
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977268
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.4, Problem 7.95P
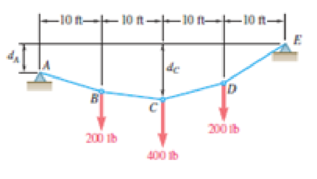
If dA = 8 ft and dc = 10 ft, determine the components of the reaction at E.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
(read image) (answer given)
11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar
when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the
steel is 230 MPa.
265 kN
100 mm
600 kN
25 mm thickness
X
Z
600 kN
450 mm
E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25
265 kN
T₁
F
Rd = 0.2 m
md =
2 kg
T₂
Tz1
Rc = 0.4 m
mc = 5 kg
m = 3 kg
Chapter 7 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Ch. 7.1 - 7.1 and 7.2 Determine the internal forces (axial...Ch. 7.1 - Prob. 7.2PCh. 7.1 - Determine the internal forces at point J when =...Ch. 7.1 - Fig. P7.3 and P7.4 7.4 Determine the internal...Ch. 7.1 - Determine the internal forces at point J when =...Ch. 7.1 - Fig. P7.5 and P7.6 7.6 Determine the internal...Ch. 7.1 - An archer aiming at a target is pulling with a...Ch. 7.1 - For the bow of Prob. 7.7, determine the magnitude...Ch. 7.1 - A semicircular rod is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 7.1 - A semicircular rod is loaded as shown. Determine...
Ch. 7.1 - A semicircular rod is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 7.1 - Fig. P7.11 and P7.12 7.12 A semicircular rod is...Ch. 7.1 - The axis of the curved member AB is a parabola...Ch. 7.1 - Knowing that the axis of the curved member AB is a...Ch. 7.1 - Knowing that the radius of each pulley is 120 mm...Ch. 7.1 - Fig. P7.15 and P7.16 7.16 Knowing that the radius...Ch. 7.1 - A 5-in.-diameter pipe is supported every 9 ft by a...Ch. 7.1 - For the frame of Prob. 7.17, determine the...Ch. 7.1 - Knowing that the radius of each pulley is 200 mm...Ch. 7.1 - Fig. P7.19 and P7.20 7.20 Knowing that the radius...Ch. 7.1 - and 7.22 A force P is applied to a bent rod that...Ch. 7.1 - and 7.22 A force P is applied to a bent rod that...Ch. 7.1 - A quarter-circular rod of weight W and uniform...Ch. 7.1 - For the rod of Prob. 7.23, determine the magnitude...Ch. 7.1 - A semicircular rod of weight W and uniform cross...Ch. 7.1 - A semicircular rod of weight W and uniform cross...Ch. 7.1 - 7.27 and 7.28 A half section of pipe rests on a...Ch. 7.1 - 7.27 and 7.28 A half section of pipe rests on a...Ch. 7.2 - 7.29 through 7.32 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 7.2 - 7.29 through 7.32 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 7.2 - 7.29 through 7.32 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 7.2 - 7.29 through 7.32 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 7.2 - 7.33 and 7.34 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - 7.33 and 7.34 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - 7.35 and 7.36 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - 7.35 and 7.36 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - 7.37 and 7.38 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - 7.37 and 7.38 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.2 - Assuming the upward reaction of the ground on beam...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Problem 7.43 knowing that P = 3wa. PROBLEM...Ch. 7.2 - Assuming the upward reaction of the ground on beam...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.45 assuming that the 12-kip load has...Ch. 7.2 - Assuming the upward reaction of the ground on beam...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.48PCh. 7.2 - Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the...Ch. 7.2 - Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the...Ch. 7.2 - Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the...Ch. 7.2 - Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the...Ch. 7.2 - Two small channel sections DF and EH have been...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.53 when = 60. PROBLEM 7.53 Two...Ch. 7.2 - For the structural member of Prob. 7.53, determine...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam of Prob. 7.43, determine (a) the...Ch. 7.2 - Determine (a) the distance a for which the maximum...Ch. 7.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 7.2 - A uniform beam is to be picked up by crane cables...Ch. 7.2 - Knowing that P = Q = 150 lb, determine (a) the...Ch. 7.2 - Knowing that P = Q = 150 lb, determine (a) the...Ch. 7.2 - In order to reduce the bending moment in the...Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.29....Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.64PCh. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.31....Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.66PCh. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.33....Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.34....Ch. 7.3 - 7.69 and 7.70 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.3 - 7.69 and 7.70 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.39....Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.40....Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.41....Ch. 7.3 - Using the method of Sec. 7.3, solve Prob. 7.42....Ch. 7.3 - 7.75 and 7.76 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.76PCh. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7.3 - (a) Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for...Ch. 7.3 - Solve Prob. 7.83 assuming that the 300-lb force...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) write the...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) write the...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) write the...Ch. 7.3 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) write the...Ch. 7.3 - The beam AB supports the uniformly distributed...Ch. 7.3 - Solve Prob. 7.89 assuming that the uniformly...Ch. 7.3 - The beam AB is subjected to the uniformly...