
Identify each of the following unbalanced reaction equations as belonging to one or more of the following categories: precipitation, acid—base, or oxidation—reduction.
l type='a'>
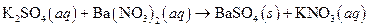
i>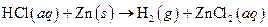
i>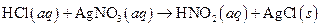
i>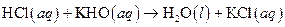
i>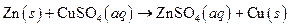
i>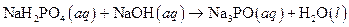
i>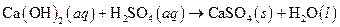
i>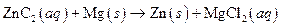
i>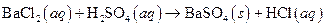
(a)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
(b)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation −reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
(c)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
(d)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(e)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation −reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
(f)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(g)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(h)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation−reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
i)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
(d)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(e)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation −reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
(f)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(g)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(h)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation−reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
i)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
(d)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(e)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation −reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
(f)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(g)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of acid -base reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of acid −base or neutralization reaction because here salt and water will form.
(h)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of oxidation−reduction reaction because in the above reaction oxidation number changed.
i)
Interpretation:
To complete and balance the given combustion reaction.
Concept Introduction:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation that contains same number of atoms as well as of each element of reactants and products of reaction.
For example, the reaction between lead sulphide and oxygen is as follows:
Oxidation-reduction reaction is known as redox reaction. In these types of reaction one reactant is oxidized and another is reduced.
Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Gaining of oxygen atoms.
- Loss of electrons.
- Loss of hydrogen atom.
Reduction: Reduction is a process in which either 1 or all following changes occurs:
- Loss of oxygen atoms.
- Gaining of electrons.
- Gaining of hydrogen atom.
Precipitation reaction means formation of solids or formation of any Precipitate; when solutions of two ionic substances are mixed and any solid will forms in the solution mixture, the reaction is known as Precipitation reaction. The reaction of barium hydroxide and sodium sulphate is an example of precipitate reaction, where barium sulphate a precipitate is formed as follows:
When an acid is reacted with base creating water or solvent and an ionic salt, the reaction is known as Acid-base neutralization reaction for example the reaction of strong acid, hydrochloric acid with strong base sodium hydroxide is as follows:
Answer to Problem 53QAP
The given reaction is an example of precipitation reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The balance reaction is as follows:
This is an example of precipitation reaction because here a solid
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry
- The table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which is the most brittle and which is the most tough (or most resistant). Breaking strength Elastic modulus Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain A (MPa) 415 (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) 550 0.15 500 310 B 700 850 0.15 720 300 C Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardMaterials. The following terms are synonyms: tension, effort and stress.arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardThe table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which material will be the most ductile and which the most brittle. Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain Breaking strength Elastic modulus (MPa) (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) A 310 340 0.23 265 210 B 100 120 0.40 105 150 с 415 550 0.15 500 310 D 700 850 0.14 720 210 E - Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardConsider the following Figure 2 and two atoms that are initially an infinite distance apart, x =00, at which point the potential energy of the system is U = 0. If they are brought together to x = x, the potential energy is related to the total force P by dU dx = P Given this, qualitatively sketch the variation of U with x. What happens at x=x? What is the significance of x = x, in terms of the potential energy? 0 P, Force 19 Attraction Total Repulsion x, Distance Figure 2. Variation with distance of the attractive, repulsive, and total forces between atoms. The slope dP/dx at the equilibrium spacing xe is proportional to the elastic modulus E; the stress σb, corresponding to the peak in total force, is the theoretical cohesive strength.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning




