
Interest Rate Risk Laurel, Inc., and Hardy Corp. both have 6.5 percent coupon bonds outstanding, with semiannual interest payments, and both are priced at par value. The Laurel, Inc., bond has 3 years to maturity, whereas the Hardy Corp. bond has 20 years to maturity. If interest rates suddenly rise by 2 percent, what is the percentage change in the price of these bonds? If interest rates were to suddenly fall by 2 percent instead, what would the percentage change in the price of these bonds be then? Illustrate your answers by graphing
To determine:The percentage change in the price of the bonds in the given situations and the graph showing the changes.
Coupon Rate:
The coupon rate refers to the rate at which interest is earned on the face value of a bond every year. This is the rate at which yield is funded from a fixed-income security.
Yield to Maturity:
The yield to maturity is the total yield or return which is derived from a bond until the time of the maturity. For this, it is assumed that the bond will be held until the maturity and would not be called.
Interest Rate Risk:
The interest rate risk refers to the risk which is associated with a bond because of the fluctuations of the interest rate. The value of the bond differs with the change in the interest rate.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The yield to maturity of the bonds of both companies is 6.5%.
The bonds of L Company mature after 3 years.
The bonds of H Company mature after 20 years.
Calculation of the change in the price of bonds when the interest rate is increased by 2%:
The formula to calculate the change in price is,
For L company,
Substitute $947.47(refer working note) for the new price and $1,000 for the original pricein the above formula.
The change in bonds price is (5.25%).
For H company,
Substitute $809 (refer working note) for the new price and $1,000 for the original price in the above formula.
The change in bonds price is (19.1%).
Calculation of the change in the price of bonds when the interest rate is decreased by 2%:
The formula to calculate the change in price is,
For L company,
Substitute $1.055.51 (refer working note) for the new price and $1,000 for the original price in the above formula.
The change in bonds price is 5.55%.
For H company,
Substitute $1,262.31 (refer working note) for the new price and $1,000 for the original price in the above formula.
The change in bonds price is 26.23%.
The graph showing the changes in the price is:
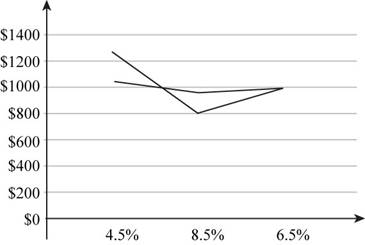
Fig 1
- The graph shows the change in prices of the L Company and H Company.
- The x-axisrepresents the yield to maturity.
- The y-axisrepresents the value of the bonds.
- The line in the graph shows the change in the prices of the bond with the increase and decrease in the yield to maturity.
Working note:
Calculation of thesemi-annual interest on bonds of L Company,
The semi-annual interest is $32.5.
Calculation of the semi-annual interest on bonds of H Company,
The semi-annual interest is $32.5.
Calculation of the price of bonds if yield to maturity is 8.5%:
For L Company,
The value of the bond is $947.97.
For H Company,
The value of the bond is $809.
Calculation of the price of bonds if yield to maturity is 4.5%:
For L Company,
The value of the bond is $1,055.51.
For H Company,
The value of the bond is $1,262.31.
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Calculation of
Thus, the percentage change in price when the rate is increased by 2% for L Company is 5.25%and for H Company is19.1%. The percentage change in price when the rate is decreased by 2% for L Company is5.55% and for H Company is 26.23%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- Ends Feb 23 Explain in detail what is Risk as defined for financial assets and what is Beta? Also discuss in detail what is the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and its purpose.arrow_forwardThe slope parameter ß1 measures the change in annual salary, in thousands of dollars, when return on equity increases by one percentage point. Because a higher roe is good for the company, we think ß1 > 0.The data set CEOSAL1 contains information on 209 CEOs for the year 1990; these data were obtained from Business Week (5/6/91). In this sample, the average annual salary is $1,281,120, with the smallest and largest being $223,000 and $14,822,000, respectively. The average return on equity for the years 1988, 1989, and 1990 is 17.18%, with the smallest and largest values being 0.5% and 56.3%, respectively.Using the data in CEOSAL1, the OLS regression line relating salary to roe is :arrow_forwardFor the population of people in the workforce in 1976, let y = wage, where wage is measured in dollars per hour. Thus, for a particular person, if wage = 6.75, the hourly wage is $6.75. Let x = educ denote years of schooling; for example, educ =12 corresponds to a complete high school education. Because the average wage in the sample is $5.90, the Consumer Price Index indicates that this amount is equivalent to $24.90 in 2016 dollars.Using the data in WAGE1 where n = 526 individuals, we obtain the following OLS regression line (or sample regression function):arrow_forward
- Define the following: Callable bond Puttable bond Zero-coupon bond Premium bond Discount bond Crossover bonds Even though most corporate bonds in the United States make coupon payments semiannually, bonds issued elsewhere often have annual coupon payments. Suppose a German company issues a bond with a par value of EUR 1,000, 15 years to maturity, a coupon rate of 7.2%. If the yield to maturity is 6.3%, what is the current price of the bond? Rhiannon Corporation has bonds on the market with 13 years to maturity, a YTM of 7.6%, a par value of $1,000, a current market price of $1,075. The bonds make semiannual payments. What must the coupon rate be on these bonds? What would be coupon rate if the current market price is $962.68? What would be the coupon rate if the bonds make quarterly payments? Suppose that a bond has a face value of $1,000 and a YTM of 8% per annum. If the bond pays monthly coupons with an annual coupon rate of 9.6%, what will be the current price of…arrow_forwardWildcat, Incorporated, has estimated sales (in millions) for the next four quarters as follows: Q1 Q2 Q3 Sales $ 195 $ 215 $ 235 Q4 $ 265 Sales for the first quarter of the following year are projected at $210 million. Accounts receivable at the beginning of the year were $83 million. Wildcat has a 45-day collection period. Wildcat's purchases from suppliers in a quarter are equal to 50 percent of the next quarter's forecast sales, and suppliers are normally paid in 36 days. Wages, taxes, and other expenses run about 20 percent of sales. Interest and dividends are $18 million per quarter. Wildcat plans a major capital outlay in the second quarter of $98 million. Finally, the company started the year with a $84 million cash balance and wishes to maintain a $40 million minimum balance. a-1. Assume that Wildcat can borrow any needed funds on a short-term basis at a rate of 3 percent per quarter and can invest any excess funds in short-term marketable securities at a rate of 2 percent per…arrow_forwardConsider the following two bonds: Bond A Bond B Face value $1,000 $1,000 Coupon rate (annual) 8% 8% YTM 9% 7% Maturity 10 years 10 years Price (PV) ? ? Calculate the price for each bond. What is the primary factor affecting the prices of the bonds? Indicate which bond is premium and which one is discount. Is there any relationship between the YTM and the coupon rate in case of premium/discount bonds? Now, consider the following two bonds: Bond X Bond Y Face value $1,000 $1,000 Coupon rate (annual) 8% 8% YTM 11% 11% Maturity 5 years 10 years Price (PV) ? ? Calculate the price for each bond. What is the relationship between bond price and maturity, all else equal? A bond with a par value of $1,000 and a maturity of 8 years is selling for $925. If the annual coupon rate is 7%, what’s the yield on the bond? What would be the yield if the bond had semiannual payments?…arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardAssume an investor deposits $116,000 in a professionally managed account. One year later, the account has grown in value to $136,000 and the investor withdraws $43,000. At the end of the second year, the account value is $107,000. No other additions or withdrawals were made. During the same two years, the risk-free rate remained constant at 3.94 percent and a relevant benchmark earned 9.58 percent the first year and 6.00 percent the second. Calculate geometric average of holding period returns over two years. (You need to calculate IRR of cash flows over two years.) Round the answer to two decimals in percentage form.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


