
Concept explainers
a.
To describe: The physical significance of center of mass of a thin plate.
a.
Answer to Problem 9RCC
Center of mass of a thin plate is a point on which a thin plate balances horizontally.
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
The plate is thin.
Center of mass of a system is a point where we can assume entire mass is concentrated.
Hence, centre of mass of a thin plate is a point on which a thin plate balances horizontally.
b.
The expression for the coordinates of the center of mass of a given plate.
b.
Answer to Problem 9RCC
The center of mass of the plate is located at the point
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
The plate lies between
Formula used :
Moment of the system about the Y-axis to be
Moment of the system about X-axis to be
The coordinates of center of mass is
Next we consider a flat plate (called a lamina) with uniform density
Region
the centroid of
principle says that if
is reflected about
defined so that if the entire mass of a region is concentrated at the center of mass, then its
moments remain unchanged. Also, the moment of the union of two nonoverlapping regions
should be the sum of the moments of the individual regions.
Suppose that the region
the lines
continuous function. We divide the interval into
and equal width
subinterval, that is,
This determines the polygonal approximation to
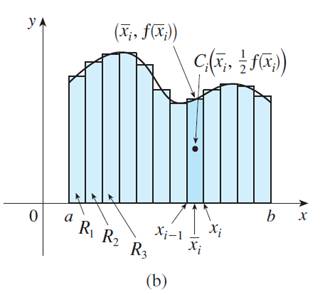
The centroid of ith approximating rectangle
. Its area is
so its mass is
The moment
The Y -axis, which is
Adding these moments, we obtain the moment of the polygonal approximation to
then by taking the limit as
In a similar fashion we compute the moment of
mass and the distance from
Again we add these moments and take the limit to obtain the moment of
X-axis:
Just as for systems of particles, the center of mass of the plate is defined so that
and
And so,
The center of mass of the plate is located at the point
Chapter 6 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Concepts and Contexts, Enhanced Edition
- a -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forwardEvaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forward
- I need help in ensuring that I explain it propleryy in the simplifest way as possiblearrow_forwardI need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardEvaluate F³ - dr where ♬ = (4z, -4y, x), and C' is given by (t) = (sin(t), t, cos(t)), 0≤t≤ñ .arrow_forwardMid-Term Review Find the formula for (f + g)(x). f(x) = x² - 10x + 25 and g(x) = x² - 10x + 24 (f + g) (x) = [ 2 ]x² X + DELL Skip Sarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





