
a.
To find
a.
Answer to Problem 13E
The sum is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The matrices are,
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
The sum of both matrices is,
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
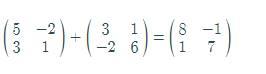
Hence, the result is verified.
b.
To find
b.
Answer to Problem 13E
The difference is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The matrices are,
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
The difference of both matrices is,
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
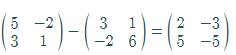
Hence, the result is verified.
c.
To find
c.
Answer to Problem 13E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The matrices are,
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
The difference of both matrices is,
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
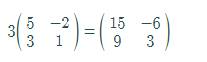
Hence, the result is verified.
d.
To find
d.
Answer to Problem 13E
The differenceis
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The matrices are,
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
The difference of both matrices is,
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
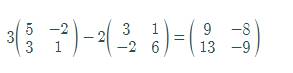
Hence, the result is verified.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- Explain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse identity (1+x+x2+...+xn)*(1-x)=1-xn+1 to derive the result of 12.2.2. Please notice that identity doesn't work when x=1.arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 11.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forward
- To explain how to view "Infinite Series" from "Infinite Sequence"’s perspective, refer to 12.2.1arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.2.5 and 12.2.6arrow_forward8. For x>_1, the continuous function g is decreasing and positive. A portion of the graph of g is shown above. For n>_1, the nth term of the series summation from n=1 to infinity a_n is defined by a_n=g(n). If intergral 1 to infinity g(x)dx converges to 8, which of the following could be true? A) summation n=1 to infinity a_n = 6. B) summation n=1 to infinity a_n =8. C) summation n=1 to infinity a_n = 10. D) summation n=1 to infinity a_n diverges.arrow_forward
- PLEASE SHOW ME THE RIGHT ANSWER/SOLUTION SHOW ME ALL THE NEDDED STEP 13: If the perimeter of a square is shrinking at a rate of 8 inches per second, find the rate at which its area is changing when its area is 25 square inches.arrow_forwardDO NOT GIVE THE WRONG ANSWER SHOW ME ALL THE NEEDED STEPS 11: A rectangle has a base that is growing at a rate of 3 inches per second and a height that is shrinking at a rate of one inch per second. When the base is 12 inches and the height is 5 inches, at what rate is the area of the rectangle changing?arrow_forwardplease answer by showing all the dfalowing necessary step DO NOT GIVE ME THE WRONG ANSWER The sides of a cube of ice are melting at a rate of 1 inch per hour. When its volume is 64 cubic inches, at what rate is its volume changing?arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





