
Organic Chemistry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260119107
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith
Publisher: McGraw Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.3, Problem 3P
By taking into account electronegativity differences, draw the products formed by heterolysis of the carbon-heteroatom bond in each molecule. Classify the organic reactive intermediate as a carbocation or a carbanion.
a.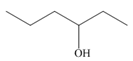 b.
b. 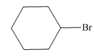 c.
c. 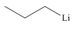
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Highlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers.
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
Using wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration.
NH
H
Br
X
टे
Provide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms)
1,2-dichloropropane
2,3,3-trimethylhexane
2-bromo-3-methybutane
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (6th Edition)
Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 6.3 - Problem 6.3 By taking into account...Ch. 6.3 - Problem 6.4 Use curved arrows to show the movement...Ch. 6.3 - Problem 6.5 Follow the curved arrows and draw the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 6.4 - Problem 6.7 Use the values in Table 6.2 to...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 6.5 - aWhich Keq corresponds to a negative value of G,...Ch. 6.5 - Given each of the following values, is the...Ch. 6.5 - Given each of the following values, is the...
Ch. 6.5 - The equilibrium constant for the conversion of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 6.6 - For a reaction with H=40kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6.6 - For a reaction with H=20kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6.7 - Draw an energy diagram for a reaction in which the...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 17PCh. 6.7 - Prob. 18PCh. 6.8 - Problem 6.19 Consider the following energy...Ch. 6.8 - Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction,...Ch. 6.9 - Which value if any corresponds to a faster...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 22PCh. 6.9 - Problem 6.23 For each rate equation, what effect...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 24PCh. 6.10 - Identify the catalyst in each equation. a....Ch. 6 - Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of...Ch. 6 - Explain why the bond dissociation energy for bond...Ch. 6 - Classify each transformation as substitution,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 29PCh. 6 - 6.31 (a) Add curved arrows for each step to show...Ch. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - 6.39. a. Which value corresponds to a negative...Ch. 6 - Prob. 40PCh. 6 - For which of the following reaction is S a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 42PCh. 6 - Prob. 43PCh. 6 - 6.44 Consider the following reaction: .
Use curved...Ch. 6 - Prob. 45PCh. 6 - 6.50 The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl...Ch. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Prob. 53P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How could you separate a mixture of the following compounds? The reagents available to you are water, either, 1...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Some people consider Pasteur or Koch to be the Father of Microbiology, rather than Leeuwenhoek. Why might they ...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
2. Which of the following is the best example of the use of a referent? _
a. A red bicycle
b. Big as a dump tru...
Physical Science
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardGiven a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forward
- TRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forwardRelative Transmittance 0.995 0.99 0.985 0.98 Please draw the structure that is consistent with all the spectral data below in the box and alphabetically label the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc ....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. Label the absorption bands in the IR spectrum indicated by the arrows. INFRARED SPECTRUM 1 0.975 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 Structure with assigned H peaks 1 3 180 160 140 120 100 f1 (ppm) 80 60 40 20 0 C-13 NMR note that there are 4 peaks between 120-140ppm Integral values equal the number of equivalent protons 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 fl (ppm)arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of 0.0025 M phenol.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY