
On average, every minute of every day, 158 babies are born. The bar graph represents the results of a single day of births, deaths, and population increase worldwide. Exercises 25-26 are based on the information displayed by the graph.
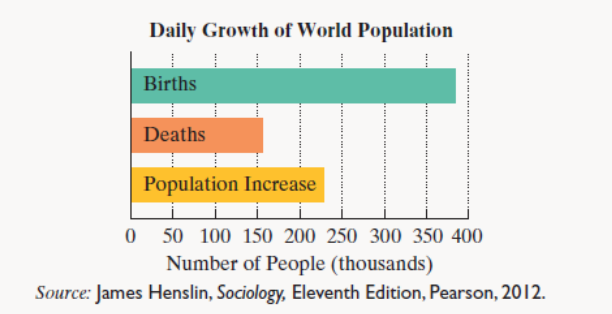
Each day, the number of births in the world exceeds twice the number of deaths by 72 thousand.
a. If the population increase in a single day is 228 thousand, determine the number of birth and deaths per day.
b. If the population increase in a single day is 228 thousand, by how many millions of people does the worldwide population increase each year? Round to the nearest million.
c. Based on your answer to part (b), approximately how many years does it take for the population of the world to increase by an amount greater than the entire U.S. population (315 million)?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Thinking Mathematically, Books A La Carte Edition Format: Unbound (saleable)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- Practice k Help ises A 96 Anewer The probability that you get a sum of at least 10 is Determine the number of ways that the specified event can occur when two number cubes are rolled. 1. Getting a sum of 9 or 10 3. Getting a sum less than 5 2. Getting a sum of 6 or 7 4. Getting a sum that is odd Tell whether you would use the addition principle or the multiplication principle to determine the total number of possible outcomes for the situation described. 5. Rolling three number cubes 6. Getting a sum of 10 or 12 after rolling three number cubes A set of playing cards contains four groups of cards designated by color (black, red, yellow, and green) with cards numbered from 1 to 14 in each group. Determine the number of ways that the specified event can occur when a card is drawn from the set. 7. Drawing a 13 or 14 9. Drawing a number less than 4 8. Drawing a yellow or green card 10. Drawing a black, red, or green car The spinner is divided into equal parts. Find the specified…arrow_forwardProblem 1.We consider a two-period binomial model with the following properties: each period lastsone (1) year and the current stock price is S0 = 4. On each period, the stock price doubleswhen it moves up and is reduced by half when it moves down. The annual interest rateon the money market is 25%. We consider four options on this market: A European call option with maturity T = 2 years and strike price K = 5; A European put option with maturity T = 2 years and strike price K = 5; An American call option with maturity T = 2 years and strike price K = 5; An American put option with maturity T = 2 years and strike price K = 5.(a) Find the price at time 0 of both European options.(b) Find the price at time 0 of both American options. Compare your results with (a)and comment.(c) For each of the American options, describe the optimal exercising strategy.(d) We assume that you sell the American put to a market participant A for the pricefound in (b). Explain how you act on the market…arrow_forwardWhat is the standard scores associated to the left of z is 0.1446arrow_forward
- 2. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.5.015. Use the Trapezoidal Rule, the Midpoint Rule, and Simpson's Rule to approximate the given integral with the specified value of n. (Round your answers to six decimal places.) ASK YOUR TEACHER 3 1 3 + dy, n = 6 (a) the Trapezoidal Rule (b) the Midpoint Rule (c) Simpson's Rule Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardThis question builds on an earlier problem. The randomized numbers may have changed, but have your work for the previous problem available to help with this one. A 4-centimeter rod is attached at one end to a point A rotating counterclockwise on a wheel of radius 2 cm. The other end B is free to move back and forth along a horizontal bar that goes through the center of the wheel. At time t=0 the rod is situated as in the diagram at the left below. The wheel rotates counterclockwise at 1.5 rev/sec. At some point, the rod will be tangent to the circle as shown in the third picture. B A B at some instant, the piston will be tangent to the circle (a) Express the x and y coordinates of point A as functions of t: x= 2 cos(3πt) and y= 2 sin(3πt) (b) Write a formula for the slope of the tangent line to the circle at the point A at time t seconds: -cot (3πt) (c) Express the x-coordinate of the right end of the rod at point B as a function of t: 2 cos(3πt) +41/1 (d) Express the slope of the rod…arrow_forwardConsider the proof below: Proposition: If m is an even integer, then 5m +4 is an even integer. Proof: We see that |5m+4=10n+4 = 2(5n+2). Therefore, 5m+4 is an even integer. **Note: you may assume the proof is valid, just poorly written. Based upon the Section 1.3 screencast and the reading assignment, select all writing guidelines that are missing in the proof. Proof begins by stating assumptions ✓ Proof has an invitational tone/uses collective pronouns Proof is written in complete sentences Each step is justified ☐ Proof has a clear conclusionarrow_forward
- Note: The purpose of this problem below is to use computational techniques (Excelspreadsheet, Matlab, R, Python, etc.) and code the dynamic programming ideas seen inclass. Please provide the numerical answer to the questions as well as a sample of yourwork (spreadsheet, code file, etc.).We consider an N-period binomial model with the following properties: N = 60, thecurrent stock price is S0 = 1000; on each period, the stock price increases by 0.5% whenit moves up and decreases by 0.3% when it moves down. The annual interest rate on themoney market is 5%. (Notice that this model is a CRR model, which means that thebinomial tree is recombining.)(a) Find the price at time t0 = 0 of a (European) call option with strike price K = 1040and maturity T = 1 year.(b) Find the price at time t0 = 0 of a (European) put option with strike price K = 1040and maturity T = 1 year.(c) We consider now, that you are at time t5 (i.e. after 5 periods, which represents 1month later). Assume that the stock…arrow_forward4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.5.024. Find the approximations Tη, Mn, and S, to the integral computer algebra system.) ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER 4 39 √ dx for n = 6 and 12. Then compute the corresponding errors ET, EM, and Es. (Round your answers to six decimal places. You may wish to use the sum command on a n Tn Mn Sp 6 12 n ET EM Es 6 12 What observations can you make? In particular, what happens to the errors when n is doubled? As n is doubled, ET and EM are decreased by a factor of about Need Help? Read It ' and Es is decreased by a factor of aboutarrow_forward6. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.5.001. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Let I = 4 f(x) dx, where f is the function whose graph is shown. = √ ² F(x 12 4 y f 1 2 (a) Use the graph to find L2, R2 and M2. 42 = R₂ = M₂ = 1 x 3 4arrow_forward
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage





