
-3 An element of aluminum in the form of a rectangular parallelepiped (see figure) of dimensions a = 5.5 in., h = 4.5 in, and c = 3.5 in. is subjected to iriaxial stresses = 12,500 psi, o. = —5000 psi, and ci. = —1400 psi acting on the x,i, and z faces, respectively.
Determine the following quantities: (a) the maxim um shear stress in the material; (b) the changes ..la, .11. and 1c in the dimensions of the element:
(C) the change .IJ’ in the volume: (d) the strain energy U stored in the element: (e) the maximum value of cr1
when the change in volume must be limited to 0.021%; and (f) the required value of o when the strain energy must be 900 in.-lb. (Assume E = 10,400 ksi and v = 0.33.)
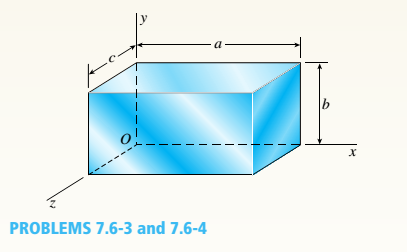
(a)
The maximum shear stress in the material.
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The maximum shear stress on the material is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The aluminium element of length
Explanation:
Write the expression for the maximum shear stress.
Here, the maximum shear stress is
Calculation:
Since no shear stresses act on the parallelepiped,
Substitute,
Conclusion:
The maximum shear stress on the material is
(b)
The changes in the dimensions of the element.
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The change in length is
The change in height is
The change in width is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the strain along
Here, the strain in the
Write the expression for strain in
Here, the strain in
Write the expression for strain in
Here, the strain in
Write the expression for the change in length.
Here, the length of element is
Write the expression for change in height.
Here, the height of element is
Write the expression for the change in width.
Here, the width of the element is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The change in length is
The change in height is
The change in width is
(c)
The change in the volume of the element.
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The change in the volume is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the change in the volume.
Here, the change in volume is
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The change in the volume is
(d)
The strain energy stored in the element.
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The strain energy stored in the element is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the strain energy.
Here, the strain energy is
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The strain energy stored in the element is
(e)
The maximum value of normal stress along the
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The maximum value of normal stress along the
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The change in volume is limited to
Explanation:
Write the expression for the change in volume.
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum value of normal stress along the
(f)
The required value of normal stress along the
Answer to Problem 7.6.3P
The required value of the normal stress along the
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The strain energy of the system is
Explanation:
Write the expression for the strain energy in terms of stresses using Hooke’s law.
Calculation:
Substitute
Solve the quadratic equation for obtaining the value of
Conclusion:
The required value of the normal stress along the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 2 Terms (12 Months) Printed Access Card
- Solve this probem and show all of the workarrow_forwardThe differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: WRITE OUT SOLUTION DO NOT USE A COPIED SOLUTION Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Determine the minimum applied force P required to move wedge A to the right. The spring is compressed a distance of 175 mm. Neglect the weight of A and B. The coefficient of static friction for all contacting surface is μs = 0.35. Neglect friction at the rollers. k = = 15 kN/m P A B 10°arrow_forwardDO NOT COPY SOLUTION- will report The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwarda box shaped barge 37m long, 6.4 m beam, floats at an even keel draught of 2.5 m in water density 1.025 kg/m3. If a mass is added and the vessel moves into water density 1000 kg/m3, determine the magnitude of this mass if the fore end and aft end draughts are 2.4m and 3.8m respectively.arrow_forward
- a ship 125m long and 17.5m beam floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 at a draught of 8m. the waterplane coefficient is 0.83, block coefficient 0.759 and midship section area coefficient 0.98. calculate i) prismatic coefficient ii) TPC iii) change in mean draught if the vessel moves into water of 1.016 t/m3arrow_forwardc. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40) handplot only, and solve for eacharrow_forwardA ship of 9000 tonne displacement floats in fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 at a draught 50 mm below the sea water line. The waterplane area is 1650 m2. Calculate the mass of cargo which must be added so that when entering seawater of 1.025 t/m3 it floats at the seawater line.arrow_forward
- A ship of 15000 tonne displacement floats at a draught of 7 metres in water of 1.000t/cub. Metre.It is required to load the maximum amount of oil to give the ship a draught of 7.0 metre in seawater ofdensity 1.025 t/cub.metre. If the waterplane area is 2150 square metre, calculate the massof oil requiredarrow_forwardA ship of 8000 tonne displacement floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 and has a TPC of 14. The vessel moves into fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 and loads 300 tonne of oil fuel. Calculate the change in mean draught.arrow_forwardAuto Controls DONT COPY ANSWERS - will report Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
