
Concept explainers
This problem concerns the m. o module from Figure 7.5 and the following version of the swap, c function that counts the number of times it has been called:

For each symbol that is defined and referenced in swap. o, indicate if it will have a symbol table entry in the symbol section in module swap. o. If so, indicate the module that defines the symbol (swap .o or m. o), the symbol type (local, global, or extern), and the section (.text, .data, or bss) it occupies in that module.
Sections in relocatable object files:
There are many sections in a relocatable object file. They are given below:
- “.text”:
- It is the machine code of the compiled program.
- “.rodata”:
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- Strings in “printf” statements.
- Jump tables for switch statements.
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- “.data”:
- This section is used in the initialized “C” variables of global variable and static “C” variables.
- Local “C” variables are initialized at execution time on the stack.
- It does not show in either the “.data” or “.bss” sections.
- “.bss”:
- It is used in the uninitialized global and static “C” variables, along with any global or static variables that are assigned to zero.
- “.symtab”:
- It is a symbol table.
- It contains the information about functions and global variables that are defined and referenced in the program.
- “.rel.text”:
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- It will require to be changed once the linker merges this object file with others.
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- “.rel.data”:
- This section contains relocation information for any global variables that are referenced or defined by the module.
- “.debug”:
- It is a symbol table for debugging
- It contains entries for following
- Definition of Local variables, global variables and typedefs variables and original “C” source file.
- “.line”:
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- That is in original “C” source program and machine code instructions in the “.text” section.
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- “.strtab”:
- It is a string table.
- It contains symbol tables in the “.symtab” and “.debug” sections.
- It is the table for section names in the section headers.
- It is a string table.
Explanation of Solution
For symbol “buf”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is an “extern” type. Because, the variable “buf” is declared in “extern” type which is present in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “buf” type is defined in “m.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “buf” are defined in “m.c” file”.
- When converting source file “m.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “m.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “buf” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “m.c” file.
For symbol “bufp0”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” symbol type. Because, the variable “bufp0” is declared outside the function in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp0” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp0” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp0” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “bufp1”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “bufp1” with “static” type in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp1” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp1” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp1” is defined in “.bss” section. It is the uninitialized static “C” variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “swap”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” type. Because, the symbol “swap” is used in the entire program.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “temp”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
- So, it does not have a symbol type, module defined position and section.
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
For symbol “incr”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the function “incr” uses return type of “static” in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “count”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “count” declared in “static” type in the “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.bss” section. Here, the static variables “count” are initialized to “0” in “swap.c” file.
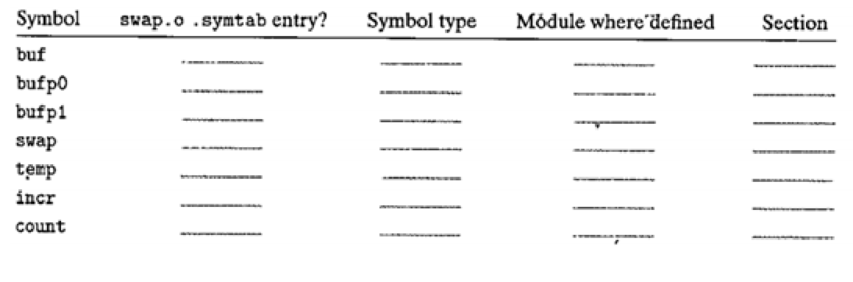
The final table is
| Symbol | .symtab entry? | Symbol type | Module where defined | Section |
| buf | Yes | extern | m.o | .data |
| bufp0 | Yes | global | swap.o | .data |
| bufp1 | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
| swap | Yes | global | swap.o | .text |
| temp | No | - | - | - |
| incr | Yes | local | swap.o | .text |
| count | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
COMPUTER SYSTEMS&MOD MSGT/ET SA AC PKG
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
