
The final velocities of the resulting pieces in terms of
Answer to Problem 47QAP
The final velocities of the resulting pieces in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Mass of object
Object breaks into masses of
Formula used:
Momentum,
Where m= mass and
And principle of conservation of linear momentum
Calculation:
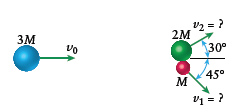
After the piece break into two pieces, Piece
Piece
We can use conservation of momentum in order to calculate thefinal velocities of the two pieces.
Since this is a two-dimensional problem, we will need to splitthe momenta into components and solve the x and y component equations.
y component:
x component:
Therefore,
Conclusion:
Thus, for piece
Thus, for piece
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS-ACHIEVE AC (1-TERM)
- Solve by the quadratic formula or completing the square to obtain exact solutions. 2 e 104 OA) -16±3√6 B) 8±√10 O c) -8±√10 OD) 8±3√√6 Uarrow_forwardQuestion 14 (1 point) Listen The frame on a picture is 18 in by 22 in outside and is of uniform width. Using algebraic methods, what is the width of the frame if the inner area of the picture shown is 250 in²2? Write answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number with no units). 18 in Your Answer: 22 inarrow_forward◄ Listen A vacant lot is being converted into a community garden. The garden and a walkway around its perimeter have an area of 560 square feet. Find the width of the walkway (x) if the garden measures 15 feet wide by 19 feet long. Write answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number without units). X 15 feet Your Answer: 19 feet Xarrow_forward
- Listen A stuntman jumps from a roof 440 feet from the ground. How long will it take him to reach the ground? Use the formula, distance, d = 16t2, (where t is in seconds). Write answer to 1 decimal place. (Write the number, not the units). Your Answer:arrow_forwardSolve x² - 10x + 24 = 0 ○ A) 4,6 B) -12, -2 C) 12,2 D) -4, -6arrow_forwardc7. = -(9 - x) 25 A a) -1, 11 b) 31 c) 11 d) 1, 11arrow_forward
- 2 4x² - 12x-7=0 A) 7 ON 1,-1 4 OB)-, 7 1 C) 2,2 Oa½½-½ c) 17/17, - 1/1/1 D) 2, 2 ODI-,-arrow_forwardSolve using the quadratic equation formula 4x² + 12x=-6 ○ a) -12±√√3 2 b) -3±√15 -3+√15 2 ○ c) c) -3±√√√3 2 d) -3±√3 8arrow_forwardListen Solve the quadratic equation by factoring. One solution is 0. Find the other. 2x² + 16x = 0 Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



