
Concept explainers
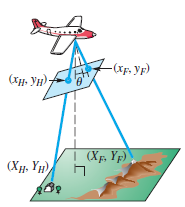
Aerial Photography Aerial photographs can be used to provide coordinates of ordered pairs to determine distances on the ground. Suppose we assign coordinates as shown in the figure. If an object’s photographic coordinates are (x, y), then its ground coordinates (X. Y) in feet can be computed using the following formulas.
Here. f is focal length of the camera in inches, a is altitude in feet of the airplane, and h is elevation in feet of the object. Suppose that a house has photographic coordinates (xH' yH) = (0.9. 3.5) with elevation 150 ft. and a nearby forest fire has photographic coordinates (xF. yF) = (2.1. -2.4) and is at elevation 690 ft. Also suppose the photograph was taken at 7400 ft by a camera with focal length 6 in. and tilt
(a) Use the formulas to find the ground coordinates of the house and the fire to the nearest tenth of a foot.
(b) Use the distance formula
to find the distance on the ground between the house and the fire to the nearest tenth of a foot.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Trigonometry plus MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- T2.2 Prove that a sequence s d₁, d₂,..., dn with n ≥ 3 of integers with 1≤d; ≤ n − 1 is the degree sequence of a connected unicyclic graph (i.e., with exactly one cycle) of order n if and only if at most n-3 terms of s are 1 and Σ di = 2n. (i) Prove it by induction along the lines of the inductive proof for trees. There will be a special case to handle when no d₂ = 1. (ii) Prove it by making use of the caterpillar construction. You may use the fact that adding an edge between 2 non-adjacent vertices of a tree creates a unicylic graph.arrow_forward= == T2.1: Prove that the necessary conditions for a degree sequence of a tree are sufficient by showing that if di 2n-2 there is a caterpillar with these degrees. Start the construction as follows: if d1, d2,...,d2 and d++1 = d = 1 construct a path v1, v2, ..., vt and add d; - 2 pendent edges to v, for j = 2,3,..., t₁, d₁ - 1 to v₁ and d₁ - 1 to v₁. Show that this construction results vj in a caterpillar with degrees d1, d2, ..., dnarrow_forward4 sin 15° cos 15° √2 cos 405°arrow_forward
- 2 18-17-16-15-14-13-12-11-10 -9 -8 -6 -5 -4-3-2-1 $ 6 8 9 10 -2+ The curve above is the graph of a sinusoidal function. It goes through the points (-10, -1) and (4, -1). Find a sinusoidal function that matches the given graph. If needed, you can enter π-3.1416... as 'pi' in your answer, otherwise use at least 3 decimal digits. f(x) = > Next Questionarrow_forwardketch a graph of the function f(x) = 3 cos (표) 6. x +1 5 4 3 3 80 9 2+ 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1 -2 -3+ -4 5 -6+ Clear All Draw: пи > Next Questionarrow_forwardDraw the following graph on the interval πT 5π < x < 2 2 y = 2 sin (2(x+7)) 6. 5. 4 3 3 2 1 +3 /2 -π/3 -π/6 π/6 π/3 π/2 2π/3 5π/6 π 7π/6 4π/3 3π/2 5π/311π/6 2π 13π/67π/3 5π Clear All Draw:arrow_forward
- ketch a graph of the function f(x) = 3 cos (표) 6. x +1 5 4 3 3 80 9 2+ 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1 -2 -3+ -4 5 -6+ Clear All Draw: пи > Next Questionarrow_forward3 2 20-10-18-17-16-15-14-13-12-11-10-9 -8 -7 -6 -$4-3-2-1 -1 -2 -3 4- -5+ The curve above is the graph of a sinusoidal function. It goes through the points (-8, -4) and (6,-4). Find a sinusoidal function that matches the given graph. If needed, you can enter π=3.1416... as 'pi' in your answer, otherwise use at least 3 decimal digits. f(x) = > Next Question Barrow_forwardX Grades for X Assignmen X A-Z Datab XE Biocultural X EBSCO-Ful X Review es/119676/assignments/3681238 Review Quiz 8.1-p2 points possible Answered: 3/5 ● Question 1 4+ 3. 2 1 13 /12-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 -3 -4- 5 2 6 The curve above is the graph of a sinusoidal function. It goes through the points (-7,0) and (3,0). Find a sinusoidal function that matches the given graph. If needed, you can enter π=3.1416... as 'pi' in your answer, otherwise use at least 3 decimal digits. f(x) = > Next Question 申 J % F 刀 Q Search S € t ח Y 7 I * 00 J ப I Darrow_forward
- 2 d) Draw the following graph on the interval k 5π Next Questionarrow_forwardDraw the following graph on the interval 5л Next Questionarrow_forwardDraw the following graph on the interval πT 5π < x < x≤ 2 2 y = 2 cos(3(x-77)) +3 6+ 5 4- 3 2 1 /2 -π/3 -π/6 Clear All Draw: /6 π/3 π/2 2/3 5/6 x 7/6 4/3 3/2 5/311/6 2 13/67/3 5 Question Help: Video Submit Question Jump to Answerarrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage





