
a.
Show the effect of the given transactions using horizontal statement model.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Liabilities:
Liabilities are an obligation of the business to pay to the creditors in future for the goods and services purchased on account or any for other financial benefit received. It can be current liabilities or a non-current liabilities depending upon the time period in which it is paid.
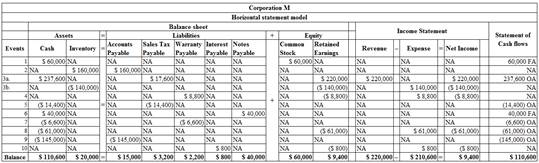
Table (1)
- Receiving money of $60,000 from the issue of common stock increases the value of an asset and the
stockholder’s equity and affects the statement ofcash flow by increasing the financing activity. - Purchasing equipment for $160,000 on account increase the value of an asset and the value of liability of the company.
- Sale of equipment for $220,000 cash increases the value of an asset and the value of the stockholder’s equity. Sale of equipment increases the net income of the company by increasing the value of the revenue in the income statement and it affects the statement of cash flow by increasing the operating activity.
- The cost of the goods sold (inventory) $140,000 decreases the value of an asset and the value of the stockholder’s equity; cost of the merchandise decreases the net income of the company by increasing the value of an expense.
- Providing six month warranty on the equipment increases the value of a liability and decreases the value of the stockholder’s equity; providing six month warranty on the equipment decreases the net income of the company by increasing the value of an expense.
- Paying sales tax to the state agency decreases the value of assets and it affects the statement of the cash flow by decreasing the value of an operating activity.
- Borrowing $40,000 note from the local bank increases the value of an asset and the liability; borrowing money from the local bank affects the statement of cash flow by increasing the value of the financing activity.
- Amount paid on warranty repairs during the year decreases the value of an asset and the liability; paying $6,600 for warranty repairs affects the statement of the cash flow by decreasing the value of an operating activity.
- Amount paid on operating expense decreases the value of an asset and the value of the stockholder’s equity; it decreases the value of the income by increasing the value of an expenses and amount paid on operating expense affects the statement of the cash flow by decreasing the value of an operating activity.
- Amount paid on accounts payable decreases the value of an asset and the liability; amount paid on accounts payable affects the statement of the cash flow by decreasing the value of an operating activity.
- Recording accrued interest on the note issued increases the value of a liability and decreases the value of a stockholder’s equity; it decreases the value of the income by increasing the value of an expenses.
b.
Prepare the income statement,
b.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Statement of cash flows:
This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Balance Sheet:
Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the income statement of the Company M for the year 2014:
| Company M | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Sales Revenue | 220,000 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | (140,000) | |
| Gross Margin | 80,000 | |
| Expense: | ||
| Operating expense | 61,000 | |
| Warranty expense | 8,800 | |
| Total operating expense | (69,800) | |
| Operating income | 10,200 | |
| Interest expense | (800) | |
| Net Income | 9,400 | |
(Table 3)
Therefore, Company M reported and $9,400 in its income statement for the year 2014.
Prepare the balance sheet of the Company M for the year 2014:
| Company M | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Assets: | ||
| Cash | 110,600 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 20,000 | |
| Total Assets | 130,600 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Liabilities: | ||
| Accounts Payable | 15,000 | |
| Sales Tax Payable | 3,200 | |
| Warranties Payable | 2,200 | |
| Interest Payable | 800 | |
| Notes Payable | 40,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | 61,200 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Common Stock | 60,000 | |
| 9,400 | ||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 69,400 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | 130,600 | |
(Table 4)
Therefore, the balance sheet of the Company M for the year 2014 is $130,600.
Prepare the statement of cash flow of the Company M for the year 2014:
| Company M | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Inflow from Customers | 220,000 | |
| Inflow from Sales Tax | 17,600 | |
| Outflow to Purchase Inventory | (145,000) | |
| Outflow for Expenses (1) | (67,600) | |
| Outflow for Sales Tax | (14,400) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 10,600 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | 0 | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Inflow from Stock Issue | 60,000 | |
| Inflow from Loan | 40,000 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | 100,000 | |
| Net Change in Cash | 110,600 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | 0 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | 110,600 | |
(Table 5)
Therefore, Company M reported an amount of $110,600 in its statement of cash flow for the year 2014.
Working Note 1: Compute the outflow of expense.
c.
Calculate the total amount of current liabilities at December 31, 2014.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Current liability: Current liability is a debt that the companies need to pay the debts from existing current assets or creation of other current liabilities within a fiscal year or the operating cycle whichever is higher.
Calculate the total amount of current liabilities at December 31, 2014:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Current Liabilities: | |
| Accounts Payable | 15,000 |
| Sales Tax Payable | 3,200 |
| Warranty Payable | 2,200 |
| Interest Payable | 800 |
| Notes Payable | 40,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | 61,200 |
(Table 6)
Therefore, the total amount of current liabilities at December 31, 2014 is $61,200.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- A bearer plant under IAS 41 is accounted for as____. a. Biological asset at fair value b. Property, plant and equipment c. Inventory d. Investment property MCQarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardBetter Value Hardware began 2010 with a credit balance of $37,500 in the allowance for sales returns account. Sales and cash collections from customers during the year were $1,025,000 and $675,000, respectively. Better Value estimates that 8% of all sales will be returned. During 2010, customers returned merchandise for a credit of $31,000 to their accounts. Better Value's 2010 income statement would report net sales of $__?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





