
FUND. OF PHYSICS (LL)-W/WILEY+NEXTGEN(2)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119787235
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 18P
(a) In Problem 7, what is the speed of the ball at the lowest point? (b) Does the speed increase, decrease, or remain the same if the mass is increased?
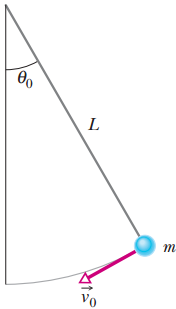
Figure 8-34 Problems 7, 18 and 21.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
need help part e
Critical damping is the case where the mass never actually crosses over equilibrium position, but reaches equilibrium as fast as possible. Experiment with changing c to find the critical damping constant. Use the same initial conditions as in the last problem. Zoom in a bit to make sure you don't allow any oscillations to take place - even small ones.
Chapter 8 Solutions
FUND. OF PHYSICS (LL)-W/WILEY+NEXTGEN(2)
Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-18, a horizontally moving block can take...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-19 gives the potential energy function of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-20 shows one direct path and four...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-21, a small, initially stationary block...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-22, a block slides from A to C along a...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-23a, you pull upward on a rope that is...Ch. 8 - The arrangement shown in Fig. 8-24 is similar to...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-25, a block slides along a track that...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-26 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-27 shows three plums that are launched...
Ch. 8 - When a particle moves from f to i and from j to i...Ch. 8 - SSM What is the spring constant of a spring that...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-29, a single frictionless roller-coaster...Ch. 8 - You drop a 2.00 kg book to a friend who stands on...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-31 shows a ball with mass m = 0.341 kg...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-32, a 2.00 g ice flake is released...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-33, a small block of mass m = 0.032 kg...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a thin rod, of length L = 2.00 m...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg snowball is fired from a cliff 12.5 m...Ch. 8 - GO In Problem 2, what is the speed of the car at a...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 3, what is the speed of the book when...Ch. 8 - SSM WWW a In Problem 5, what is the speed of the...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 8, using energy techniques rather...Ch. 8 - SSM A 5.0 g marble is fired vertically upward...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 4, what initial speed must be given...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-35, a runaway truck with failed...Ch. 8 - A 700 g block is released from rest at height h0...Ch. 8 - In Problem 6, what are the magnitudes of a the...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 7, what is the speed of the ball at...Ch. 8 - GO Figure 8-36 shows an 8.00 kg stone at rest on a...Ch. 8 - GO A pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg stone swinging...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a pendulum of length L = 1.25 m....Ch. 8 - A 60 kg skier starts from rest at height H = 20 m...Ch. 8 - ILW The string in Fig. 8-38 is L = 120 cm long,...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 2.0 kg is dropped from height...Ch. 8 - At t = 0 a 1.0 kg ball is thrown from a tall tower...Ch. 8 - A conservative force F=(6.0x12)i N, where x is in...Ch. 8 - Tarzan, who weighs 688 N, swings from a cliff at...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-41a applies to the spring in a cork gun...Ch. 8 - SSM WWW In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 12 kg is...Ch. 8 - GO A 2.0 kg breadbox on a frictionless incline of...Ch. 8 - ILW A block with mass m = 2.00 kg is placed...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-45, a chain is held on a frictionless...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-46, a spring with k = 170 N/m is at...Ch. 8 - GO A boy is initially seated on the top of a...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 3.20 kg...Ch. 8 - GO Two children are playing a game in which they...Ch. 8 - A uniform cord of length 25 cm and mass 15 g is...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-49 shows a plot of potential energy U...Ch. 8 - GO Figure 8-50 shows a plot of potential energy U...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a diatomic molecule a...Ch. 8 - A single conservative force Fx acts on a 1.0 kg...Ch. 8 - A worker pushed a 27 kg block 9.2 m along a level...Ch. 8 - A collie drags its bed box across a floor by...Ch. 8 - A horizontal force of magnitude 35.0 N pushes a...Ch. 8 - SSM A rope is used to pull a 3.57 kg block at...Ch. 8 - An outfielder throws a baseball with an initial...Ch. 8 - A 75 g Frisbee is thrown from a point 1.1 m above...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-51, a block slides down an incline. As...Ch. 8 - SSM ILW A 25 kg bear slides, from rest, 12 m down...Ch. 8 - A 60 kg skier leaves the end of a ski-jump ramp...Ch. 8 - During a rockslide, a 520 kg rock slides from rest...Ch. 8 - A large fake cookie sliding on a horizontal...