
a)
To determine: The standard time for the operation.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
a)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Formula:
Calculation of standard time of operation:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | Observed time | Normal time | Afjob | Standard time | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 1.198 | 1.317 | 1.15 | 1.52 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.83 | 0.954 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 | 0.564 | 0.592 | 1.15 | 0.68 |
| Standard time for operation | 3.29 | |||||||||||
Excel Worksheet:
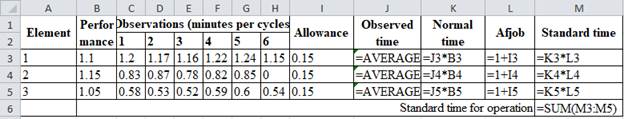
Element 1:
Observed time is calculated by taking mean for the 1.2, 1.17, 1.16, 1.22, 1.24 and 1.15 which gives 1.198.
Normal time is calculated by multiplying observed timing, 1.198 and performance rating, 1.1 which yields 1.317 minutes.
Allowance factor is calculated by adding 1 with the allowance factor 0.15 to give 1.15.
Standard time for element 1 is calculated by multiplying normal time of 1.317 minutes with allowance factor of 1.15 which gives 1.52 minutes.
Same process applies for element 2 and 3 which yields the standard times as 1.10 and 0.68. The standard time for operation is obtained by adding 1.52, 1.10 and 1.68 minutes which gives 3.29 minutes.
Hence, the standard time for the operation is 3.29 minutes.
b)
To determine: The number of observations for element 2.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
b)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Confidence= 95.5%
1% of true value
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element A:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
Calculation of standard deviation:
| Element 2 | Differences | Square of differences | Standard deviation |
| 0.83 | 0 | 0 | 0.0339 |
| 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.0016 | |
| 0.78 | -0.05 | 0.0025 | |
| 0.82 | -0.01 | 0.0001 | |
| 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.0004 | |
| Mean=0.83 | SSQ=0.0046 |
Excel worksheet:
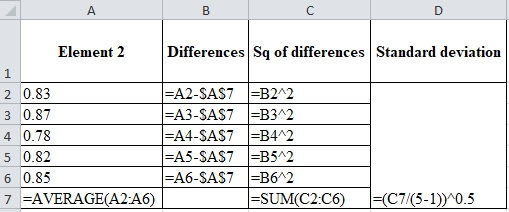
Z value for confidence interval of 95.5% is 2.00.
The confidence interval
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5% is calculated by dividing the product of 2.00 and 0.0339 with product of 0.01 and 0.83 and squaring the resultant which gives 66.7272.
- Using z = 2.01:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5% is calculated by dividing the product of 2.01 and 0.0339 with product of 0.01 and 0.83 and squaring the resultant which gives 67.3962.
Hence, the number of observation is 68.
c)
To determine: The number of observations needed to estimate the mean time for element 2 within 0.01 minute of its true value.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
c)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Confidence= 95.5%
0.10 minute of actual value.
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element C:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
Z value for confidence interval of 95.5% is 2.00.
The confidence interval
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5 is calculated by dividing the product of 2.00 and 0.0339 with 0.01 and squaring the resultant which gives 45.9684.
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5 is calculated by dividing the product of 2.01 and 0.0339 with 0.01 and squaring the resultant which gives 46.4292.
