
(a)
To find: The monthly payment that must be made in order to pay off the debt in exactly three years and the total amount paid.
(a)
Answer to Problem 60PPS
The total amount to be paid is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The formula for the payment that must be made is,
The credit card debt of the average American is $8600 and the annual rate is
Calculation:
Consider the given formula for the payment to be made is,
Consider the average American is $8600 and the annual rate is
Then,
Thus, the total amount that must be paid is,
(b)
To find: The completed given table,
(b)
Answer to Problem 60PPS
The completed table is shown in Table 2
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The formula for the number of years necessary for the payment is,
The given table for the payment schedule is shown in Table 1
| Payment (m) | Years (t) |
| $50 | |
| $100 | |
| $150 | |
| $200 | |
| $250 | |
| $300 |
Table 1
Calculation:
Consider the formula for the number of years necessary for the payment is,
Consider the payment is of $50. Then,
From the above equation the table for the payment schedule is,
Table 2
| Payment (m) | Years (t) |
| $50 | Non real |
| $100 | Non real |
| $150 | 11.42 |
| $200 | 5.87 |
| $250 | 4.09 |
| $300 | 3.2 |
(c)
To find: The graph for the table of part (b)
(c)
Answer to Problem 60PPS
The graph is shown in Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the table shown in Table 2
The graph for the payment schedule is shown in Figure 1
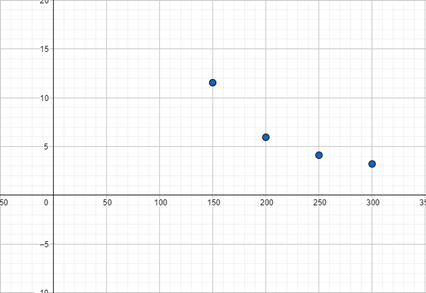
Figure 1
(d)
To find: Whether an individual is able to pay the debt and time for the payment.
(d)
Answer to Problem 60PPS
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The money that the individual can afford to pay is
Calculation:
Consider the given formula for the payment to be made is,
Consider money that the individual can afford to pay is
From above, the value of
(e)
To find: The minimum monthly payment that will work toward paying off the debt.
(e)
Answer to Problem 60PPS
The value of the minimum monthly payment is of
Explanation of Solution
Consider to determine the monthly payment that will work toward paying off the debt, find the domain of
Then,
Chapter 7 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- Problem #5 Suppose you flip a two sided fair coin ("heads" or "tails") 8 total times. a). How many ways result in 6 tails and 2 heads? b). How many ways result in 2 tails and 6 heads? c). Compare your answers to part (a) and (b) and explain in a few sentences why the comparison makes sense.arrow_forwardA local company has a 6 person management team and 20 employees. The company needs to select 3 people from the management team and 7 employees to attend a regional meeting. How many different possibilities are there for the group that can be sent to the regional meeting?arrow_forwardI have 15 outfits to select from to pack for my business trip. I would like to select three of them to pack in my suitcase. How many packing possibilities are there?arrow_forward
- There are 15 candidates running for any of 5 distinct positions on the local school board. In how many different ways could the 5 positions be filled?arrow_forwardCelina is picking a new frame for a custom piece of artwork. She has to select a frame size, material, and color. There are four different frame sizes, three different frame materials, and six different frame colors. She must chose one option only from each category. How many different possible frames could Celina pick from?arrow_forwardA research study in the year 2009 found that there were 2760 coyotes in a given region. The coyote population declined at a rate of 5.8% each year. How many fewer coyotes were there in 2024 than in 2015? Explain in at least one sentence how you solved the problem. Show your work. Round your answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





