
MORTON SALT
Introduction
Morton Salt is a subsidiary of Morton International, a manufacturer of specialty chemicals, air bags, and salt products. The Morton salt-processing facility in Silver Springs, New York, between Buffalo and Rochester, is one of six similar Morton salt-processing facilities in the United States. The Silver Springs plant employs about 200 people, ranging from unskilled to skilled. It produces salt products for water conditioning, grocery, industrial, and agricultural markets. The grocery business consists of 26-oz. round cans of iodized salt. Although the grocery business represents a relatively small portion of the total output (approximately 15 percent), it is the most profitable.
Salt production
The basic raw material, salt, is obtained by injecting water into salt caverns that are located some 2,400 feet below the surface. There, the salt deposits dissolve in the water. The resulting brine is pumped to the surface where it is converted into salt crystals. The brine is boiled, and much of the liquid evaporates, leaving salt crystals and some residual moisture, which is removed in a drying process. This process is run continuously for about six weeks at a time. Initially, salt is produced at the rate of 45 tons per hour. But the rate of output decreases due to scale buildup, so that by the sixth week, output is only 75 percent of the initial rate. At that point, the process is halted to perform maintenance on the equipment and remove the scale, after which salt production resumes.
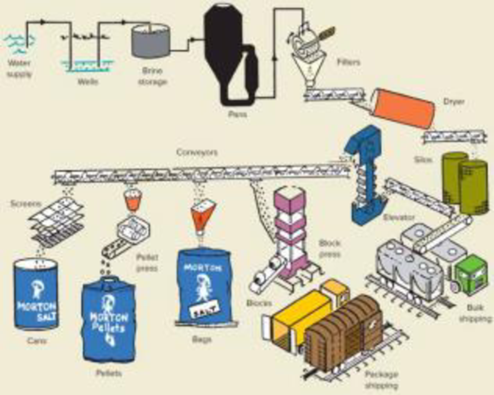
The salt is stored in silos until it is needed for production, or it is needed for production, or it is shipped in bulk to industrial customers. Conveyors move the salt to each of the four dedicated production areas, one of which is round can production (see diagram.). The discussion here focuses exclusively on round can production.
Round Can Production
Annual round can production averages roughly 3.8 million cans. Approximately 70 percent of the output is for the Morton label, and the rest is for private label. There are two parallel, high-speed production lines. The lines share common processes at the beginning of the lines, and then branch out into two identical lines. Each line is capable of producing 9,600 cans per hour (160 cans per minute). The equipment is not flexible, so the production rate is fixed. The operations are completely standardized; the only variable is the brand label that is applied. One line requires 12 production workers, while both lines together can be operated by 18 workers because of the common processes. Workers on the line perform low-skilled, repetitive tasks.
The plant produces both the salt and the cans the salt is packaged in. The cans are essentially a cylinder with a top and a bottom; they are made of cardboard, except for a plastic pour spout in the top. The cylinder portion is formed from two sheets of chip board that are glued together and then rolled into a continuous tube. The glue not only binds the material, it also provides a moisture barrier. The tube is cut in a two-step process. It is first cut into long sections, and those sections are then cut into can-size pieces. The top and bottom pieces for the cans are punched from a continuous strip of cardboard. The separate pieces move along conveyor belts to the lines where the components are assembled into cans and glued. The cans are then filled with salt and the pour spout is added. Finally, the cans are loaded onto pallets and placed into inventory, ready to be shipped to distributors.
Quality
Quality is checked at several points in the production process. Initially, the salt is checked for purity when it is obtained from the wells, Iodine and an anti-caking compound are added to the salt, and their levels are verified using chemical analysis. Crystal size is important. In order to achieve the desired size and to remove lumps, the salt is forced through a scraping screen, which can cause very fine pieces of metal to mix with the salt. However, these pieces are effectively removed by magnets that are placed at appropriate points in the process. If, for any reason, the salt is judged to be contaminated, it is diverted to a nonfood product.
Checking the quality of the cans is done primarily by visual inspection, including verifying the assembly operation is correct, checking filed cans for correct weight, inspecting cans to see that labels are labels are properly aligned, and checking to see that plastic pour spouts are correctly attached.
The equipment on the production line is sensitive to misshapen or damaged cans, and frequently jams, cussing production delays. This greatly reduces the chance of a defective can getting through the process, but it reduces productivity, and the salt in the defective cans must be scrapped. The cost of quality is fairly high, owing to the amount of product that is scrapped, the large number of inspectors, and the extensive laboratory testing that is needed.
Production Planning and Inventory
The plant can sell all of the salt it produces. The job of the production
Equipment Maintenance and Repair
The equipment is 1950s vintage, and it requires a fair amount of maintenance to keep it in good working order. Even so, breakdowns occur as parts wear out. The plant has its own tool shop where skilled workers repair parts or make new parts because replacement parts are no longer available for the old equipment.
6. What improvements can you suggest for the plant?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Connect Online Access for Operations Management
- 1) View the two video excerpts (Ctrl+Click on the two links), Preview 1 to the Goal Movie (Goldratt) (11.17 minutes), https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2RVMgV37O_k and Preview 2 to the Goal Movie – How to Version (Goldratt) (9.40 minutes) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_oM9LvK0rU and answer the following questions: a) What problems is UniCo facing and how are they tackling these problems currently? b) What advice did Jonah give to Rogo, and what lessons did Rogo learn from “Herbie’s Hike”? c) How do you think Rogo can leverage Jonah’s advice (as well as the lessons learnt from “Herbie’s Hike”) to solve UniCo’s problems? 2) A business program has the facilities and faculty to handle an enrollment of 2,000 new students per semester. However, in an effort to limit class sizes to a “reasonable” level the business dean, placed a ceiling on enrollment of 1,500 new students. Although there was ample demand for business courses last semester, conflicting schedules allowed only 1,450 new…arrow_forwardThe global marketplace has undergone a dramatic transformation, demanding that businesses adapt their supply chain management and implement new strategies to ensure the reliable sourcing of materials and goods. Please choose an organisation that you are currently working for or you are familiar with where its procurement operations has been greatly affected. You may pick a commercial or public institution as a choice for your study. You will need to briefly describe the institution and explain its category management structure which support the strategic procurement. You are required to provide an overview and discuss how spend are identified along with the types of categories purchased Briefly describe the organisation that you have chosen. Analyse the criticality of both the category management and strategic sourcing that will impact the business needs of the institution that you have chosen. Laing oxemples from the institution you have selected appraise and recommend COarrow_forwardThe Ideal Spot in the Segment Circles So, where should you try to position your product in the segment circles? As a basic rule, the 'Ideal Spot' will help guide you. The ideal spot represents the position with the highest point of demand for each consumer base – or segment. The ideal spot is made up by the product’s performance (speed) and size. As the perceptual map drifts down and to the right each year, the ideal spot will change as customers demand sensors with decreased size (smaller) and increased performance (faster). Although it would seem that the Ideal Spot would be in the center of the segment circle, the positioning actually varies due to the customer focus of each segment. For example, in the High End segment, the Ideal Spot is at the leading edge of the segment because those customers want the best possible product. Each segment’s ideal spot is represented by the pink dots on the Perceptual Map. Ideal Spots offset from segment center Calculating the Ideal Spot To…arrow_forward
- In Ecuador, cut roses are one of the country’s leading exports. Prior to advancements in the air transportation industry, this would have been impossible as roses must be sold within three to five days once cut. Today Ecuador is one of the world’s top producers of roses.arrow_forwardThe World Trade Organization is the only global trade organization and has 164 member nations representing 98 percent of world trade. How does the WTO help nations improve trade relations? What are some of the major challenges facing the WTO today?arrow_forwardWhat is a good example of a letter of recommendation for a 5th grade Language Arts Teaching Position at an elementary school from a school principal?arrow_forward
- Problem 1 (10 Points) Davison Electronics manufactures three LED television monitors, identified as Model A, Model B, and Model C. Davison Electronics four manufacturing plants. Each model has its lowest possible production cost when produced at Plant 1. However, Plant 1 does not have the capacity to handle the total production of all three models. As a result, at least some of the production must be routed to the other manufacturing plants. The following table shows the minimum production requirements for next month, the plant capacities in units per month, and the production cost per unit at each plant: Model Production Cost per Unit Minimum Production Requirements Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 A $25 $28 $37 $34 48,000 B $26 $35 $36 $41 75,000 C $20 $31 $26 $23 60,000 Production Capacity 65,000 50,000 32,000 43,000 Davison’s objective is to determine the cost-minimizing production plan. We have…arrow_forwardLead Story: Identify the key story or insight based on your visualizations. Shaffer’s 4C Framework: Describe how you applied Shaffer’s 4C principles in the design of your charts. Gestalt Principles or Preattentive Attributes: Explain how you applied at least one Gestalt principle or preattentive attribute in your chartarrow_forwardFor the purpose of process analysis, which of the following measures would be considered an appropriate flow unit for analyzing the main operation of a local accounting firm? Instructions: You may select more than one answer. a. Number of accountants working each week b. Number of tax returns completed each week c. Number of customers with past-due invoices d. Number of reams of paper received from suppliersarrow_forward
- 4. Based on the data provided in Table 2.5, what is the flow rate of callers from 8:00 a.m. to 8:20 a.m.? TABLE 2.5 Time Stamps of the Eight Callers Who Called from 8:00 a.m. to 8:20 a.m. to the Reservation Desk of a Ferry Service Caller Time In Time Out 1 8:01 8:05 2 3 4 5 6 8:02 8:07 8:06 8:08 8:09 8:12 8:10 8:15 8:12 8:20 7 8:16 8:19 8 8:17 8:19 5. Based on the data provided in Table 2.5, what is the flow time of callers from 8:00 a.m. to 8:20 a.m.? 6. Based on the data provided in Table 2.6, what is the flow rate of customers from 9:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.? TABLE 2.6 Time Stamps of 10 Customers Who Visited a Local Bank Branch from 9:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. Customer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Time In Time Out 9:01 9:07 9:06 9:21 9:08 9:20 9:14 9:19 9:20 9:28 9:26 9:33 9:31 9:39 9:40 9:46 9:44 9:59 9:53 9:57 7. Based on the data provided in Table 2.6, what is the flow time of customers from 9:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.?arrow_forwardHow is Little’s Law currently used in today’s supply chains? Provide an example of where it is used.arrow_forwardHow would you Briefly state your views on music for a Christian school interview?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,


