
(a)
Interpretation:
The given substrates should be determined that whether they favor
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
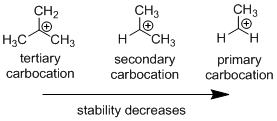
Carbo-cation Rearrangement:
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
(b)
Concept introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays an major role in the reactivity of
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves the chemical compound with pair of electrons in a heterolytic bond cleavage. The
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
(c)
Concept introduction:
Factors that favors both
Secondary substrates, benzylic and allylic substrates undergoes via both the reaction mechanism.
Secondary substrates being in the middle between tertiary and primary they will undergo via both the mechanisms.
Allylic halides results in secondary substrate as halide group leaves and it favors
Benzylic halides also react via both mechanisms since it forms sterically unhindered secondary substrate and more stable resonance stabilized cation.
(d)
Concept introduction:
Factors that favors both
Secondary substrates, benzylic and allylic substrates undergoes via both the reaction mechanism.
Secondary substrates being in the middle between tertiary and primary they will undergo via both the mechanisms.
Allylic halides results in secondary substrate as halide group leaves and it favors
Benzylic halides also react via both mechanisms since it forms sterically unhindered secondary substrate and more stable resonance stabilized cation.
(e)
Concept introduction:
Substrates that do not undergo in either of the two given mechanism are vinyl and aryl substrates. They do not follow
Vinyl group: It is
Aryl group: It is functional group derived from
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY GGC>CUSTOM<-TEXT
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





