
Concept explainers
For the frame of Prob. 7.17, determine the magnitude and location of the maximum bending moment in member BC.
The bending moment of the couple exerted at the point
Answer to Problem 7.18P
The magnitude of the bending moment of couple exerted at the point
Explanation of Solution
Sketch the free body diagram for the pipe as shown in the Figure 1.
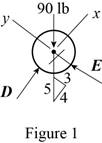
Write the equation of the axial force exerted at the axial point of the pipe from x direction.
Here, the pipe is supported by a small frame on the member is
Write the equation of the axial force exerted at the point on the pipe from y direction.
Here, the force exerted on the pipe at y direction in equilibrium condition is
Sketch the free body diagram for the frame as shown in the Figure 2.
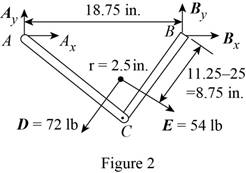
Write the equation of the moment of couple formed in the bending moment of the frame at the point
Here, the force exerted on the member of the pipe at point
Write the equation of the axial force exerted at the point on the pipe from y direction (Refer fig 2).
Here, the force exerted on the member of the pipe on frame at the point
Write the equation of the axial force exerted at the axial point of the pipe from x direction (Refer fig 2).
Sketch the free body diagram for the member of the frame from the point
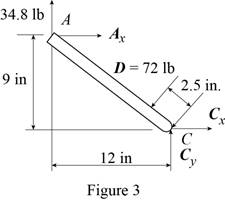
Write the equation of the moment of couple formed in the bending moment supported at the point
Here, the distance of the frame
Sketch the free body diagram for the member of the frame from the portion
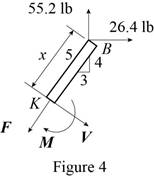
Write the equation of the moment of couple formed in the bending moment supported at the point
Sketch the free body diagram for the member of the frame from the portion
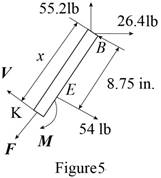
Write the equation of the moment of couple formed in the bending moment supported at the point
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of the bending moment of couple exerted at the point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Need helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forwardProblem 1 8 in. in. PROBLEM 15.109 Knowing that at the instant shown crank BC has a constant angular velocity of 45 rpm clockwise, determine the acceleration (a) of Point A, (b) of Point D. 8 in. Answer: convert rpm to rad/sec first. (a). -51.2j in/s²; (b). 176.6 i + 50.8 j in/s²arrow_forward
- Problem 4 The semicircular disk has a radius of 0.4 m. At one instant, when 0-60°, it is rotating counterclockwise at 0-4 rad/s, which is increasing in the same direction at 1 rad/s². Find the velocity and acceleration of point B at this instant. (Suggestion: Set up relative velocity and relative acceleration that way you would for a no-slip disk; remember what I told you to memorize on the first day of class.) (Answer: B = −2.98î - 0.8ĵ m/s, ãB = 2.45î - 5.74ĵ m/s²) B 0.4 m y Xarrow_forwardA C C 2r A 2r B B (a) (b) Problem 3 Refer to (b) of the figure shown above. The disk OA is now rolling with no slip at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = 2wk, AB = w²k)arrow_forwardProblem 2 Refer to (a) of the figure shown below, where the disk OA rotates at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and link BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = wk, AB = w²k) A 2r C B (a) A 2r B (b)arrow_forward
- Example Two rotating rods are connected by slider block P. The rod attached at A rotates with a constant clockwise angular velocity WA. For the given data, determine for the position shown (a) the angular velocity of the rod attached at B, (b) the relative velocity of slider block P with respect to the rod on which it slides. b = 8 in., w₁ = 6 rad/s. Given: b = 8 in., WA = 6 rad/s CW constant Find: (a). WBE (b). Vp/Frame E 60° 20° Barrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin + N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f (t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: • Analytically (hand calculations) Creating Simulink Model Plot solutions for first two, three and four non-zero terms as well as the Simulink solution on the same graph for the first 15 sec. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward
- Two springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m² = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. (y₁ = 0) www k₁ = 3 Jm₁ = 1 k2=2 www (Net change in spring length =32-31) (y₂ = 0) m₂ = 1 32 32 System in static equilibrium System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁ (t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Produce an animation of the system for all solutions for the first minute.arrow_forwardTwo large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min 1 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t≥ 0: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Plot all solutions on the same graph for the first 15 min. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward5. Estimate the friction pressure gradient in a 10.15 cm bore unheated horizontal pipe for the following conditions: Fluid-propylene Pressure 8.175 bar Temperature-7°C Mass flow of liquid-2.42 kg/s. Density of liquid-530 kg/m³ Mass flow of vapour-0.605 kg/s. Density of vapour-1.48 kg/m³arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





