
Concept explainers
Subpart (a):
The impact of falling prices of computers and its impact on typewriters.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
When the cost of producing computers falls, the supply of the computers in the economy will increase. This will lead to a rightward shift in the supply curve of the computers. As a result of this rightward shift, the price of the computers will fall and the quantity demanded will increase. This can be illustrated as follows:
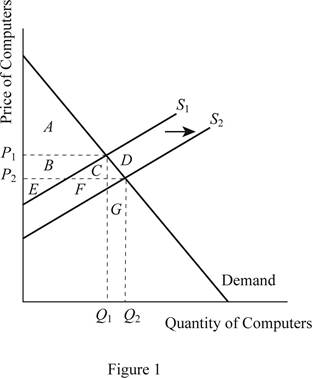
From the above graph, it can be identified that when there is a rightward shift in the supply curve for the computers due to the fall in the cost of producing the computers, there will be a new equilibrium and this will be determined below the existing one. As a result of this, the price will fall from P1 to P2 and the quantity will rise from Q1 to Q2.
Before the shift in the supply curve, the
Before the shift in the supply curve towards the right due to the fall in the cost of producing computer, the
The quantity demanded increases from Q1 to Q2, which means that more quantity is sold and it increases the producer surplus, but at the same time the fall in the price reduces the producer surplus. Thus, the total change in the total surplus can be calculated by summating the changes in the consumer surplus and the producer surplus as follows:
Thus, the total surplus increases by the area of C+D+F+G.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the
Subpart (b):
The impact of falling prices of computers and its impact on typewriters.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
Typewriters and the computers are the substitutes and the fall in the cost of production of the computers implies a fall in the price of computers as explained above. When the computers become cheaper, people will substitute the typewriters with the computers. As a result, there will be a decline in the
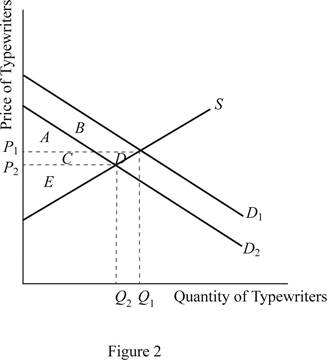
From the above graph of the typewriter market, it can be easily identified that the fall in the production cost of the computers leads to substitution of typewriters with computers. As a result, the demand curve for the typewriter shifts leftward and it results in the lower new equilibrium price of typewriters but lower quantity demanded of typewriters.
Before the shift in the demand curve, the consumer surplus was the area of A+B and after the shift in the demand curve, the consumer surplus changes to area of A+C. Thus, the consumer surplus changes by C - B.
The producer surplus prior to the shift in the demand curve was area of C+E+D. It changes only to the area of D. Thus, the typewriter producers face a loss of surplus by the area of C+D. Hence, the technological advancement is harmful to the typewriter producers because it reduces price, quantity demanded of typewriter and the producer surplus.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpart (c):
The impact of falling prices of computers and its impact on typewriters.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
Software and the computers are the complementary goods and they are correlated positively. When the demand for computers increases, it will lead to an increase in the demand for the software. Thus, the market for the software will witness a shift in the demand curve for the software, which will shift the demand curve towards the right. As a result, the price of the software will increase and the quantity demanded will also increase. This can be illustrated as follows:
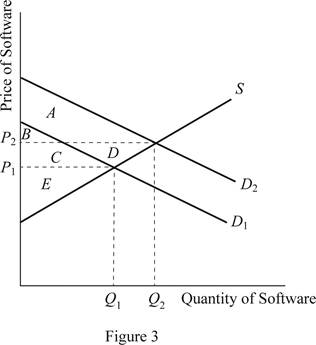
When the demand for the software increases, it will lead to a rightward shift in the demand curve for the software. Thus, as a result of the rightward shift in the demand curve, the D2 will form and it will intersect with the supply curve at a point higher than the existing point to determine new higher equilibrium price and quantity demanded. Thus, the price becomes P2 and the quantity becomes Q2.
Prior to the shift in the demand curve, the consumer surplus was area of B+C and it changes to area of A+B. Thus, the net change in the consumer surplus is by the area of A - C. Similarly, the producer surplus was the area of E before the shift in the demand. It increased to area of C+D+E, where the net increase in the producer surplus is by the area of C+D.
