
Concept explainers
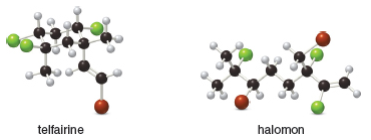
Telfairine, a naturally occurring insecticide, and halomon, an antitumor agent, are two
polyhalogenated compounds isolated from red algae. (a) Classify each halide bonded to an
hybridized carbon as 1°, 2°, or 3°. (b) Label each halide as vinyl, allylic, or neither.
(a)
Interpretation: The halide bonded to
Concept introduction: A halide is classified as
Answer to Problem 7.1P
The halide bonded to
Explanation of Solution
The ball and stick model of telfarine and halomon shows that black balls represent carbon atom, white balls represent hydrogen atom, green and brown balls represent chlorine and bromine atom, respectively.
The actual structure of telfarine and halomon is shown in Figure 1.
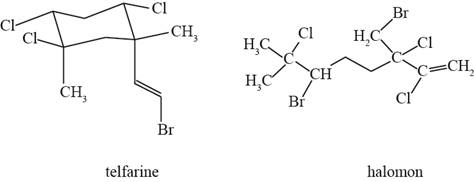
Figure 1
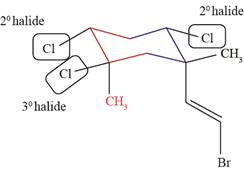
A halide is classified as
The
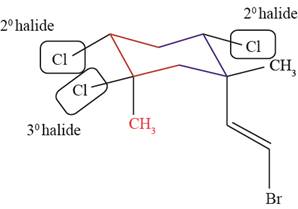
Figure 2
The
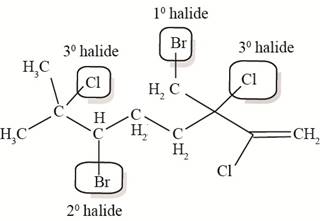
Figure 3
The halide bonded to
(b)
Interpretation: Each halide is to be labeled as vinyl, allylic or neither.
Concept introduction: In allyl halide, halogen atom is bonded to
Answer to Problem 7.1P
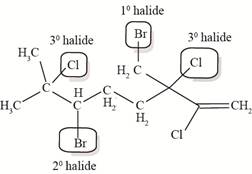
The allylic and vinyl halides of telfarine and halomon are shown below.
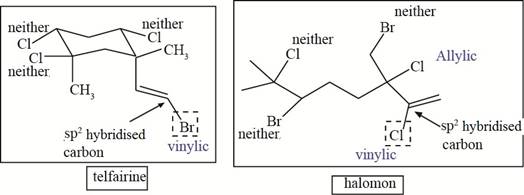
Explanation of Solution
In allyl halide, halogen atom is bonded to
The allylic and vinyl halides of telfarine and halomon are shown in Figure 4.
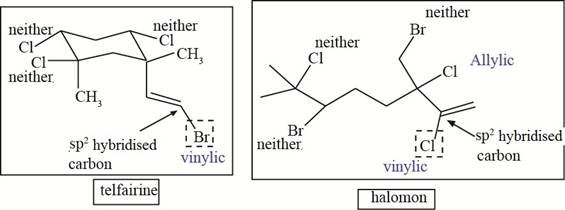
Figure 4
Each halide is labeled as allylic, vinyl and neither as shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Draw the major product of the following reaction. Do not draw inorganic byproducts. H3PO4 OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Explanation Check X ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacyarrow_forwardFor the structure below, draw the resonance structure that is indicated by the curved arrow(s). Be sure to include formal charges. :ÖH Modify the second structure given to draw the new resonance structure. Include lone pairs and charges in your structure. Use the + and - tools to add/remove charges to an atom, and use the single bond tool to add/remove double bonds.arrow_forward
- Using the table of Reactants and Products provided in the Hints section, provide the major product (with the correct stereochemistry when applicable) for questions below by selecting the letter that corresponds to the exact chemical structures for the possible product. OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp A/arrow_forwardUsing arrows to designate the flow of electrons, complete the reaction below and provide a detailed mechanism for the formation of the product OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp All chemical structures should be hand drawn on a piece of paper Paragraph BI UAE +varrow_forwarddraw out the following structures plesearrow_forward
- Draw everything on a piece of paper outlining the synthesis from acetaldehyde to 2 cyclopentene carboxaldehyde using carbon based reagants with 3 carbons or fewers. Here is the attached image.arrow_forwardManoharan Mariappan, FR.D., 34) Complete the following reaction starting from hex-1-yne proceeding via different substitution reactions forming 2-heptanone. (25 pts). A Sia₂BH H₂O₂ NaOH Br D Mechanism for reaction D - ether-cleavage: 10 B Ph-MgCI, THF H₁₂O+ D HBr (XS) C TsCl, Py CH3-CH2-CH2-ONaarrow_forwardIn the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardWhy is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forwardIn the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
