
Concept explainers
Concept Check In Exercise 69, for the rain gauge to collect the maximum amount of water, what should he true about
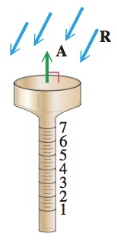
(Modeling) Measuring Rainfall Suppose that vector R models the amount of rainfall in inches and the direction it falls, and vector A models the area in square inches and the orientation of the opening of a rain gauge, as illustrated in the figure. The total volume V of water collected in the rain gauge is given by
V= |R · A|.
This formula calculates the volume of water collected even if the wind is blowing the rain in a slanted direction or the rain gauge is not exactly vertical. Let R = i - 2j and A = 0.5i + j.
(a) Find | R | and | A | to the nearest tenth. Interpret the results.
(b) Calculate V to the nearest tenth, and interpret this result.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Trigonometry plus MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- For the given right triangle, the longer leg is 8 units long and the shorter leg is 6 units long. sina=arrow_forwardWrite the equation of the trigonometric function shown in the graph. LO 5 4 3 2 1 y -5 -5 4 8 8 500 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 x 5 15л 5л 25л 15л 35π 5л 4 8 2 8 4 8arrow_forward2. If log2 (sin x) + log₂ (cos x) = -2 and log2 (sin x + cos x) = (-2 + log2 n), find n.arrow_forward
- If cscx- cotx = -4, find cscx + cotx.arrow_forwardQuestion 10 (5 points) (07.04 MC) Vectors u and v are shown in the graph. -12-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 What is proju? a -6.5i - 4.55j b -5.2i+2.6j с -4.7631 3.334j d -3.81i+1.905j < + 10 6 5 4 3 2 -3 -2 -10 1 -1 -2 -3 u -4 -5 -6 -7arrow_forwardFind the lengths of PR and OR in terms of the angles α and β. Find the angles ∠ONQ and ∠NPQ. Find the lengths of ON and PN in terms of the angle β. Find the length of PQ. Find the length of QR. Find the length of OM. Find the length of RM. What formula can you write down by noting that PR = QR + PQ? What formula can you write down by noting that OR = OM - RM?arrow_forward
- 5) Solve the triangle. 2 95° 4 B с A) c=3.63, A=59.5°, B = 25.5° C) c = 4.63, A = 59.5°, B = 25.5° A B) c 4.63, A 25.5°, B = 59.5° = = D) c 5.63, A = 25.5°, B = 59.5°arrow_forwardFind zw. Leave your answer in polar form. = လ 3π 2 z = 6 cos 6 cos 37 3π + i sin 2 57 W = 12 cos + i sin 6 6 ༠།ལྦ་arrow_forward10 Write the expression (1 – i) i)in the standard form a + bi.arrow_forward
- 11) The letters r and 0 represent polar coordinates. Write the equation r sine = 10 using rectangular coordinates (x, y). A) x = 10y B) y = 10 C) x = 10 D) y = 10xarrow_forward18) Find all the complex cube roots of - 8i. Leave your answers in polar form with the argument in degrees.arrow_forwardWrite the complex number √3 - i in polar form.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,