Thus, with the technological advancement, the software producers will be happy because it increases the price of the software, quantity demanded of the software along with the producer surplus.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
The impact of falling prices of computers and its impact on typewriters.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
This analysis helps us to understand how the computer-associated technological markets develop, when there is a technological advancement in the economy. When there is a technological advancement that reduces the cost of producing computers, it will lead to the development of complementary markets such as software. Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft software is world famous example. His company produces different types of software required for the computers and the analysis helps us to explain how Bill Gates emerged as one of the richest people in the world.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Principles of Economics
- C. Regression Discontinuity Birth weight is used as a common sign for a newborn's health. In the United States, if a baby has a birthweight below 1500 grams, the newborn is classified as having “very low birth weight". Suppose you want to study the effect of having very low birth weight on the number of hospital visits made before the baby's first birthday. You decide to use Regression Discontinuity to answer this question. The graph below shows the RD model: Number of hospital visits made before baby's first birthday 5 1400 1450 1500 1550 1600 Birthweight (in grams) a. What is the running variable? (5 points) b. What is the cutoff? (5 points) T What is the discontinuity in the graph and how do you interpret it? (10 points)arrow_forwardExperiments Research suggests that if students use laptops in class, it can have some effect on student achievement. While laptop usage can help students take lecture notes faster, some argue that the laptops may be a source of distraction for the students. Suppose you are interested in looking at the effect of using laptops in class on the students' final exam scores out of 100. You decide to conduct a randomized control trial where you randomly assign some students at UIC to use a laptop in class and other to not use a laptop in class. (Assume that the classes are in person and not online) a. Which people are a part of the treatment group and which people are a part of the control group? (10 points) b. What regression will you run? Define the variables where required. (10 points)arrow_forwardExperiments Research suggests that if students use laptops in class, it can have some effect on student achievement. While laptop usage can help students take lecture notes faster, some argue that the laptops may be a source of distraction for the students. Suppose you are interested in looking at the effect of using laptops in class on the students' final exam scores out of 100. You decide to conduct a randomized control trial where you randomly assign some students at UIC to use a laptop in class and other to not use a laptop in class. (Assume that the classes are in person and not online) a. Which people are a part of the treatment group and which people are a part of the control group? (10 points) b. What regression will you run? Define the variables where required. (10 points)arrow_forward
- Dummy variables News reports claim that in the last year television watching has increased. You believe that rising unemployment during Covid may be one of the causes for this. Suppose you are interested in looking at the effect of being unemployed on the hours spent watching Netflix per day. You collect data on 10,000 people from Chicago who are between the age of 20 and 60. You define the dummy variable Unemployed which takes the value 1 for those who are unemployed and 0 for those who are employed. Equation 1: Hours spent watching Netflix₁ = ßo + B₁Unemployed; + ε¿ Following is the output for equation 1: reg hours spent_watching_netflix unemployed Source SS df MS Number of obs 10,000 F(1, 9998) = 14314.03 Model Residual 3539.70065 2472.39364 9,998 1 3539.70065 .247288822 Prob F R-squared == 0.0000 = 0.5888 Total 6012.09429 9,999 . 601269556 Adj R-squared Root MSE = 0.5887 .49728 hours spen~x Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] unemployed cons 1.189908 .0099456 119.64…arrow_forwardDummy variables News reports claim that in the last year television watching has increased. You believe that rising unemployment during Covid may be one of the causes for this. Suppose you are interested in looking at the effect of being unemployed on the hours spent watching Netflix per day. You collect data on 10,000 people from Chicago who are between the age of 20 and 60. You define the dummy variable Unemployed which takes the value 1 for those who are unemployed and 0 for those who are employed. Equation 1: Hours spent watching Netflix₁ = ßo + B₁Unemployed; + ε¿ Following is the output for equation 1: reg hours spent_watching_netflix unemployed Source SS df MS Number of obs 10,000 F(1, 9998) = 14314.03 Model Residual 3539.70065 2472.39364 9,998 1 3539.70065 .247288822 Prob F R-squared == 0.0000 = 0.5888 Total 6012.09429 9,999 . 601269556 Adj R-squared Root MSE = 0.5887 .49728 hours spen~x Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] unemployed cons 1.189908 .0099456 119.64…arrow_forward17. The South African government's distributive stance is clear given its prioritisation of social spending, which includes grants and subsidised goods. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of an in-kind subsidy versus a cash grant. Use a graphical illustration to support your arguments. [15] 18. Redistributive expenditure can take the form of direct cash transfers (grants) and/or in-kind subsidies. With references to the graphs below, discuss the merits of these two transfer types in the presence and absence of a positive externality. [14] 19. Expenditure on education and healthcare have, by far, the biggest redistributive effect in South Africa' by one estimate dropping the Gini-coefficient by 10 percentage points. Discuss the South African government's performance in health and education provision by evaluating both the outputs and outcomes in these areas of service delivery. [15] 20. Define the following concepts and provide an example in each case: tax rate structure, general…arrow_forward
- Summarise the case for government intervention in the education marketarrow_forwardShould Maureen question the family about the history of the home? Can Maureen access public records for proof of repairs?arrow_forward3. Distinguish between a direct democracy and a representative democracy. Use appropriate examples to support your answers. [4] 4. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery [2] 5. A R1000 tax payable by all adults could be viewed as both a proportional tax and a regressive tax. Do you agree? Explain. [4] 6. Briefly explain the displacement effect in Peacock and Wiseman's model of government expenditure growth and provide a relevant example of it in the South African context. [5] 7. Explain how unbalanced productivity growth may affect government expenditure and briefly comment on its relevance to South Africa. [5] 8. South Africa has recently proposed an increase in its value-added tax rate to 15%, sparking much controversy. Why is it argued that value-added tax is inequitable and what can be done to correct the inequity? [5] 9. Briefly explain the difference between access to education and the quality of education, and why we should care about the…arrow_forward
- 20. Factors 01 pro B. the technological innovations available to companies. A. the laws that regulate manufacturers. C. the resources used to create output D. the waste left over after goods are produced. 21. Table 1.1 shows the tradeoff between different combinations of missile production and home construction, ceteris paribus. Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both missiles and houses. Then answer the indicated question(s). Combination Number of houses Opportunity cost of houses in Number of missiles terms of missiles J 0 4 K 10,000 3 L 17,000 2 1 M 21,000 0 N 23,000 Opportunity cost of missiles in terms of houses Tutorials-Principles of Economics m health carearrow_forwardIn a small open economy with a floating exchange rate, the supply of real money balances is fixed and a rise in government spending ______ Group of answer choices Raises the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market Raises the interest rate, so that income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market.arrow_forwardSuppose a country with a fixed exchange rate decides to implement a devaluation of its currency and commits to maintaining the new fixed parity. This implies (A) ______________ in the demand for its goods and a monetary (B) _______________. Group of answer choices (A) expansion ; (B) contraction (A) contraction ; (B) expansion (A) expansion ; (B) expansion (A) contraction ; (B) contractionarrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





