
Concept explainers
To find: The counterexample for the given statement.
Answer to Problem 53HP
The counter-example is that all rectangles are similar as the hypothesis is true and the conclusion false.
Explanation of Solution
Consider that the two polygons are similar when the corresponding
Consider the following rectangles is shown in Figure 1
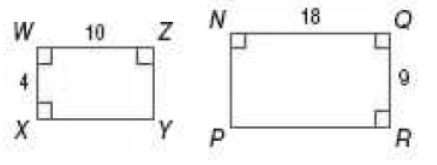
Figure 1
By the theorem of similar
Then, compare the angles as,
Since,
Thus, the counter-example is that all rectangles are similar as the hypothesis is true and the conclusion false.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Geometry, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- find the value of each variablearrow_forwardName: Date: Bell: Unit 11: Volume & Surface Area Homework 2: Area of Sectors Directions: Find the area of each shaded sector. Round to the hundredths place. 1. GH 11 in 2. KL 20 ft H F 64 G L 119 M K 3. BA 6.5 cm 4. YZ 14.2 m B 23 X 87° Y Z 5. KL = 27.1 mm J 32 L X:360-32.1 K A-3 360 7. BD 18 cm E 136 B X=32.8 127.0 (271) A: 069.13 Amm² 19=2102.13 A-136 360.16912 A:300cm² A=96.13 6. PQ = 2.8 in P R 311° 8. WZ 5.3 km V = Z 108 W D 9. HK = 25 ft G H KO 26 X 10. SR 26 m = S 73 T R Gina Wilson (All Things Algebarrow_forward538 Chapter 13 12. Given: Points E(-4, 1), F(2, 3), G(4, 9), and H(-2, 7) a. Show that EFGH is a rhombus. b. Use slopes to verify that the diagonals are perpendicular. 13. Given: Points R(-4, 5), S(-1, 9), T(7, 3) and U(4, -1) a. Show that RSTU is a rectangle. b. Use the distance formula to verify that the diagonals are congruent. 14. Given: Points N(-1, -5), O(0, 0), P(3, 2), and 2(8, 1) a. Show that NOPQ is an isosceles trapezoid. b. Show that the diagonals are congruent. Decide what special type of quadrilateral HIJK is. Then prove that your answer is correct. 15. H(0, 0) 16. H(0, 1) 17. H(7, 5) 18. H(-3, -3) I(5, 0) I(2,-3) 1(8, 3) I(-5, -6) J(7, 9) K(1, 9) J(-2, -1) K(-4, 3) J(0, -1) K(-1, 1) J(4, -5) K(6,-2) 19. Point N(3, - 4) lies on the circle x² + y² = 25. What is the slope of the (Hint: Recall Theorem 9-1.) - line that is tangent to the circle at N? 20. Point P(6, 7) lies on the circle (x + 2)² + (y − 1)² = 100. What is the slope of the line that is tangent to the circle at…arrow_forward
- Can you cut the 12 glass triangles from a sheet of glass that is 4 feet by 8 feet? If so, how can it be done?arrow_forwardCan you cut 12 glass triangles from a sheet of glass that is 4 feet by 8 feet? If so, draw a diagram of how it can be done.arrow_forwardIn triangle with sides of lengths a, b and c the angle a lays opposite to a. Prove the following inequality sin a 2√bc C α b a Warrow_forward
- Find the values of x, y, and z. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 8, 23arrow_forward11 In the Pharlemina's Favorite quilt pattern below, vega-pxe-frame describe a motion that will take part (a) green to part (b) blue. Part (a) Part (b)arrow_forward5. 156 m/WXY = 59° 63 E 7. B E 101 C mFE = 6. 68° 8. C 17arrow_forward
- 1/6/25, 3:55 PM Question: 14 Similar right triangles EFG and HIJ are shown. re of 120 √65 adjacent E hypotenuse adjaca H hypotenuse Item Bank | DnA Er:nollesup .es/prist Sisupe ed 12um jerit out i al F 4 G I oppe J 18009 90 ODPO ysma brs & eaus ps sd jon yem What is the value of tan J? ed on yem O broppo 4 ○ A. √65 Qx oppoEF Adj art saused taupe ed for yem 4 ○ B. √65 29 asipnisht riod 916 zelprisht rad √65 4 O ○ C. 4 √65 O D. VIS 9 OD elimiz 916 aelonsider saused supsarrow_forwardFind all anglesarrow_forwardFind U V . 10 U V T 64° Write your answer as an integer or as a decimal rounded to the nearest tenth. U V = Entregararrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