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.92PCh. 7.4 - Three loads are suspended as shown from the cable...Ch. 7.4 - Knowing that the maximum tension in cable ABCDE is...Ch. 7.4 - If dA = 8 ft and dc = 10 ft, determine the...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 7.96PCh. 7.4 - Knowing that dc = 5 m, determine (a) the distances...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 7.98PCh. 7.4 - Knowing that dc = 9 ft, determine (a) the...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 7.100PCh. 7.4 - Knowing that mB = 70 kg and mC = 25 kg, determine...Ch. 7.4 - Fig. P7.101 and P7.102 7.102 Knowing that mB = 18...Ch. 7.4 - Cable ABC supports two loads as shown. Knowing...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 7.104PCh. 7.4 - If a = 3 m, determine the magnitudes of P and Q...Ch. 7.4 - If a = 4 m, determine the magnitudes of P and Q...Ch. 7.4 - An electric wire having a mass per unit length of...Ch. 7.4 - The total mass of cable ACB is 20 kg. Assuming...Ch. 7.4 - The center span of the George Washington Bridge,...Ch. 7.4 - The center span of the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge...Ch. 7.4 - Each cable of the Golden Gate Bridge supports a...Ch. 7.4 - Two cables of the same gauge are attached to a...Ch. 7.4 - A 76-m length of wire having a mass per unit...Ch. 7.4 - A cable of length L + is suspended between two...Ch. 7.4 - The total mass of cable AC is 25 kg. Assuming that...Ch. 7.4 - Cable ACB supports a load uniformly distributed...Ch. 7.4 - Each cable of the side spans of the Golden Gate...Ch. 7.4 - A steam pipe weighing 45 lb/ft that passes between...Ch. 7.4 - A cable AB of span L and a simple beam AB of the...Ch. 7.4 - Making use of the property established in Prob....Ch. 7.4 - 7.120 through 7.123 Making use of the property...Ch. 7.4 - 7.120 through 7.123 Making use of the property...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 7.123PCh. 7.4 - Prob. 7.124PCh. 7.4 - Using the property indicated in Prob. 7.124,...Ch. 7.4 - If the weight per unit length of the cable AB is...Ch. 7.5 - A 25-ft chain with a weight of 30 lb is suspended...Ch. 7.5 - A 500-ft-long aerial tramway cable having a weight...Ch. 7.5 - A 40-m cable is strung as shown between two...Ch. 7.5 - A 50-m steel surveying tape has a mass of 1.6 kg....Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.131PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.132PCh. 7.5 - A 20-m length of wire having a mass per unit...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the sag of a 30-ft chain that is...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.135PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.136PCh. 7.5 - A cable weighing 2 lb/ft is suspended between two...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.138PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.139PCh. 7.5 - Fig. P7.139 and P7.140 7.140 A motor M is used to...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.141PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.142PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.143PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.144PCh. 7.5 - To the left of point B, the long cable ABDE rests...Ch. 7.5 - Fig. P7.145 and P7.146 7.146 To the left of point...Ch. 7.5 - The 10-ft cable AB is attached to two collars as...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.148PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.149PCh. 7.5 - (a) Determine the maximum allowable horizontal...Ch. 7.5 - A cable has a mass per unit length of 3 kg/m and...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the sag-to-span ratio for which the...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.153PCh. 7 - Knowing that the turnbuckle has been tightened...Ch. 7 - Knowing that the turnbuckle has been tightened...Ch. 7 - Two members, each consisting of a straight and a...Ch. 7 - Knowing that the radius of each pulley is 150 mm,...Ch. 7 - For the beam shown, determine (a) the magnitude P...Ch. 7 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear...Ch. 7 - For the beam shown, draw the shear and...Ch. 7 - The beam AB, which lies on the ground, supports...Ch. 7 - Two loads are suspended as shown from the cable...Ch. 7 - A wire having a mass per unit length of 0.65 kg/m...Ch. 7 - A 10-ft rope is attached to two supports A and B...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. (x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2arrow_forward1. Find a power series solution in powers of x. y" - y' + x²y = 0arrow_forward3. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. 8x2y" +10xy' + (x 1)y = 0 -arrow_forward
- Hello I was going over the solution for this probem and I'm a bit confused on the last part. Can you please explain to me 1^4 was used for the Co of the tubular cross section? Thank you!arrow_forwardBlood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cParrow_forwardQ2: Find the shear load on bolt A for the connection shown in Figure 2. Dimensions are in mm Fig. 2 24 0-0 0-0 A 180kN (10 Markarrow_forward
- determine the direction and magnitude of angular velocity ω3 of link CD in the four-bar linkage using the relative velocity graphical methodarrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forward
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forward(Read image) (Answer given)arrow_forwardProblem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and (y2), respectively. Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s]. Givens: y1 = 4.112 m y2 = 0.387 m b = 0.942 m Answers: ( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s ( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s ( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s ( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Extent of Reaction; Author: LearnChemE;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__stMf3OLP4;License: Standard Youtube License