Hence, the number of observations needed to estimate the mean time for element 2 within 0.01 minute of its true value is 46.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT W/ CNCT+
- Sam's Pet Hotel operates 50 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $13.00 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 75 bags/week > Order cost = $52.00/order > Annual holding cost = 20 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent >Lead time = 5 weeks (30 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 75 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 50 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardYellow Press, Inc., buys paper in 1,500-pound rolls for printing. Annual demand is 2,250 rolls. The cost per roll is $625, and the annual holding cost is 20 percent of the cost. Each order costs $75. a. How many rolls should Yellow Press order at a time? Yellow Press should order rolls at a time. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forwardPlease help with only the one I circled! I solved the others :)arrow_forward
- Osprey Sports stocks everything that a musky fisherman could want in the Great North Woods. A particular musky lure has been very popular with local fishermen as well as those who buy lures on the Internet from Osprey Sports. The cost to place orders with the supplier is $40/order; the demand averages 3 lures per day, with a standard deviation of 1 lure; and the inventory holding cost is $1.00/lure/year. The lead time form the supplier is 10 days, with a standard deviation of 2 days. It is important to maintain a 97 percent cycle-service level to properly balance service with inventory holding costs. Osprey Sports is open 350 days a year to allow the owners the opportunity to fish for muskies during the prime season. The owners want to use a continuous review inventory system for this item. Refer to the standard normal table for z-values. a. What order quantity should be used? lures. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forwardIn a P system, the lead time for a box of weed-killer is two weeks and the review period is one week. Demand during the protection interval averages 262 boxes, with a standard deviation of demand during the protection interval of 40 boxes. a. What is the cycle-service level when the target inventory is set at 350 boxes? Refer to the standard normal table as needed. The cycle-service level is ☐ %. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardOakwood Hospital is considering using ABC analysis to classify laboratory SKUs into three categories: those that will be delivered daily from their supplier (Class A items), those that will be controlled using a continuous review system (B items), and those that will be held in a two bin system (C items). The following table shows the annual dollar usage for a sample of eight SKUs. Fill in the blanks for annual dollar usage below. (Enter your responses rounded to the mearest whole number.) Annual SKU Unit Value Demand (units) Dollar Usage 1 $1.50 200 2 $0.02 120,000 $ 3 $1.00 40,000 $ 4 $0.02 1,200 5 $4.50 700 6 $0.20 60,000 7 $0.90 350 8 $0.45 80arrow_forward
- A part is produced in lots of 1,000 units. It is assembled from 2 components worth $30 total. The value added in production (for labor and variable overhead) is $30 per unit, bringing total costs per completed unit to $60 The average lead time for the part is 7 weeks and annual demand is 3800 units, based on 50 business weeks per year. Part 2 a. How many units of the part are held, on average, in cycle inventory? enter your response here unitsarrow_forwardassume the initial inventory has no holding cost in the first period and back orders are not permitted. Allocating production capacity to meet demand at a minimum cost using the transportation method. What is the total cost? ENTER your response is a whole number (answer is not $17,000. That was INCORRECT)arrow_forwardRegular Period Time Overtime Supply Available puewag Subcontract Forecast 40 15 15 40 2 35 40 28 15 15 20 15 22 65 60 Initial inventory Regular-time cost per unit Overtime cost per unit Subcontract cost per unit 20 units $100 $150 $200 Carrying cost per unit per month 84arrow_forward
- assume that the initial inventory has no holding cost in the first period, and back orders are not permitted. Allocating production capacity to meet demand at a minimum cost using the transportation method. The total cost is? (enter as whole number)arrow_forwardThe S&OP team at Kansas Furniture, led by David Angelow, has received estimates of demand requirements as shown in the table. Assuming one-time stockout costs for lost sales of $125 per unit, inventory carrying costs of $30 per unit per month, and zero beginning and ending inventory, evaluate the following plan on an incremental cost basis: Plan B: Vary the workforce to produce the prior month's demand. Demand was 1,300 units in June. The cost of hiring additional workers is $35 per unit produced. The cost of layoffs is $60 per unit cut back. (Enter all responses as whole numbers.) Note: Both hiring and layoff costs are incurred in the month of the change (i.e., going from production of 1,300 in July to 1300 in August requires a layoff (and related costs) of 0 units in August). Hire Month 1 July Demand 1300 Production (Units) Layoff (Units) Ending Inventory Stockouts (Units) 2 August 1150 3 September 1100 4 October 1600 5 November 1900 6 December 1900arrow_forwardThe S&OP team at Kansas Furniture, led by David Angelow, has received estimates of demand requirements as shown in the table. Assuming one-time stockout costs for lost sales of $100 per unit, inventory carrying costs of $20 per unit per month, and zero beginning and ending inventory, evaluate the following plan on an incremental cost basis: Plan A: Produce at a steady rate (equal to minimum requirements) of 1,100 units per month and subcontract additional units at a $65 per unit premium cost. Subcontracting capacity is limited to 800 units per month. (Enter all responses as whole numbers). Ending Month Demand Production Inventory Subcontract (Units) 1 July 1300 1,100 0 2 August 1150 1,100 0 3 September 1100 1,100 0 4 October 1600 1,100 0 5 November 1900 1,100 0 6 December 1200 1,100 0arrow_forward
 Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,



