
(a)
To find: The direction and magnitude of the resultant of the forces when
(a)
Answer to Problem 103E
Magnitude
Direction
Explanation of Solution
Given: Forces with magnitudes of 150 newtons and 220 newtons act on a book, as shown in the figure.
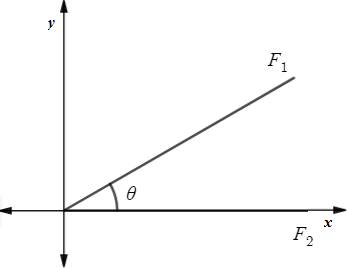
First make the vertical and horizontal component of both forces.
For force 1:
For force 2:
The resultant of both forces,
For
Direction of F,
Hence, the magnitude of resultant forces is 357.85 N and direction
(b)
To find: The magnitude and direction in form of
(b)
Answer to Problem 103E
Explanation of Solution
Given: Forces with magnitudes of 150 newtons and 220 newtons act on a book, as shown in the figure.
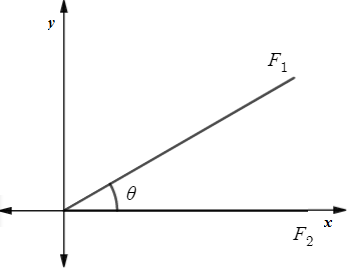
First make the vertical and horizontal component of both forces.
For force 1:
For force 2:
The resultant of both forces,
Magnitude of forces,
Let direction of resultant force is
(c)
To complete: The table for different value of
(c)
Answer to Problem 103E
Explanation of Solution
Given: Forces with magnitudes of 150 newtons and 220 newtons act on a book, as shown in the figure.
The magnitude of resultant forces,
The direction of the resultant forces,
Using graphing utility to complete the table.
(d)
To graph: The function of magnitude and direction of resultant forces.
(d)
Answer to Problem 103E
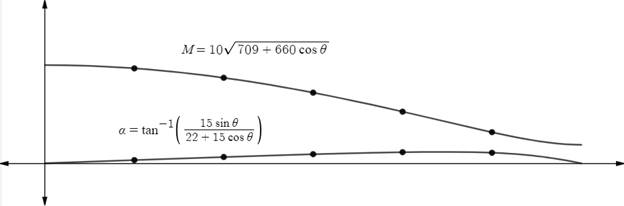
Explanation of Solution
Given: Forces with magnitudes of 150 newtons and 220 newtons act on a book, as shown in the figure.
Using graphing utility to graph the function.
The magnitude of resultant forces,
The direction of the resultant forces,
Where , y -axis represents magnitude and direction and x -axis represents angle
(e)
To graph: The function of magnitude and direction of resultant forces.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given: Forces with magnitudes of 150 newtons and 220 newtons act on a book, as shown in the figure.
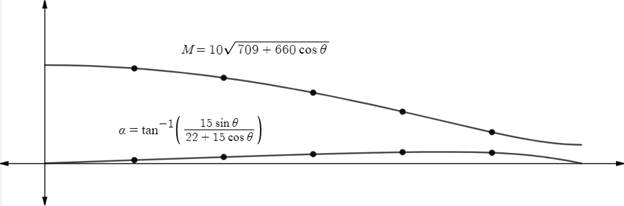
Using graphing utility to graph the function.
The magnitude of resultant forces,
The direction of the resultant forces,
Where , y -axis represents magnitude and direction and x -axis represents angle
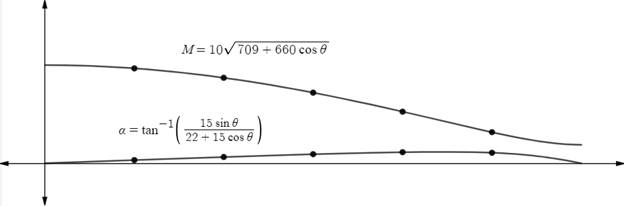
The graph of magnitude of resultant of two forces is decreases as
The graph of direction of resultant of two forces is increase as
Chapter 6 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- Find the following limit lim x-4 X-72 3x-6arrow_forwardFind the one sided limit Tim f(x) where f(x)= (2x-1 X>1+ *arrow_forwardFind the limit lim X-700 4 13x-15 3x4+x³-12arrow_forwardFind the slope of the line secant to the curve F(x) = 13-x³ (from x=1 to x=2]arrow_forwardFind the ONe sided limit lim 2x X-2 1-xarrow_forwardFor each function, identify all points of discontinuity and label them as removable, jump, or infinite. A) f(x) = x-4 (X+15)(x-4) B) f(x) = (x²-1 x ≤2 14-2x 2arrow_forwardFind the one sided limit 2 lim Flx) where f(x) = (x²-4_xarrow_forwardRequired information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. T₁ 15° A 25° T₂ I B Using trigonometry, determine the corresponding magnitude of R. The corresponding magnitude of R is lb.arrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DC a Determine the corresponding magnitude of R. The magnitude of R is N.arrow_forwardLet y(t) represent your retirement account balance, in dollars, after t years. Each year the account earns 7% interest, and you deposit 8% of your annual income. Your current annual income is $34000, but it is growing at a continuous rate of 2% per year. Write the differential equation modeling this situation. dy dtarrow_forwardDetermine Whether series converge or diverge if it converge what is the limit. $\{ \frac {(-1)^{n-2}n^{2}}{4+n^{3}}\} _{n=0}^{\infty }$arrow_forwardLet y(t) represent your retirement account balance, in dollars, after t years. Each year the account earns 7% interest, and you deposit 8% of your annual income. Your current annual income is $34000, but it is growing at a continuous rate of 2% per year. Write the differential equation modeling this situation. dy dtarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningWrite the Complex Number in Trigonometric (Polar) Form; Author: The Math Sorcerer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9kZOHHRjfIQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningWrite the Complex Number in Trigonometric (Polar) Form; Author: The Math Sorcerer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9kZOHHRjfIQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY