Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130662453
Author: Lillian C. McDermott, Peter S. Shaffer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 6.3, Problem 2cT
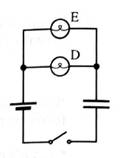
1. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb D compares to the initial brightness of bulb li. Explain.
2. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb 1) compares to the initial brightness of bulbs A, B, and C above. Explain.
3. Predict how the final charge on the capacitor compares to the final charge on the capacitor from part A. Explain.
Set up the circuit and check your predictions. If your prediction is in conflict with your observation, how can you account for your observation?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:48
Students have asked these similar questions
A block of mass m₁
=
10.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m₂
34.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 34.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 200 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is
unstretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 10.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 22.0 cm down the incline of angle = 40.0° and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the spring is again unstretched.
Vm1
×
1.32
Vm2
= 1.32
×
m/s
m/s
A block of mass m₁ = 10.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m₂ = 34.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 34.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 200 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is
unstretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 10.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 22.0 cm down the incline of angle 0 = 40.0° and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the spring is again unstretched.
m/s
Vm1
Vm2
m/s
mi
m2
k
i
Truck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as in the figure below. The helper spring engages when the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, and then helps to
support any additional load. Consider a leaf spring constant of 5.45 × 105 N/m, helper spring constant of 3.60 × 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m.
Truck body
Dyo
Axle
(a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 4.90 × 105 N?
m
(b) How much work is done compressing the springs?
]
Chapter 6 Solutions
Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
Ch. 6.1 - Obtain a battery, a light bulb, and a single piece...Ch. 6.1 - A student has briefly connected a wire across the...Ch. 6.1 - Light a bulb using a battery and a single wire....Ch. 6.1 - Carefully examine a bulb. Two wires extend from...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of the two bulb with each...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of each of the bulbs in the...Ch. 6.1 - We may think of a bulb as percentage an obstacle,...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of the bulbs in this...Ch. 6.1 - Is the brightness of each bulb in the two-bulb...Ch. 6.1 - Formulate a rule for predicting how the current...
Ch. 6.1 - Does the amount of current through a battery seem...Ch. 6.1 - Unscrew one of the bulbs in the two-bulb parallel...Ch. 6.1 - The circuit at tight contains three identical...Ch. 6.1 - Show that a simple application of the model for...Ch. 6.2 - The circuits at right contain identical batteries,...Ch. 6.2 - The circuits at right contain identical batteries...Ch. 6.2 - Predict the relative brightness of bulbs...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with a single bulb and the...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit containing two bulbs in series...Ch. 6.2 - Predict what the voltmeter would read if it were...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with two bulbs in parallel as...Ch. 6.2 - Answer the following questions based on the...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with three bulbs as shown and...Ch. 6.2 - Before setting up the circuit shown at right:...Ch. 6.2 - Both circuits al right have more than one path for...Ch. 6.3 - A capacitor is connected to a battery, bulb, and...Ch. 6.3 - Remove the capacitor and the bulb from the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose an uncharged capacitor is connected in...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that instead of connecting the uncharged...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that the bulbs were connected in parallel...Ch. 6.3 - After completing the experiments above, two...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that a different capacitor of smaller...Ch. 6.3 - Before connecting the circuit a student makes the...Ch. 6.3 - Make the following prediction on the basis of your...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In your own words, briefly distinguish between relative dates and numerical dates.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Level 2: Application/Analysis 4. Nitrifying bactcria participatc in the nitrogen cycle mainly by (A) converting...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
15. A good scientific hypothesis is based on existing evidence and leads to testable predictions. What hypothes...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
For the generic equilibrium HA(aq) ⇌ H + (aq) + A- (aq), which of these statements is true?
The equilibrium con...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
The bioremediation process shown in the photograph is used to remove benzene and other hydrocarbons from soil c...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A skier of mass 75 kg is pulled up a slope by a motor-driven cable. (a) How much work is required to pull him 50 m up a 30° slope (assumed frictionless) at a constant speed of 2.8 m/s? KJ (b) What power (expressed in hp) must a motor have to perform this task? hparrow_forwardA block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest. a x = 0 x b (a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum. cm (b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation? cmarrow_forwardA block of mass m = 3.00 kg situated on a rough incline at an angle of 0 = 37.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (see the figure below). The pulley is frictionelss. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 11.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k=100 N/m Ө marrow_forward
- 23. What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 X 103 V/m and 7.5 X 10-3 T. respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off?arrow_forward10. A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?arrow_forward9. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forward
- In the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forwardDon't use aiarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Series & Parallel - Potential Divider Circuits - GCSE & A-level Physics; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vf8HVTVvsdw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY