
To determine: The price of the bonds after 1 year, 3 years, 8 years, 12 years and 13 years and prepare a graph of bond prices versus time to maturity.
Yield to Maturity:
The yield to maturity is the total yield or return, which is derived from a bond until the time of the maturity. For this, it is assumed that the bond will be held until its maturity and would not be called.
Effective Annual Rate:
The effective annual rate is the rate, which is incurred or received on various investment or loans. The effective annual rate is affected by the increase in compounding years.
Current Yield:
The current yield represents the return on the bond, which is held by the owner for a year. The current yield is calculated by dividing the annual cash inflow from the current market price.
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
Given,
For M Company,
The bond is a premium bond and makes semi-annual payments.
The coupon rate is 8.5%.
The yield to maturity is 7%.
The maturity period is 13 years.
For MG Company,
The bond is a discount bond and makes semi-annual payments.
The coupon rate is 7%.
The yield to maturity is 8.5%.
The maturity period is 13 years.
Calculation of the value of the bond after 1 year:
The formula to calculate the value of the bond is,
For M Company,
Substitute $42.5 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 1.9 for
The value of the bond is $1,014.25.
For MG Company,
Substitute $35 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 1.88 for
The value of the bond is $985.9.
Calculation of the value of bond after 3 years:
For M Company,
Substitute $42.5 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 5.329 for
The value of the bond is $1,039.98.
For MG Company,
Substitute $35 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 5.2 for
The value of the bond is $961.
Calculation of the value of bond after 8 years:
For M Company,
Substitute $42.5 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 12.094 for
The value of the bond is $1,089.695.
For MG Company,
Substitute $35 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 11.44 for
The value of the bond is $914.1.
Calculation of the value of bond after 12 years:
For M Company,
Substitute $42.5 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 16.06 for
The value of the bond is $1,120.45.
For MG Company,
Substitute $35 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 14.86 for
The value of the bond is $888.3.
Calculation of the value of the bond after 13 years:
For M Company,
Substitute $42.5 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 16.89 for
The value of the bond is $1,126.625.
For MG Company,
Substitute $35 for interest value, $1,000 for the interest value, 15.57 for
The value of the bond is $853.75.
The graph showing the change in the value of bonds with the maturity period is:
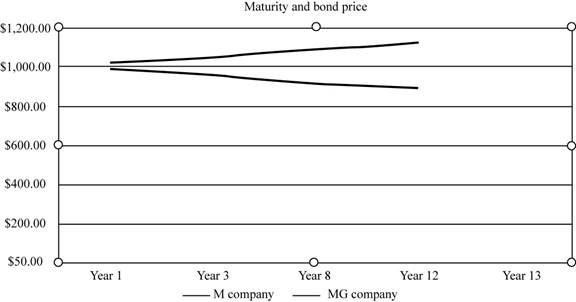
Fig 1
- The graph shows the change in the price of bonds with the maturity period.
- The x-axis shows the years of maturity.
- The y-axis shows the price of the bond.
- The value of the bonds of M Company increases with time.
- The value of the bonds of MG Company decreases with time.
Working note:
Calculation of the semi-annual interest for M Company:
The semi-annual interest is $42.5.
Calculation of the semi-annual interest for MG Company:
The semi-annual interest is $35.
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Calculation of the
Thus, the value of the bonds of M Company after 1 year is $1,014.25, after 3 years is $1,039.98, after 8 years is $1,089.695, after 12 years is $1,120.45, and after 13 years is $1,126.625 and the value of the bonds of MG Company after 1 year is $985.9, after 3 years is $961, after 8 years is $914.10, after 12 years is $888.3, and after 13 years is $853.75.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- All computations must be done and shown manually. Kindly no spreadsheetcomputations. So that I am able to follow and understand clearly please.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardOne year ago, the Jenkins Family Fun Center deposited $3,700 into an investment account for the purpose of buying new equipment four years from today. Today, they are adding another $5,500 to this account. They plan on making a final deposit of $7,700 to the account next year. How much will be available when they are ready to buy the equipment, assuming they earn a rate of return of 9 percent?arrow_forward
- It is anticipated that Pinnaclewalk will next pay an annual dividend of $2.2 per share in one year. The firm's cost of equity is 19.2% and its anticipated growth rate is 3.1%. There are 420000 outstanding. Use the Gordon Growth Model to price Pinnaclewalk's shares. {Express your answer in dollars and cents} What is Pinnaclewalk's market capitalization? {Express your answer in millions of dollars rounded to two decimal places}arrow_forwardThumbtack's capital structure is shown in table below. If taxes are paid annually and Thumbtack's combined tax rate is 36 percent, determine the weighted average cost of capital Loans Bonds 12%/yr/semi $3,000,000 8%/yr/qtr $4,500,000 Common Stock $72/share price; $2,000,000 $8/shr/yr dividend; Retained Earnings (Answer should be in %) 1%/yr share price growth $1,500,000arrow_forwardYou have an investment worth $61,345 that is expected to make regular monthly payments of $1,590 for 20 months and a special payment of $X in 3 months. The expected return for the investment is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X? Note: X is a positive number.arrow_forward
- A bond with a par value of $1,000 and a maturity of 8 years is selling for $925. If the annual coupon rate is 7%, what’s the yield on the bond? What would be the yield if the bond had semiannual payments?arrow_forwardYou want to buy equipment that is available from 2 companies. The price of the equipment is the same for both companies. Silver Fashion would let you make quarterly payments of $14,930 for 8 years at an interest rate of 1.88 percent per quarter. Your first payment to Silver Fashion would be today. Valley Fashion would let you make X monthly payments of $73,323 at an interest rate of 0.70 percent per month. Your first payment to Valley Fashion would be in 1 month. What is X?arrow_forwardYou just bought a new car for $X. To pay for it, you took out a loan that requires regular monthly payments of $1,940 for 12 months and a special payment of $25,500 in 4 months. The interest rate on the loan is 1.06 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X?arrow_forward
- You own 2 investments, A and B, which have a combined total value of $38,199. Investment A is expected to pay $85,300 in 6 years and has an expected return of 18.91 percent per year. Investment B is expected to pay $37,200 in X years and has an expected return of 18.10 percent. What is X?arrow_forwardYou own 2 investments, A and B, which have a combined total value of $51,280. Investment A is expected to pay $57,300 in 5 years and has an expected return of 13.13 percent per year. Investment B is expected to pay $X in 11 years and has an expected return of 12.73 percent per year. What is X?arrow_forwardEquipment is worth $225,243. It is expected to produce regular cash flows of $51,300 per year for 9 years and a special cash flow of $27,200 in 9 years. The cost of capital is X percent per year and the first regular cash flow will be produced in 1 year. What is X?arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





