and standard deviation.
Introduction:
Return: In financial context, return is seen as percentage that represents the profit in an investment.
Explanation of Solution
The annual average
Using equation (1) the annual average return of Miller’s Fund (MF) is calculated as follows:
The annual average return of Miller’s Fund (MF) is 24.325%..
Using equation (1) the annual average return of S&P is calculated as follows:
The annual average return of S&P is 14.925%.
By the annual average returns, Miller’s Fund performed better than the S&P over the given period of time.
If money investment of $1,000 is made in Miller’s Fund in 2009, the money reaped at the end of 2012 would be $1,243.25
If money investment of $1,000 is made in S&P in 2009, the money reaped at the end of 2012 would be $1,149.25
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund can be calculated as follows using excel functions as in table1.
Table 1
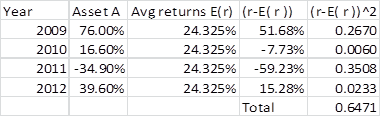
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund is calculated as follows:
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund is 46.44%.
The standard deviation of S&P can be calculated as follows using excel functions as in table 2.
Table 2
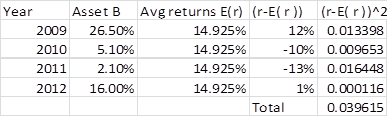
The standard deviation of S&P is calculated as follows:
The standard deviation of S&P is 11.5%.
By the value of standard deviation, Millers Fund is more volatile than S&P.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Managerial Finance, Student Value Edition (15th Edition) (The Pearson Series in Finance)
- 3-7. (Working with an income statement and balance sheet) Prepare a balance sheet and income statement for Kronlokken Company from the following scrambled list of items. a. Prepare a common-sized income statement and a common-sized balance sheet. Interpret your findings. Depreciation expense $66,000 Cash 225,000 Long-term debt 334,000 Sales 573,000 Accounts payable 102,000 General and administrative expense 79,000 Buildings and equipment 895,000 Notes payable 75,000 Accounts receivable 153,000 Interest expense 4,750 Accrued expenses 7,900 Common stock 289,000 Cost of goods sold 297,000 Inventory 99,300 Taxes 50,500 Accumulated depreciation 263,000 Prepaid expenses 14,500 Taxes payable 53,000 Retained earnings 262,900 ||arrow_forwardx3-3. (Preparing an income statement) Prepare an income statement and a common- sized income statement from the following information. MyLab Sales Cost of goods sold General and administrative expenses Depreciation expenses Interest expense Income taxes $525,000 200,000 62,000 8,000 12,000 97,200arrow_forward3-9. (Working with a statement of cash flows) Given the following information, prepare LO3 a statement of cash flows. Increase in accounts receivable Increase in inventories Operating income Interest expense Increase in accounts payable Dividends $25 30 75 25 25 15 20 Increase in net fixed assets 23 Depreciation expense Income taxes 12 17 Beginning cash 20 Increase in common stockarrow_forward
- 3-4. (Preparing a balance sheet) Prepare a balance sheet from the following informa- LO2 tion. What is the net working capital and debt ratio? Cash $50,000 Account receivables 42,700 Accounts payable 23,000 Short-term notes payable 10,500 Inventories 40,000 Gross fixed assets 1,280,000 Other current assets 5,000 Long-term debt 200,000 Common stock 490,000 Other assets 15,000 Accumulated depreciation 312,000 Retained earnings ? MyLabarrow_forwardPlease help with questions.arrow_forwardWhat is the research design? How does it work? What are the differences between Research design and Case Study research?arrow_forward
- How to judge the quality of research designs? Could you help explain and give examples?arrow_forwardConsider a situation involving determining right and wrong. Do you believe utilitarianism provides a more objective viewpoint than moral rights in this context? Why or why not? How about when comparing utilitarianism to principles of justice? Share your thoughts. Reflect on this statement: "Every principle of distributive justice, whether that of the egalitarian, the capitalist, the socialist, the libertarian, or Rawls, in the end is illegitimately advocating some type of equality." Do you agree or disagree with this assertion? Why might someone claim this, and how would you respond?arrow_forwardI need help checking my spreadsheet. Q: Assume that Temp Force’s dividend is expected to experience supernormal growth of 73%from Year 0 to Year 1, 47% from Year 1 to Year 2, 32% from Year 2 to Year 3 and 21% from year3 to year 4. After Year 4, dividends will grow at a constant rate of 2.75%. What is the stock’sintrinsic value under these conditions? What are the expected dividend yield and capital gainsyield during the first year? What are the expected dividend yield and capital gains yield duringthe fifth year (from Year 4 to Year 5)?arrow_forward
- what are the five components of case study design? Please help explain with examplesarrow_forwardCommissions are usually charged when a right is exercised. a warrant is exercised. a right is sold. all of the above will have commissions A and B are correct, C is not correctarrow_forwardWhat is Exploratory Research Case Study? What is the main purpose of Exploratory Research?arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