- Why is JAVA OOP is really difficult to study?arrow_forwardMy daughter is a Girl Scout and it is time for our cookie sales. There are 15 neighbors nearby and she plans to visit every neighbor this evening. There is a 40% likelihood that someone will be home. If someone is home, there is an 85% likelihood that person will make a purchase. If a purchase is made, the revenue generated from the sale follows the Normal distribution with mean $18 and standard deviation $5. Using @RISK, simulate our door-to-door sales using at least 1000 iterations and report the expected revenue, the maximum revenue, and the average number of purchasers. What is the probability that the revenue will be greater than $120?arrow_forwardQ4 For the network of Fig. 1.41: a- Determine re b- Find Aymid =VolVi =Vo/Vi c- Calculate Zi. d- Find Ay smid e-Determine fL, JLC, and fLE f-Determine the low cutoff frequency. g- Sketch the asymptotes of the Bode plot defined by the cutoff frequencies of part (e). h-Sketch the low-frequency response for the amplifier using the results of part (f). Ans: 28.48 2, -72.91, 2.455 KS2, -54.68, 103.4 Hz. 38.05 Hz. 235.79 Hz. 235.79 Hz. 14V 15.6ΚΩ 68kQ 0.47µF Vo 0.82 ΚΩ V₁ B-120 3.3kQ 0.47µF 10kQ 1.2k0 =20µF Z₁ Fig. 1.41 Circuit forarrow_forward
- a. [10 pts] Write a Boolean equation in sum-of-products canonical form for the truth table shown below: A B C Y 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 a. [10 pts] Minimize the Boolean equation you obtained in (a). b. [10 pts] Implement, using Logisim, the simplified logic circuit. Include an image of the circuit in your report.arrow_forwardUsing XML, design a simple user interface for a fictional app. Your UI should include at least three different UI components (e.g., TextView, Button, EditText). Explain the purpose of each component in your design-you need to add screenshots of your work with your name as part of the code to appear on the interface-. Screenshot is needed.arrow_forwardQ4) A thin ring of radius 5 cm is placed on plane z = 1 cm so that its center is at (0,0,1 cm). If the ring carries 50 mA along a^, find H at (0,0,a).arrow_forward
- 4. [15 pts] A logic function F of four variables a; b; c; d is described by the following K-map. Derive the fully minimized SOP logic expression form of F. cd ab 00 01 11 10 00 0 0 0 1 01 1 0 0 1 11 1 0 1 1 10 0 0 1 1arrow_forward2. [20 pts] Student A B will enjoy his picnic on sunny days that have no ants. He will also enjoy his picnic any day he sees a hummingbird, as well as on days where there are ants and ladybugs. a. Write a Boolean equation for his enjoyment (E) in terms of sun (S), ants (A), hummingbirds (H), and ladybugs (L). b. Implement in Logisim, the logic circuit of E function. Use the Circuit Analysis tool in Logisim to view the expression, include an image of the expression generated by Logisimarrow_forwardHow would I go about creating this computer database in MariaDB with sql? Create a database name "dbXXXXXX" Select the database using the "use [database name]" command. Now you are in the database. Based on the above schema from Enrolment System database, create all the tables with the last 6 digits of "123456", then the table name for table Lecturer should be "123456_Lecturer". Refer to basic SQL lecture note to create table that has primary keys and Foreign Keys. Provide the datatype of each attributes. Add a column called "Department" with datatype "VARCHAR(12)" to the table "Lecturer". Shows the metadata of the updated "Lecturer" table. (Use Describe command) Drop the "Department" column from the table "Lecturer", and show the metadata of the updated "Lecturer" table. Insert three (3) data to each of the table in the tables created. Note: If you have foreign key issues, please disable foreign key constraints before inserting the data, see below SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;…arrow_forward
- CSE330 Discrete Mathematics 1. In the classes, we discussed three forms of floating number representations as given below, (1) Standard/General Form, (2) Normalized Form, (3) Denormalized Form. 3. Consider the real number x = (3.395) 10 (a) (b) Convert the decimal number x into binary format up to 7 binary places (7 binary digits after decimal) Convert the calculated value into denormalized form and calculate fl(x) for m=4 Don't use any Al tool show answer in pen a nd paper then take pi ctures and sendarrow_forwardSimplify the following expressions by means of a four-variable K-Map. AD+BD+ BC + ABDarrow_forwardCSE330 Discrete Mathematics 1. In the classes, we discussed three forms of floating number representations as given below, (1) Standard/General Form, (2) Normalized Form, (3) Denormalized Form. 2. Let ẞ 2, m = 6, emin = -3 and emax = 3. Answer the following questions: Compute the minimum of |x| for General and Normalized form (a) Compute the Machine Epsilon value for the General and Denormalized form. If we change the value of emax to 6 then how will it affect the value of maximum scale invariant error for the case of Normalized form? Explain your answer. show answer in pen a Don't use any Al tool nd paper then take pi ctures and sendarrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning





