
Concept explainers
Hypothesis Testing Using a P-Value In Exercises 31–36,
- (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha.
- (b) find the standardized test statistic z.
- (c) find the corresponding P-value.
- (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
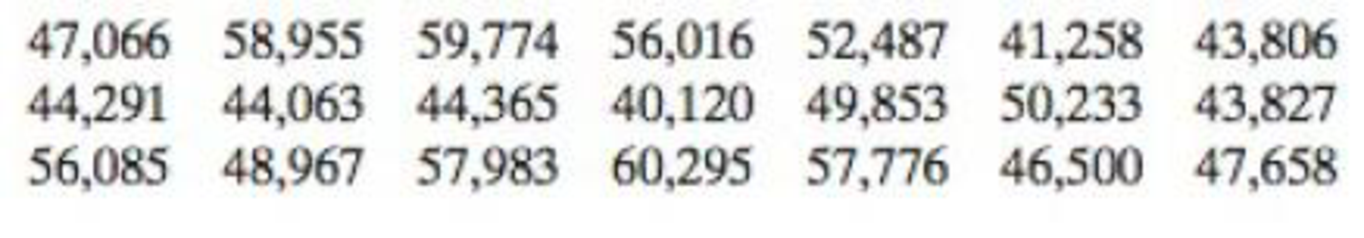
 36. Salaries An analyst claims that the
36. Salaries An analyst claims that the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Statistics for Business and Economics (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (6th Edition)
Statistics for Psychology
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition (13th Edition)
- Testing Claims About Proportions. In Exercises 7–22, test the given claim. Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value or critical value(s), then state the conclusion about the null hypothesis, as well as the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Cell Phones and Handedness A study was conducted to investigate the association between cell phone use and hemispheric brain dominance. Among 216 subjects who prefer to use their left ear for cell phones, 166 were right-handed. Among 452 subjects who prefer to use their right ear for cell phones, 436 were right-handed (based on data from “Hemispheric Dominance and Cell Phone Use,” by Seidman et al., JAMA Otolaryngology—Head & Neck Surgery, Vol. 139, No. 5). We want to use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the rate of right-handedness for those who prefer to use their left ear for cell phones is less than the rate of right-handedness for those who prefer to use their right ear…arrow_forwardData set presents a sample of the number of defective flash drives produced by a small manufacturing company over the last 30 weeks. The company's operations manager believes that the number of defects produced by the process is less than seven defective flash drives per week. Construct a hypothesis test to verify the operations manager's claim. Hypothesis test should include a t test statistic value, a p value, a decision, and a conclusion. This is the null hypotheses (see attachment): Data: Mean 7.0300 SD 1.3700 SEM 0.2501 N 30arrow_forwardData set presents a sample of the number of defective flash drives produced by a small manufacturing company over the last 30 weeks. The company's operations manager believes that the number of defects produced by the process is less than seven defective flash drives per week. Construct a hypothesis test to verify the operations manager's claim. Hypothesis test should include a t test statistic value, a p value, a decision, and a conclusion. This is the alternative hypotheses (see attachment): Data: Mean 7.0300 SD 1.3700 SEM 0.2501 N 30arrow_forward
- Hypothesis Testingarrow_forwardData set presents a sample of the number of defective flash drives produced by a small manufacturing company over the last 30 weeks. The company's operations manager believes that the number of defects produced by the process is less than seven defective flash drives per week. Construct a hypothesis test to verify the operations manager's claim. Hypothesis test should include a t test statistic value, a p value, a decision, and a conclusion. This is the null and alternative hypotheses (see attachment): Data: Mean 7.0300 SD 1.3700 SEM 0.2501 N 30arrow_forwardTesting Claims About Proportions. In Exercises 7–22, test the given claim. Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value or critical value(s), then state the conclusion about the null hypothesis, as well as the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Accuracy of Fast Food Drive-Through Orders In a study of Burger King drive-through orders, it was found that 264 orders were accurate and 54 were not accurate. For McDonald’s, 329 orders were found to be accurate while 33 orders were not accurate (based on data from QSR magazine). Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that Burger King and McDonald’s have the same accuracy rates. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. b. Test the claim by constructing an appropriate confidence interval. c. Relative to accuracy of orders, does either restaurant chain appear to be better?arrow_forward
- Q3 Part 2arrow_forwardK Describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim. A furniture store claims that at least 75% of its new customers will return to buy their next piece of furniture. Describe the type I error. Choose the correct answer below. OA. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return piece furniture is no more than 0.75, but you reject Ho: ps 0.75. OB. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return. piece of furniture is at least 0.75, but you reject Ho: p20.75. buy their next buy their next OC. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece furniture is at least 0.75, but you fail to reject Ho: p20.75. OD. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return buy their next piece of furniture is no more than 0.75, but you fail to reject Ho: p≤0.75. Describe the type Il error. Choose the correct answer below. OA.…arrow_forwardbartam 40. GUeTticient of skewness and interpret the result : Age below (yrs) No. of employees 25 8. 30 20 35 40 40 65 45 80 50 92 55 100arrow_forward
- Do people walk faster in the airport when they are departing (getting on a plane) or do they walk faster when they are arriving (getting off a plane)? A reputable researcher measured the walking speed of random travelers in two International Airports. His findings are summarized in the table. Complete parts (a)-(c) below. Click the icon to view the findings. Walking Speed - X Direction of Travel Departure Mean speed 254 Arrival 267 = 0.05 level of significance? Let μ₁ represent the mean speed of people departing and H2 represent the mean speed of (feet per minute) Standard 47 38 deviation (feet Print Done Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) B. Ho: H1 H2 H₁: H₁>H₂ D. Ho: H1 H2 H₁: H1 H2.arrow_forwardActivity in Statistics please solve & explain your answerarrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls show all work.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