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-52, a 3.5 kg block is accelerated...Ch. 8 - A child whose weight is 267 N slides down a 6.1 m...Ch. 8 - ILW In Fig. 8-53, a block of mass m = 2.5 kg...Ch. 8 - You push a 2.0 kg block against a horizontal...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-54, a block slides along a track from...Ch. 8 - A cookie jar is moving up a 40 incline. At a point...Ch. 8 - A stone with a weight of 5.29 N is launched...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - When a click beetle is upside down on its back, it...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-55, a block slides along a path that...Ch. 8 - The cable of the 1800 kg elevator cab in Fig. 8-56...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-57, a block is released from rest at...Ch. 8 - GO A particle can slide along a track with...Ch. 8 - A 3.2 kg sloth hangs 3.0 m above the ground. a...Ch. 8 - SSM A spring k = 200 N/m is fixed at the top of a...Ch. 8 - From the edge of a cliff, a 0.55 kg projectile is...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-60, the pulley has negligible mass,...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-38, the string is L = 120 cm long,...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-51, a block is sent sliding down a...Ch. 8 - Two snowy peaks are at heights H = 850 m and h =...Ch. 8 - SSM The temperature of a plastic cube is monitored...Ch. 8 - A skier weighing 600 N goes over a frictionless...Ch. 8 - SSM To form a pendulum, a 0.092 kg ball is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 76PCh. 8 - Prob. 77PCh. 8 - At a certain factory, 300 kg crates are dropped...Ch. 8 - SSM A 1500 kg car begins sliding down a 5.0...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-65, a 1400 kg block of granite is pulled...Ch. 8 - A particle can move along only an x axis, where...Ch. 8 - For the arrangement of forces in Problem 81, a...Ch. 8 - SSM A 15 kg block is accelerated at 2.0 m/s2 along...Ch. 8 - A certain spring is found not to conform to Hookes...Ch. 8 - SSM Each second, 1200 m3 of water passes over a...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-67, a small block is sent through...Ch. 8 - SSM A massless rigid rod of length L has a ball of...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg water balloon is shot straight up with...Ch. 8 - A 2.50 kg beverage can is thrown directly downward...Ch. 8 - A constant horizontal force moves a 50 kg trunk...Ch. 8 - GO Two blocks, of masses M = 2.0 kg and 2M, are...Ch. 8 - A volcanic ash flow is moving across horizontal...Ch. 8 - A playground slide is in the form of an arc of a...Ch. 8 - The luxury liner Queen Elizabeth 2 has a...Ch. 8 - A factory worker accidentally releases a 180 kg...Ch. 8 - If a 70 kg baseball player steals home by sliding...Ch. 8 - A 0.50 kg banana is thrown directly upward with an...Ch. 8 - A metal tool is sharpened by being held against...Ch. 8 - A swimmer moves through the water at an average...Ch. 8 - An automobile with passengers has weight 16 400 N...Ch. 8 - A 0.63 kg ball thrown directly upward with an...Ch. 8 - The summit of Mount Everest is 8850 m above sea...Ch. 8 - A sprinter who weighs 670 N runs the first 7.0 m...Ch. 8 - A 20 kg object is acted on by a conservative force...Ch. 8 - A machine pulls a 40 kg trunk 2.0 m up a 40 ramp...Ch. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - The only force acting on a particle is...Ch. 8 - In 1981, Daniel Goodwin climbed 443 m up the...Ch. 8 - A 60.0 kg circus performer slides 4.00 m down a...Ch. 8 - A 5.0 kg block is projected at 5.0 m/s up a plane...Ch. 8 - A 9.40 kg projectile is fired vertically upward....Ch. 8 - A 70.0 kg man jumping from a window lands in an...Ch. 8 - A 30 g bullet moving a horizontal velocity of 500...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car starts from rest on a horizontal...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg snowball is shot upward at an angle of...Ch. 8 - A 68 kg sky diver falls at a constant terminal...Ch. 8 - A 20 kg block on a horizontal surface is attached...Ch. 8 - Resistance to the motion of an automobile consists...Ch. 8 - SSM A 50 g ball is thrown from a window with an...Ch. 8 - A spring with a spring constant of 3200 N/m is...Ch. 8 - A locomotive with a power capability of 1.5 MW can...Ch. 8 - SSM A 0.42 kg shuffleboard disk is initially at...Ch. 8 - A river descends 15 m through rapids. The speed of...Ch. 8 - The magnitude of the gravitational force between a...Ch. 8 - Approximately 5.5 106 kg of water falls 50 m over...Ch. 8 - To make a pendulum, a 300 g ball is attached to...Ch. 8 - In a circus act, a 60 kg clown is shot from a...Ch. 8 - A 70 kg firefighter slides, from rest, 4.3 m down...Ch. 8 - The surface of the continental United States has...Ch. 8 - A spring with spring constant k = 200 N/m is...Ch. 8 - Fasten one end of a vertical spring to a ceiling,...Ch. 8 - The maximum force you can exert on an object with...Ch. 8 - Conservative force Fx acts on a particle that...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-73a shows a molecule consisting of two...Ch. 8 - Repeat Problem 83, but now with the block...Ch. 8 - A spring with spring constant k = 620 N/m is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is the significance of interphase?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Furan undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution. Use resonance structures for possible arenium ion intermed...
