
Concept explainers
Knowing that P = Q = 150 lb, determine (a) the distance a for which the maximum absolute value of the bending moment in beam AB is as small as possible, (b) the corresponding value of |M|max. (See the hint for Prob. 7.55.)
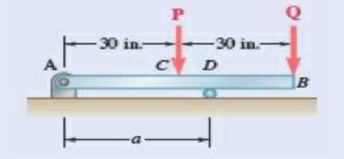
Fig. P7.60
(a)
The distance a from the ends of the beam to the points where the cables should be attached if the maximum absolute value of the bending moment in the beam AB is the smallest.
Answer to Problem 7.60P
The distance a from the ends of the beam to the points where the cables should be attached if the maximum absolute value of the bending moment in the beam AB is the smallest is
Explanation of Solution
Refer Figures 1.
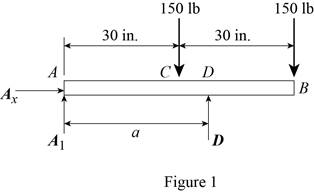
Write an expression to calculate the counter clockwise moment at point A.
Here,
Write an expression to calculate the counter clockwise moment at point A.
Here,
Write an expression to calculate the counter clockwise moment at point A.
Here,
Conclusion:
Refer Figure 1:
Calculate the moment about point A.
Here,
Rearrange the equation to calculate the D.
Substitute
Refer figure 2.
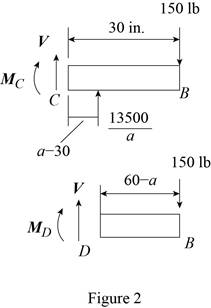
Calculate the moment about point C.
Rearrange the equation to calculate the
Substitute
Refer figure 2.
Calculate the moment about point D.
Rearrange the equation to calculate the
Substitute
The magnitude of the maximum moment is equal to the magnitude of the minimum moment.
Substitute (I) and (II) in above equation to find a.
Rearrange the equation to find a.
Thus, the distance a from the ends of the beam to the points where the cables should be attached if the maximum absolute value of the bending moment in the beam AB is the smallest is
(b)
The value of
Answer to Problem 7.60P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Refer figure 4.
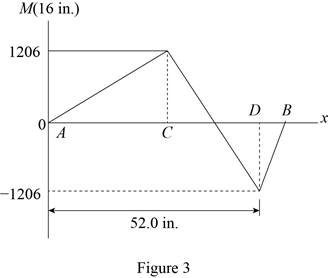
The magnitude of the maximum moment is equal to the magnitude of the minimum moment.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- A pipeline engineer is considering alternative natural gas pipeline routings. The first route is mostly over land and the second is primarily undersea. Both pipelines will need some valve and fitting replacements in year 25. Cost data for each route is shown in Table P2.21. Notice that the undersea route has a higher initial cost due to higher installation costs and extra corrosion protection for the pipeline. However, the undersea route has cheaper security and maintenance costs which substantially reduces annual costs. The MARR for the project is 15%. Determine which route should be pursued based on a present worth analysis.arrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T₂ = -14.00 kpsi. What is the maximum shear stress for this case? The maximum shear stress is kpsi. = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi,arrow_forwardThe initial cost of a proposed heat recovery system is $375,000. The annual operation andmaintenance costs are projected to be $12,000. The salvage value of the system at the end of itsuseful life (projected to be 30 years) is $60,000. The annual savings in fuel costs resulting fromthis system are estimated to be $55,000 per year.a. Assuming annual compounding, determine the rate of return for this heat recovery system.b. If management has set the MARR to be 15% for a heat recovery system like this, what is themaximum initial cost that can be spent on the system (assuming that all other costs and incomesare the same)?arrow_forward
- The initial cost of a machine for a production facility is $225,000. The machine is expected tolast for 10 years with no salvage value. The company’s tax rate is 49% and SLD is used todepreciate the machine. For this type of depreciation, the tax life of the machine is considered 8years and its salvage value is $5,000. The after-tax rate of return is 14.3%. Determine the uniformannual before-tax cash flow.arrow_forwardThree alternatives are being considered for an air cleaning system. All three systems have a lifeof 10 years with no salvage value. System A has an initial cost of $29,000. During the first fiveyears of operation, the annual costs to operate system A are $5,000. During the second five years,the annual cost of system A increases to $16,000. System B has an initial cost of $43,000. Theannual cost to operate system B is $4,000, however, after the first year, this cost increases by$1,600 per year. System C has an initial cost of $58,000 with an annual cost of $2,400. System Crequires two upgrades: one during year 4 which costs $6,000, and the other during year 8 whichcosts $3,000. The MARR for this project is 17%. Determine which air cleaning system should beinstalled based on an economic analysis.arrow_forwardShow all work as much as you can and box out answersarrow_forward
- Show as much work as possible and box out answers pleasearrow_forwardon-the-job conditions. 9 ±0.2- 0.5 M Application questions 1-7 refer to the drawing above. 1. What does the flatness tolerance labeled "G" apply to? Surface F A. B. Surfaces E and F C. Surfaces D, E, H, and I D. The derived median plane of 12 +0.2 0.5 0.5 CF) 20 ±0.2 0.1 7. O 12 ±0.2- H 0.3 ASME Y14.5-2009arrow_forwardelements, each with a length of 1 m. Determine the temperature on node 1, 2, 3, 4. 3. Solve the strong form analytically (you may choose Maple, MATLAB or Mathematica to help you solve this ODE). Compare the FE approximate temperature distribution through the block against the analytical solution. 1 (1) 200 °C 2 (2) 3 m 3 (3)arrow_forward
- Compute the horizontal and vertical components of the reaction at the pin A. B A 30° 0.75 m 1 m 60 N 0.5 m 90 N-marrow_forwardA particle is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped hill of radius R = shown below. The angular motion of the particle is governed by the following ODE: + 0.4 02 - 2 cos 0 + 0.8 sin 0 = 0 where is the angle in rad measured from the top (CCW: +), ė 5m, as = wis the velocity in rad/s, ==a is the angular acceleration in rad/s². Use MATLAB to numerically integrate the second order ODE and predict the motion of the particle. (a) Plot and w vs. time (b) How long does it take for the particle to fall off the ring at the bottom? (c) What is the particle speed at the bottom. Hint v = Rw. in de all questions the particles inside the tube. /2/07/25 Particle R 0 0 R eled witharrow_forwardIf FA = 40 KN and FB = 35 kN, determine the magnitude of the resultant force and specify the location of its point of application (x, y) on the slab. 30 kN 0.75 m 90 kN FB 2.5 m 20 kN 2.5 m 0.75 m FA 0.75 m 3 m 3 m 0.75 marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