Organic Chemistry
In rabbits, chocolate-colored fur (w+) is dominant to white fur (w), straight fur (c+) is dominant to curly fur...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Practice Exercise 2
Aspirin is composed of 60.0% carbon, 4.5% hydrogen, and 35.5% oxygen by mass, regardless o...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Which principle of relative dating did you use to determine whether fault M is older or younger than rock layer...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Give an example of interspecies H2 transfer. Why can it be said that both organisms benefit from this process?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- NASA's KC-135 Reduced Gravity Research aircraft, affectionately known as the "Vomit Comet," is used in training astronauts and testing equipment for microgravity environments. During a typical mission, the aircraft makes approximately 30 to 40 parabolic arcs. During each arc, the aircraft and objects inside it are in free-fall, and passengers float freely in apparent "weightlessness." The figure below shows the altitude of the aircraft during a typical mission. It climbs from 24,000 ft to 30,850 ft, where it begins a parabolic arc with a velocity of 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-high and exits with velocity 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-low. 31 000 45° nose high 45° nose low 24 000 Zero g 65 Maneuver time (s) (a) What is the aircraft's speed (in m/s) at the top of the parabolic arc? 110.0 m/s (b) What is the aircraft's altitude (in ft) at the top of the parabolic arc? 2.04e+04 What is the initial height at the start of the parabolic arc? What is the initial velocity at this point? What is the final…arrow_forward12. What could we conclude if a system has a phase trajectory that sweeps out larger and larger area as time goes by?arrow_forwardneed help part darrow_forward
- A cab driver heads south with a steady speed of v₁ = 20.0 m/s for t₁ = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v₂ = 25.0 m/s for t₂ = 2.80 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.80-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude direction For each straight-line movement, model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the starting point be the origin of your coordinate system. Use the relationship speed = distance/time to find the distances traveled during each segment. Write the displacement vector, and calculate its magnitude and direction. Don't forget to convert min to s! m Model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the…arrow_forwardî A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of uniform electric field E = (-5.50 x 105) i N/C at t = 0. The proton travels 7.20 cm as it comes to rest. (a) Determine the acceleration of the proton. magnitude 5.27e13 direction -X m/s² (b) Determine the initial speed of the proton. 8.71e-6 magnitude The electric field is constant, so the force is constant, which means the acceleration will be constant. m/s direction +X (c) Determine the time interval over which the proton comes to rest. 1.65e-7 Review you equations for constant accelerated motion. sarrow_forwardThree charged particles are at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below. (Let q = 2.00 μC, and L = 0.750 m.) y 7.00 με 60.0° L 9 -4.00 μC x (a) Calculate the electric field at the position of charge q due to the 7.00-μC and -4.00-μC charges. 112 Once you calculate the magnitude of the field contribution from each charge you need to add these as vectors. KN/CI + 64 × Think carefully about the direction of the field due to the 7.00-μC charge. KN/Cĵ (b) Use your answer to part (a) to determine the force on charge q. 240.0 If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mN Î + 194.0 × If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mNarrow_forward
- In the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)arrow_forwardFor which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 90° above the horizontal 45° above the horizontal 55° above the horizontal 30° above the horizontal 60° above the horizontalarrow_forwardA map from The Legend of Zelda: The Breath of the Wild shows that Zora's Domain is 7.55 km in a direction 25.0° north of east from Gerudo Town. The same map shows that the Korok Forest is 3.13 km in a direction 55.0° west of north from Zora's Domain. The figure below shows the location of these three places. Modeling Hyrule as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Gerudo Town to Korok Forest. What is the magnitude of the displacement? Find the angle of the displacement. Measure the angle in degrees north of east of Gerudo Town.arrow_forward
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.arrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forwardNeed complete solution Pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY